Introduction
A project is a collaborative or individual enterprise carefully planned, designed, and implemented to achieve the desired aim. Managing a project enables organizations to understand their strengths and add value to the organization, contributing to its success. Project management is achieved through five processes: initiating, planning, executing, monitoring/control, and closure. The critical constraints to consider in each of the five phases are time, budget, and scope. Startups can also leverage project management concepts to conduct market research and introduce new goods within the desired quantity, quality, and timelines (Ma et al., 2018). It is prudent to note that the completion of a project takes place through five distinct processes in its lifecycle. The paper covers managing a startup business that produces and sells international dishes to international students in American colleges and universities and makes international cuisines available.
A project manager must understand how to break down the project into small actions that can be achieved. Further, all the stakeholders must understand the bigger picture of the project and what tasks need to be undertaken to succeed in the project. The advancement in technology has introduced essential tools to be used in project management to document and monitor the process. The ProjectLibre software is the primary tool to document the work breakdown structure and other essential project elements such as the Gantt chart and cost allocation to achieve the project goals. The project manager’s role is to provide overall leadership and control to complete all tasks within the timeframes.
Initiating
The pre-planning stage of the project management lifecycle involves conceptualizing the business idea and gathering knowledge to facilitate the implementation. The project of producing and selling foreign dishes is a new entrant into the American food market and must be pre-planned to identify all hurdles and overcome them before starting the project. The initiation phase involves obtaining sufficient strategic project information, which can be used to make essential decisions on the risks before committing to work on the project.
Terms for the Phase
The most important terms in the project phase include strategic information, ideas, dependencies, and sprint. Strategic information results from research, while ideas refer to suggestions that can be used to close the business gap identified in the research. Dependencies are a relationship between events and how they must be arranged for the project to be completed. A sprint is a unit of time allocated for a task to be completed in project management.
Tools for the Phase
The project management tool necessary for the pre-planning stage is the force field analysis, which helps an entrepreneur analyze the decision. The project intends to initiate a food outlet for international students, force a field analysis views of the decision from the context of strategic planning, and ensure that there are numerous forces in favor of the decision (Ma et al., 2018). If the existing forces do not favor the decision, the decision needs to be changed. Trello is another project management tool suitable for the project phase because it offers a platform to collaborate, share ideas, and adjust the project goals whenever needed.
Techniques for the Phase
