Introduction
It is important to note that fiscal policy plays a critical role in the economic processes of a nation. Although it is distinct from monetary policies primarily managed and issued by the central bank, the impact can be significant since the government is the main agent of facilitating and coordinating the tax rates and spending. Unemployment is a major problem for a nation, which became even more severe under the economic recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. The problem to be discussed will be centered around the relationship of fiscal policies in regard to the unemployment rate in the United States.
Objectives
Fiscal policies specifically targeted unemployment were the most effective method of stabilization, volatility reduction, and consumer spending increase. The goal of the essay is to show how fiscal policies are able to cause such improvement. In addition, it should be noted that certain limitations and drawbacks also exist. However, in the face of a crisis, fiscal policies can be highly potent and quick in controlling and minimizing the rise of unemployment rates.
Method
The core methodological framework utilized for the given research will be centered around analyzing the recent body of works in scientific literature by primarily relying on peer-reviewed journal articles on the topic. The date of publication is of great importance since COVID-19 caused recession and lockdowns, which is why it provided an opportunity to observe the effectiveness of fiscal policies in action. Since the inception of the pandemic, highly reliable and accurate research studies emerged, which are used in the given analysis as a direct method of assessment to derive conclusive statements.
Findings and Observations
In order to properly understand how fiscal policies can impact the rate of unemployment, it is critical to highlight how the latter changes under the conditions of a recession. Research conducted on the basis of the Smooth Transition VAR model found that “a state-contingent forecast error variance decomposition analysis confirms that the contribution of EPU shocks to the volatility of unemployment at business cycle frequencies is markedly larger in recessions” (Caggiano, Castelnuovo, & Figueres, 2017, p. 31). In other words, “the response of unemployment to be statistically and economically larger in recessions” (Caggiano et al., 2017, p. 31). Therefore, one should be aware that the rate of unemployment in the US is highly sensitive to elements of recession, which can cause its further escalation without effective intervention.
The recent outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic allowed researchers to see what measures impacted unemployment the most. A study based on the nonlinear DSGE model assessment of COVID-19’s effect on the United States showed the given relationship. It is stated that “unemployment benefits are the most effective tool to stabilize income for borrowers, who are the hardest hit during a pandemic, while liquidity assistance programs are the most effective if the policy objective is to stabilize employment in the affected sector” (Faria-e-Castro, 2021, p. 1). Thus, a major framework of stabilization of unemployment took place due to the integration of fiscal policies. However, it should be pointed out that the most effective ones were in regard to employment, such as unemployment benefits and liquidity assistance programs.
One of the highlights of the fiscal policies during the initial stage of the lockdowns was federal packages. One study assessed the effectiveness of “the Federal Pandemic Unemployment Compensation (FPUC) COVID-19 supplement to Unemployment Insurance – from $0 to $600 to $300 between March and September 2020,” where the connection between earning replacement and unemployment was analyzed (Casado et al., 2020, p. 1). The findings reveal that “higher earnings replacement rates lead to significantly more consumer spending, even with increases in the unemployment claimant rate, which is consistent with the goal of the fiscal stimulus” (Casado et al., 2020, p. 1). In other words, fiscal policies targeted at employment with the additional objective of earning replacement resulted in increased consumer spending in accordance with the goal of the policy.
