Introduction
For the past two decades, Saudi Arabia has been experiencing significant developments in most aspects of its economic sectors. One of the sectors, which have had tremendous growth, is the transportation sector. The recent developments began close to two decades ago when the population of Saudi Arabia more than doubled, resulting in the government embarking on the development of roads. Presently, road length in Saudi Arabia has increased ten-fold from that of the past.
This has contributed greatly to the observed increases in the figure for registered motor vehicles. Statistics show that the number has increased by 34 times. Between 1975 and 1980, the transportation sector in Saudi Arabia recorded a 27% growth per annum. The vibrant growth of the transportation sector has led to traffic congestion, which increases the risk of accidents on the roads. The number of the accident has increased at 8.6 times; fatality has gone up 4.7 folds and injuries 4.1 times. This paper seeks to present the situation of the traffic experienced in Saudi Arabia, highlights the various causes of traffic problems, and proposes possible solutions to some of the problems found.
By exploring causes of road accidents, different safety precautions, and the role of King Fahd University in enhancing traffic safety. Increased incidences of road accidents in Saudi Arabia are because of the vibrant growth of the transportation sector. Many vehicles cause congestion on roads hence increased chances of road accidents. Reckless driving, for instance over speeding and poor driving skills, have also contributed greatly to the increased number of traffic accidents.
Traffic accidents may significantly reduce when drivers follow safety-driving procedures such as safe driving habits and obeying safety road signs. Kingfahd University has an obligation of training Saudi’s population to create awareness on traffic safety. The information used in this report may not be an accurate representation of the entire traffic situation in Saudi Arabia. Traffic accidents in Saudi Arabia have increased with the dynamic growth in the transportation sector.
Drivers and other involved parties fail to obey traffic rules such as speed limit, lack of traffic rules enforcement hence increasing risks of road accidents. The practice of safe driving measures such as safe driving practices and obeying safety road signs would significantly reduce the number of accidents incidences in Saudi Arabia.
Statistics have shown that Road accidents in Saudi Arabia have been on the rise; for instance, the deaths per 100,000 of the Arabian population rose to 21%. Many incidences of fatalities and serious accidents point to an increased number of traffic accidents. The country has experienced a fast economic development that has increased the number of vehicles owned by the citizens. The vibrant growth of the transportation sector has led to increased congestion and hence increased risks of accidents.
In the year 1998, 3,474 deaths and approximately 28,144 injuries occurred on the roads. These figures were because of at least 153,727 road accidents, which were in the statistics of the year 1998. However, researchers argue that these figures could be higher as they are not a whole representation of all the accidents that occur in Saudi Arabia since some of the cases go without entering official reports. Escalating figures of road accidents require the kingdom of Saudi Arabia to step up its traffic safety system to reduce the number of traffic accidents.
This paper aims to capture the traffic situation in Saudi Arabia Metropolitan areas to forecast a suitable future, from the challenges experienced now. In detail, the paper talks about the problems of traffic jams, it tries to identify their causes and the people responsible for such problems. The paper also dwells on other problems such as road carnages that currently present a nightmare to most road users in Saudi Arabia. The insight developed from all the resulting narratives forms the basis for our possible solutions to the problems that amount after each finding and discussion. In its methodology, the presentation depends on past data of traffic incidences recorded under different scenarios.
For instance, in a particular incidence of a road accident, an observation of the severity of the fatalities and damages involved provides us with the basis for a critical assessment of the level of risks posed by all the parties involved should such an accident occur again. Hence, through the data and such assessment criteria, we develop a model for projecting the findings to affect the future of the traffic situation in Saudi Arabia.