Brainstorming is an essential technique in the pre-planning phase of project management. It ensures that all key stakeholders understand the project’s scope and what is expected of them to perform better. The result of the brainstorming meeting results in the formation of the project title and what needs to be done to meet the needs of the people (Ma et al., 2018). Developing key deliverables is another valuable technique for the stage as it determines the scope and the expectations. Interviews are another technique used to collect views from prospective customers and what is expected of the final product.
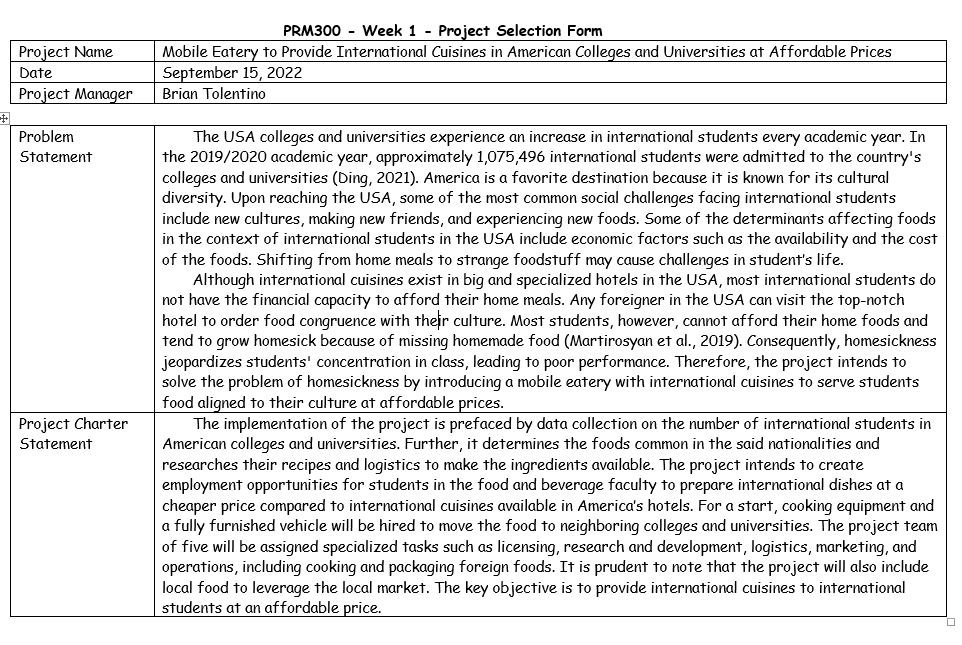
The elements in the project selection form play a significant role in the project’s overall implementation. The purpose of the project selection form is to help describe the problem and its solution. The first element is the business detail which contains the project’s name, the project manager, and the date when the project was initiated. The second element is the problem statement that led to the conception of the project ideas. The problem statement describes the number of international students in the USA and the shortage of hotels to serve foreign foods at affordable prices. The project charter statement is the last part of the project selection form, which documents the steps that would be followed to ensure that all the necessary steps are conducted to make the project successful. Project managers must ensure that the problem statement is clear and succinct to generate achievable goals and that the charter statement offers an easy-to-understand procedure that can be used to ensure that the planning and implementation phases are completed without challenges.
Planning
Project planning is essential because it boosts project performance, improves team communication, and makes it easy to track project goals. The phase is prefaced with the outline of the project, and the reason for each action carried out in the project. The project manager must incorporate a technique for reporting on the status of the activities for a smooth transition from one project phase to another.
Tools for the Phase
The planning phase of project management requires specialized tools to align the activities in the required order. ProjectLibre is an essential tool in the planning stage because it prepares the roles and assigns each person to the project. The work breakdown structure and Gantt chart are essential tools to understand the project details by breaking them down into milestones and assigning time frames for each task, respectively.
Terms for the Phase
Project dependency is an important term because it shows the relationship between project activities and how they can be broken down to achieve success in the long run. Scheduling is a necessary term for organizing tasks concerning the given time. Resource planning refers to the critical stage of organizing resources and allocating them to the given role. Delay is a term used to express lateness in the execution of a project and must be defined at the planning stage to overcome it during the execution phase.
Techniques for the Phase
Risk identification is an important technique that enables a project team to understand the impending risks in a project and offer strategic solutions to solve the challenges when they arise. The development of success criteria is a crucial technique that allows the project management team to state their expectations for the project. It eventually serves as the blueprint during the project’s execution phase. Issuing roles and responsibilities to encourage specialization and division of labor is a technique that ensures all stakeholders in the project are assigned roles aligned to their expertise.