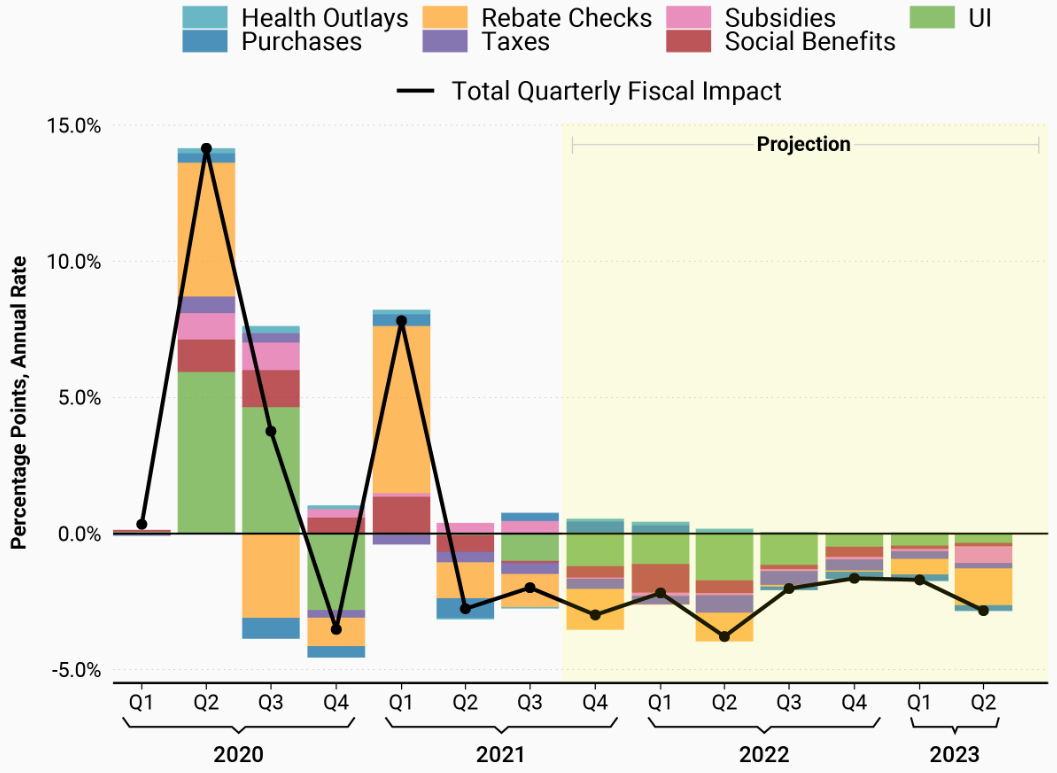
Moreover, fiscal policies aimed at unemployment also had an overall positive effect on the US economy. It is reported that “the largest boost to GDP growth in the early stages of the pandemic came from the large increases in spending on unemployment insurance and rebate checks” (Sheiner, Campbell, Kovalski, & Milstein, 2021, para. 10). Figure 1 above comprehensively illustrates how both rebate checks and unemployment insurance fiscal policies greatly stimulated the economy undergoing the economic recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. It is evident that not only do fiscal policies targeted at unemployment rate reduction benefit the unemployed directly but also preserve and protect the entirety of the economy of a nation from recession.
Conclusions
In conclusion, it should be noted that fiscal policies specifically aimed at unemployment were the most effective method of stabilization, volatility reduction, and consumer spending increase. The research on these policies and unemployment in the United States revealed a close and causal interconnection between them. The body of literature can be interpreted clearly with a conclusive statement about the potency of unemployment-focused fiscal policies, where findings reveal that not only do recessions increase the volatility of unemployment but also the fact that such measures are the most effective means to address them. In addition, a broader and well-supported argument can be made in regard to unemployment-focused fiscal policies being the most effective method of recession management for the entire economy as well. In other words, even if a recession is not heavily impacting the unemployment rate, unemployment benefits and unemployment insurance might be necessary to protect the economy.
In the case of personal and group opinions as well as consensus, it is evident that fiscal policies are the direct method of government intervention in the economic affairs of a nation. The stabilization of the economy is the main goal of the government’s policy. The stability and development of the national economy are guaranteed by the use of various instruments of macroeconomic regulation by the state. One of the most practical means of macroeconomic regulation is an effective fiscal policy, which involves influencing the value of the gross domestic product, unemployment, and inflation, as well as streamlining public finances.
Modern fiscal policy implements functions that include determining the main directions for the use of state financial resources and methods of financing and the main sources of filling the state treasury. However, it is important to form a sufficient state budget, as well as stimulate economic growth. Thus, it is necessary to effectively apply the elements of the taxation system based on the strategic priorities of socio-economic development. On the basis of evidence, it is safe to state that fiscal policy focused on unemployment plays the most important role in the development of the economy, which implies the importance of understanding its theoretical and practical frameworks.
References
Caggiano, G., Castelnuovo, E., & Figueres, J. M. (2017). Economic policy uncertainty and unemployment in the United States: A nonlinear approach. Economics Letters, 151, 31–34. Web.
Casado, M. G., Glennon, B., Lane, J., McQuown, D., Rich, D., & Weinberg, B. (2020). The aggregate effects of fiscal stimulus: Evidence from the COVID-19 unemployment supplement. National Bureau of Economic Research, 27576, 1-19. Web.
Faria-e-Castro, M. (2021). Fiscal policy during a pandemic. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 125, 1-31. Web.
Sheiner, L., Campbell, S., Kovalski, M. A., & Milstein, E. (2021). How pandemic-era fiscal policy affects the level of GDP. Brookings. Web.