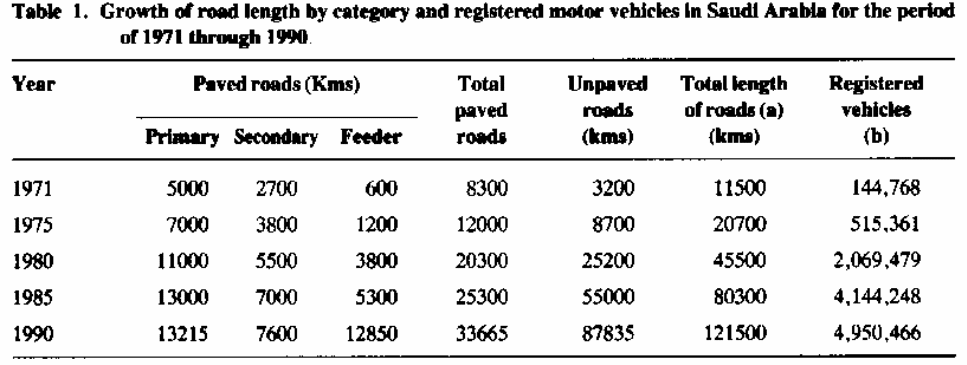
The table below shows increases in the number of paved roads as well as unpaved roads between 1971 and 1990. The development of roads led to the increased number of registered vehicles; this led to congestion on the roads hence increased risk of accidents.
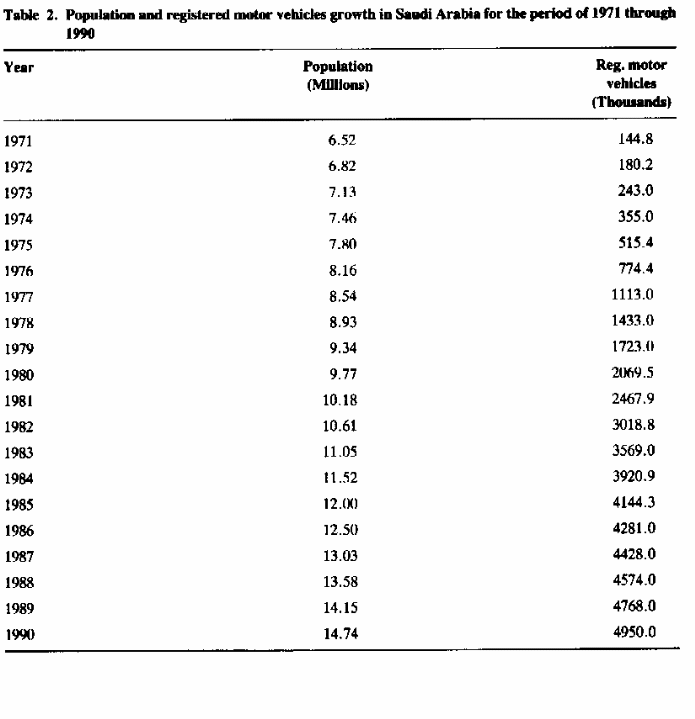
The table portrays a vibrant growth in the number of registered vehicles against the population of Saudi Arabia. As the population increases and the economy grows to accommodate this increase, the accompanying developments that lead to an increased standard of living have seen the number of registered motor vehicles also increase significantly. With this trend, a postulation that the number of registered motor vehicles will increase significantly in the future hold to the rate of three hundred vehicles per million of the population.
The two mainstream ministries charged with the responsibility of enforcing traffic safety in the kingdom would experience relative ease in managing traffic problems in the presence of good roads and strict adherence to traffic safety rules. For instance, overspeeding, poor vehicle maintenance, and ignorance of traffic warnings and other regulatory measures. The high percentage of the accidents attributed to recklessness on the part of the drivers and driving under the influence of alcohol, make the major proportion of statistical problems that require urgent attention. A study done by analyzing records from the police showed that drivers’ error was a major contributing factor to traffic accidents recorded in Saudi Arabia (Ghani 172).
The essay seeks to explore traffic concerns in Saudi Arabia by scrutinizing statistics to identify the magnitude of traffic accidents. The essay also seeks out the causes of road accidents and solutions to the increased incidences of traffic accidents.
Background information
Traffic safety concerns in Saudi Arabia (prove with figure/ statist.)