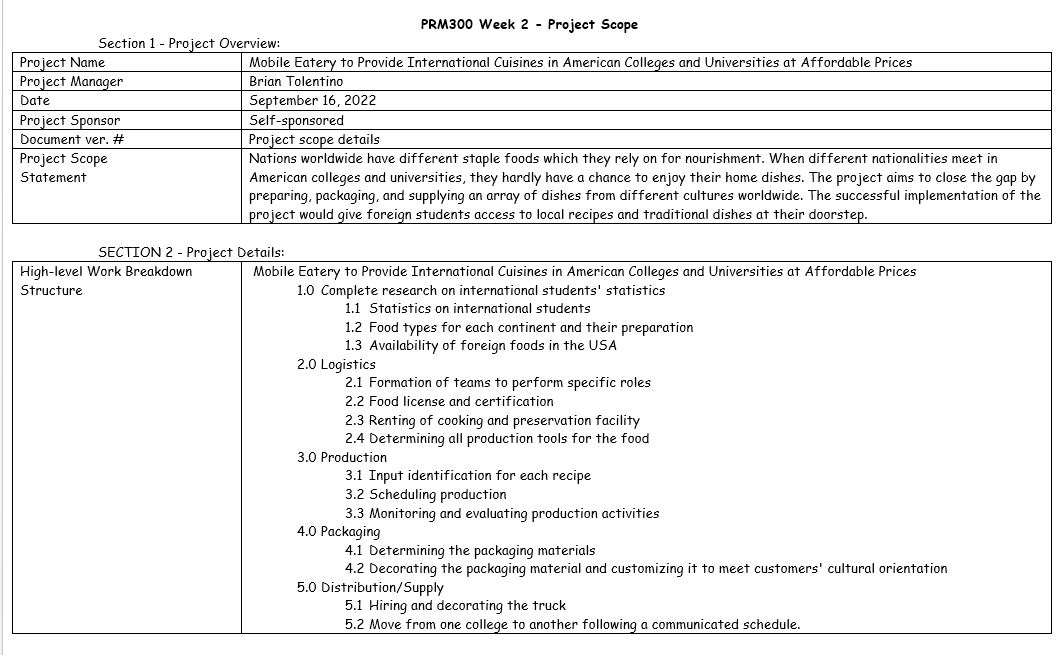
The purpose of the project scope statement is to outline the project goals and how the goals will be achieved in the long run. The statement further offers a simplified way to implement the project. A project manager uses the scope statement to share the project highlight with other relevant stakeholders and financiers.
Project Basics
The purpose of the project basics, such as name, project manager, and financiers, enables the team dealing with the project to understand what is expected of them. Some of the project basics for the selected project are:
- Project name: Mobile eatery to provide international cuisines in American colleges and universities
- Project manager: Brian Tolentino
- Sponsors: Self-sponsored through partners’ contributions (classmates)
Project Scope Statement
The project scope statement introduces the stakeholders to the business gap and proposes techniques that can be used to close the gap. In the specified project, the scope statement introduces the international students in the USA and the social challenges affecting them. Shortages of international cuisines on the college menu make students miss their home-made food. Introducing foods to cover the students’ needs is likely to be a profitable business in the long term.
Project Scope
Project scope is a vital outline showing all the projects’ components and what needs to be completed to cover the business gap. Scope includes getting information and gathering the necessary stakeholders to start the project.
Assumptions
An assumption in project management is any factor considered fundamental without empirical demonstration. The basic assumptions for the selected project include favorable custom duties, professional project implementers, and controlled inflation.
Project Milestones
Milestones are smaller, manageable tasks that are used to assist a project management team in moving toward a project’s success. The selected project is divided into five main milestones that depend on each other for successful completion. The five milestones selected for the project completion include research, logistics, production, packaging, and distribution.
Out of Scope (Exclusions)
Out-of-scope activities involve those that are crucial to ensure the project succeeds but are not included in the project planning. An example of an out-of-scope activity is marketing and advertisement because eateries already exist in the USA, and the new eatery must advertise itself to attract customers. However, it was secluded in the project plan, and the project manager must make local arrangements to ensure it is performed before the distribution phase begins.
Project Execution
Project execution is an important stage in the project management cycle which empowers all the relevant stakeholders to act and make the required goods and services available. A project manager uses a checklist to ensure that all the necessary steps are covered.
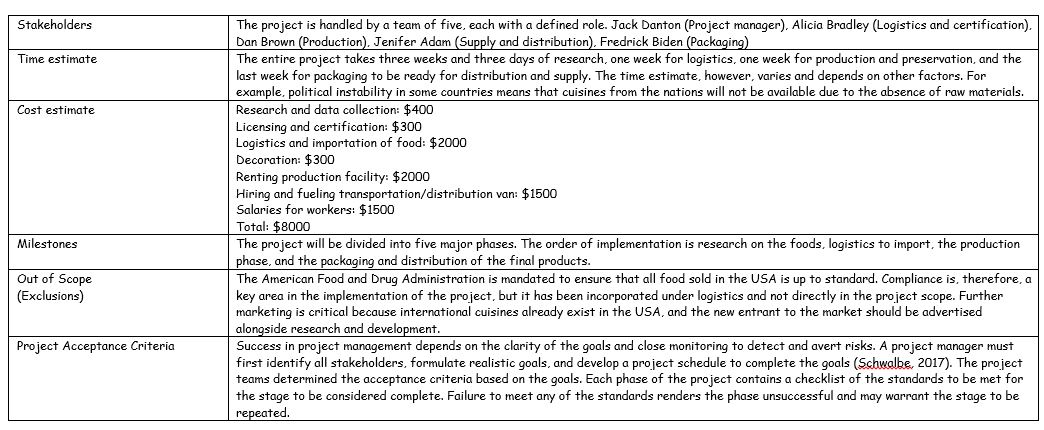
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are all people who have an interest in the project objective. In the case of the selected project, some critical stakeholders include the customers, the project team comprised of five people, the financiers, and the final users of the products and services.
Project Time Estimates
The project time estimate refers to the total time slated for the project to be completed and the time for each milestone to be completed. The time estimates help the project manager to deliver the product within the required time constraint. The entire project is expected to run within three weeks and three days. The first three days are meant for research, one week for logistics, another week for preparation, and the final week for the packaging and supply of the finished product.
Cost Estimates
Cost estimates in a project include all the financial resources required. A budget is an essential tool in estimating costs and is used for a follow-up to ensure the project is delivered within the said budget. The selected project has a total cost estimate of $8000, broken down into research, licenses, logistics, and salaries.
Project Acceptance Criteria
A project acceptance criteria is a list of performance requirements and conditions that must be met before the deliverables can be accepted. An acceptance criterion is important because it ensures that all client expectations are met.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
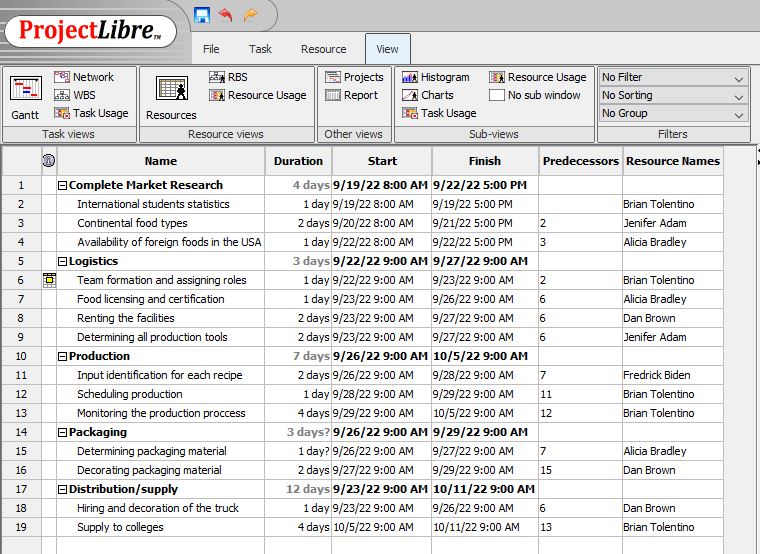
Work breakdown structure (WBS) is an essential tool in project management that breaks down a complex project into smaller tasks that can be quickly completed and supervised. The project status depends on the small tasks as indicated in the WBS. The breakdown is done in five specific milestones, which makes it easy for the project manager to follow up on the project. An alternative for the WBS is the critical path method which documents all the processes in the given path as the implementation begins. In a work breakdown structure, each of the small tasks for the project is allocated some time and assigned a person responsible for it.
The WBS provides an overview of the project steps, and the project manager can use it to follow up on the project and ensure that the deliverables have been completed by the stated date. The breakdown structure comprises all the project phases and how each phase is integrated into the final phase of the project (Schwalbe, 2017). As stated in the project scope, the work breakdown is structured into fourteen tasks that must be completed before the project can be termed as complete.