Saudi Arabia has experienced great economic challenges before its present transformation. Since many people resorted to the use of private cars as opposed to public means, the frequency of road accidents has drastically increased. Recent statistics show that, in every 100,000 of the population, 30 road users perish in road accidents involving motorists and pedestrians alone. In the Gulf States, Saudi Arabia has one of the best road leads in road accident fatalities with the rate of 38 deaths per 100,000.
While most of these occurrences could result from a myriad of other reasons, non-adherence to traffic rules and poor use of road safety measures seem to score much of the reasons attributed to road carnages. The transportation sector continues to experience major challenges in its attempt to control incidences of fatal traffic accidents. This is because of the ever-changing traffic requirements that come with the rapid growth of the transportation sector.
Increased number of the vehicle need expansion of roads as well as mounting of more traffic signs. Travel development is used as a marker of the degree of mobility in a particular region; Saudi Arabia registered a growth of 27% percent in its transportation sector within five years. This led to the increased number of vehicles owned by the citizens, increased level of transportation development, the introduction of communal transport services, development of limousine organizations and vehicle rental services, the fast growth of cities, and development of the entire economy (Ministry of Communication 51).
The current level of economic development attained by the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has had a significant influence on the rate of economic activities in the kingdom. Many people make haste movements on the road while oblivious of the looming dangers, in some incidences where drivers rush commodities and passengers to various destinations; the same drivers have often caused grisly accidents as businesspersons compete to make ends meet within a limited period. In the 1990s, the number of traffic accidents in Saudi Arabia increased from 4147 to 35799, in the same period, traffic accidents fatalities recorded increased from 570 to 2697 and the injured number of victims rose from 5483 to 22526. This shows the magnitude of road accidents in Saudi Arabia, it is evident that this situation requires improved traffic safety measures to curb the number of traffic road accidents in the country (Al-sayed 87).
The rationale for Choosing the Causes and Solutions
Traffic road accidents are a major concern in Saudi Arabian. The accidents not only lead to the death of many people every year but also leave many others with physical and psychological effects. More than two-thirds of accidents in Saudi Arabia are caused by failure to adhere to set speed limits and traffic signs. This relates to poor driving skills, habits, and failure by authorities to enforce traffic rules (Al-Sayed para. 4). The solution to a traffic accident in Saudi Arabia lies in changing the driving culture in the country. Proactive actions to enable people to respect traffic rules can help to reduce the rate of accidents by a big margin.
Causes of traffic road accidents
Over speeding
Factors, which cause an increased number of accidents, include; violent driving manners for instance over speeding (Al-sayed 1). This is driving the vehicle beyond the recommended speed limit. It then becomes hard for the driver to control the vehicle properly and, therefore, becoming more prone to accidents
Poor vehicle maintenance
This mostly concerns the wheels, brakes, and steering failures. However, the combined effect of mechanical failure contributes to less than 5% of motor cars accidents (Al-oteibi 29). Regardless of this fact, it is vital for the owners of the vehicles to have regular checks for their vehicles to avoid any chance of their failure, mechanically, to contribute to accidents.
Poor driving skills
Driving requires training from certified driving institutions to enhance the competency of the drivers. However, some individuals chose to train themselves or get training from other drivers, this leads to the increased number of incompetent drivers on roads (Al-Turki & Moha 67). This is because they do not go through comprehensive training and testing and, therefore, it becomes hazardous for them to drive vehicles.
Alcohol
Driving under influence of alcohol increases the risk of road accidents (Oxford Business Group 70). Since the driver cannot be able to concentrate and focus well on the road. The result of driving while drunk is an increase in chances of causing an accident, as the probability of collision is high because the driver cannot be able to control the vehicle well.