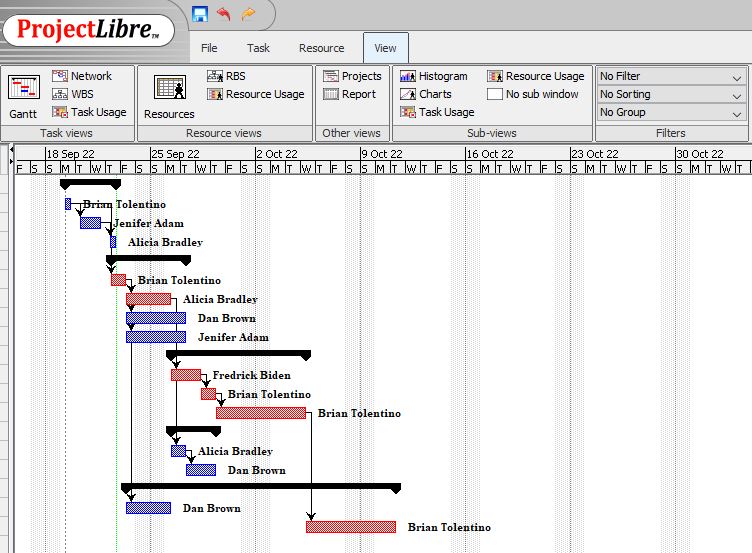
Gant Chart
The Gantt is a pictorial diagram that shows a schedule and offers a timeline through which the project manager can follow up for success. The Gantt chart shows the project details and the date each task will be performed. For example, the length of each activity and the person assigned to perform the task. In case of task delays, the Gantt chant makes it easy to follow up. The dependency arrows show how each activity relates and their respective dependencies (Tereso et al., 2019). The arrows in the improvised Gantt chart show the dependencies and how a project task cannot begin without completing another part of the project. One or more tasks can depend on one parameter, and its delay is likely to cause subsequent delays in the project tasks that depend on it.
Executing
The execution phase of project management turns plans into actions that propel the team towards success. During the implementation or execution phase of the project, a project manager’s central role is to keep the work on track and avoid delays. Further, the project manager organizes and issues tasks to the team members and ensures that the project implementation timeframes do not affect the original plan. The essential technique used in the project implementation is the seven-step strategy. The seven steps in the execution include the creation of tasks as done by the WBS and Gantt chart. Secondly, the project manager assigns tasks to the team, tracks the progress, communicates effectively, and manages change.
During the project execution phase, the team must work in tandem with each other, and communication is critical. The team leader or project manager must therefore ensure that the team members have a communication platform where members are updated periodically and have an opportunity to share their concerns. Failure to have positive communication may jeopardize project success (Hair, & Sarstedt, 2021). A daily status report is given in a communication channel where every member can access it. As the progress is communicated, any matters arising may be corrected before they have a massive impact on the project.
Change Control Process
Change control is an essential process in project management that helps individuals, teams, or organizations visualize and prepare to change without affecting the project’s initial plan. Change management is critical because the business domain is dynamic, and changes are experienced daily. The project team must ensure that they perform all their roles concerning the expected standards and incorporate any changes into their project design (Cha, & Maytorena-Sanchez, 2019). Change management can be cascaded with procurement management to ascertain that all the resources are obtained at the right time. Time and budget constraints require constant management and follow-up to avoid any looming loss.
A successful project manager must incorporate a risk management tool to ensure that all probable risks are identified and worked on to prevent loss or delays. Since each risk has a potential impact on the project, the team must clearly outline how to handle the risks whenever they are witnessed in the execution phase. Some strategies to be used include risk acceptance, risk avoidance, risk reduction, and risk transfer, as long as it does not affect the project’s overall outcome. In the discourse, an effective risk management tool helps an organization identify a risk, evaluate the impact of the risk, and eliminate or remove the threat to allow the project to run as expected (Schwalbe, 2017). Failure to control risks puts the project in danger and may fail to deliver the expected result. Finally, acceptance management is critical in ensuring that all the partners involved take ownership of the project. Acceptance management may be implemented by collecting views from international students on how they want the products to be.
Monitoring and Control
The monitoring and control occur in tandem with the project’s execution phase. The stage ensures constant evaluation of all the actions and offers real-time feedback on improvements and changes required in the project. In case of implementation obstacles, the project phase ensures that all the changes and improvements are managed without affecting the outcome of the project and its progress (Tereso et al., 2019). The monitoring reports show how the project’s current events are likely to affect the project’s overall outcome.
Terms for the Phase
Work in progress limit is a term used in the project management phase to ensure that the staff are not overworked or given tasks that are not beyond their capacity. Bottlenecks in project control is a processes where the assigned workload is beyond the capacity. Bottlenecks must be avoided for a project to be performed well. Daily scrums are daily meetings to brainstorm the challenges affecting the project for them to be solved without affecting the project.
Techniques for the Phase
Risk monitoring and control is an important technique that ensures that all the possible challenges likely to affect the project are analyzed and worked on to avoid failure. Quality assurance is an important technique to ensure that all the prepared foods are aligned to the required standards, such as ingredients and nutrition level. Issue tracking is an important technique that ensures that all the concerns raised during the daily scrums are resolved.
Tools for the Phase
A budget is an essential tool during the phase because it helps the project manager to ensure that all the expenditures are aligned with the project’s initial plan. Another essential tool is Cloudmonix which offers solutions by providing an avenue through which the team members offer automated reports and updates on the project’s status. The tool contains a performance dashboard, status dashboard, alert dashboards, and root cause analysis (Cha & Maytorena-Sanchez, 2019). The tools are paramount for the project to succeed.
Closing
The closing phase of a project management lifecycle confirms to all stakeholders and interested parties that the goals and deliverables have been achieved. In the case of the mobile eatery, the project closure occurs after all the desired foodstuffs have been packaged and ready for supply. During the closure, the stakeholders confirm that the project deliverables have been completed satisfactorily (Hair, & Sarstedt, 2021). In some cases, the documentation is archived for references in the future, and an official handing over is conducted.
Tools for the Phase
During the closure phase, specific tools are used to ensure all the lessons are recorded for improvement in a subsequent project. A checklist is a vital tool to ensure all the deliverables or the project are achieved and can be ticked accordingly. A rating scale is used on the customers to measure their satisfaction levels. At the same time, the inventories are tools filled by the project implementers to share their experiences on the project as lessons learned. A lesson learned report includes all the issues and how they were challenged so that the mistakes conducted in the previous project will not be repeated in subsequent projects.
Techniques for the Phase
As the project closes, special techniques are used to generate adequate feedback on how the project was managed and the success rate. An interview is a technique for collecting feedback from the workers and the clients to note specific areas of improvement. Summative evaluation is also essential to check whether all the project goals were achieved.
Terms for the Phase
Some essential terms commonly used during project closures include poster-mortem, handing over, and the completion of paperwork. A post-mortem is a process of determining what went wrong during the project and what mistakes should be avoided in subsequent projects. Completion of paperwork ensures all documentation and legal requirements for the project are handled before handing over.
Conclusion
Project management is an essential process that empowers organizations to introduce new products and services to the market. It improves the organization’s success by identifying a gap and mobilizing resources to cover it for more profits. The introduction of the mobile eatery in American colleges and universities is an opportunity to leverage project management principles to create new goods and services at a relatively lower price and expand the business. Force field analysis determined that the forces favored the idea during the initiation. The planning stage used ProjectLibre to organize the project into smaller tasks. Execution and monitoring go hand in hand to ensure the project succeeds. The closure is an essential step because it shares all the lessons learned. It is paramount to follow all five phases of project management for success.
References
Cha, J., & Maytorena-Sanchez, E. (2019). Prioritizing project management competencies across the software project life cycle. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business.
Hair, J. F., & Sarstedt, M. (2021). Explanation plus prediction—The logical focus of project management research. Project Management Journal, 52(4), 319-322.
Ma, X., Xiong, F., Olawumi, T. O., Dong, N., & Chan, A. P. (2018). Conceptual framework and roadmap approach for integrating BIM into lifecycle project management. Journal of Management in Engineering, 34(6), 05018011.
Schwalbe, K. (2017). Introduction to project management. Boston: Course Technology Cengage Learning.
Tereso, A., Ribeiro, P., Fernandes, G., Loureiro, I., & Ferreira, M. (2019). Project management practices in private organizations. Project Management Journal, 50(1), 6-22.