Lack of Law enforcement
Some elements of reluctance observed indicate stipulated traffic laws are not properly enforced (King Abdul-Aziz City for Science and Technology 78). This follows the administration’s lack of failure to enforce traffic laws at all times. Each time the drivers learn of the officers’ laxity, they drive with minimal adherence to traffic rules. Violation of traffic rules by the citizens will increase the chances of causing accidents as there are no checks for violation, and everybody would tend to violate these rules and as a result, there is an increased number of road accidents.
Safety driving measures
- Safer drivers’ habits: reckless driving accounts for a significant number of accidents recorded in Saudi Arabia (Ghani 89). There is, therefore, the need for the administration and related institutions to create awareness for safe driving habits to cultivate a culture that will encourage safer driving habits in Saudi Arabia.
- Safety road signs: Saudi Arabia’s transportation sector has installed traffic signals to guide drivers to control the increasing trend of road accidents in the country (El-Shabani 89). However, the strategic positioning of these signs still requires emphasis to make them more effective. In addition, driving institutions should improve their scope of covering the course content of driving with particular emphasis on road safety and the importance of obeying all the road signs.
- Safety education compliance: driving schools should make safety education compliance a compulsory exercise as part of the driver’s qualification. Unfortunately, most of the drivers on the Saudi Arabian roads omit this part of their course and may not count as qualified drivers after all. Hence, some of the avoidable circumstances still lead to road accidents. Therefore, this part of the training should form the useful time of gauging the proficiency of the driver without which, they would not get authorization to drive on the roads (Ministry of Communication 56).
- First aid care after crash: as a precautionary measure, proper first aid to road accident victims in all cases. This usually helps in reducing the adverse effects of the accident on the victims (Al skait 52). It is vital, therefore, that the drivers and the users of the roads are equipped with the necessary first aid skills for appropriate action where necessary, that is, in case of an accident. This will greatly reduce the extent of seriousness for the victims of road accidents.
Discussions
Statistics have revealed that the number of road accidents in Saudi Arabia increased due to inappropriate driving and non-motorized road users being ignorant of road rules. It cost the kingdom of Saudi Arabia more than 26 Bn. Riyals every year lose human resources and capital resources in terms of vehicles. All the authorities involved need to work in harmony to provide a safe motoring environment for all of its road users.
Most drivers tend to blame the status of the roads but investigations carried out implicate drivers’ behavior as the principal cause of road accidents. High speed kills, the higher the speed of a vehicle the higher the occurrence of an accident. Generally, drivers appreciate speed; however, it only makes sense when they can as well understand the consequences of overspending. Poor vehicle maintenance concerns wheels, brakes, and steering wheel failures. However, the combined effect of mechanical failure contributes to less than 5% of motor cars accidents. Old vehicles are more likely to experience a brake failure than new vehicles or well-maintained vehicles.
Wheel tires need constant maintenance, replacement of worn-out tires is fundamental in controlling accidents as associated with tire bursting. Uneven and worn-out tires also contributed to some of the major causes of accidents in Saudi Arabia. In some cases, vehicle wheels that play the critical role in keeping the car in uniform motion wore unevenly. This resulted in a grisly accident in certain cases since some vehicle owners took too long to replace the worn-out tires. Steering systems require checking in every 10,000 miles, suspension system failure is catastrophic notably at high speed. Ignorant drivers often neglected steering system check-up as required; this increased the risk of fatal accidents (Al-Ankary 48).
Poor driving skills; training of drivers needs to be from certified driving schools to enhance competency and accountability. However, some individuals chose to train themselves or get training from other drivers, this leads to the increased number of incompetent drivers on the roads. They are likely to wrongly change lanes, fail to signal, or fail to adhere to other traffic rules. This has led to more incidences of road accidents in Saudi Arabia.
Drivers with poor driving skills are likely to confuse other drivers and probably cause avoidable accidents. Driving under the influence of alcohol or other drugs increases the risks of road accidents. Drunk drivers are likely to violate traffic rules hence causing more road accidents than sober drivers do. Alcohol negatively influences the concentration of drivers, as they are unstable and more likely to lose control while driving since they drive carelessly. Among sober drivers, careless driving greatly contributes to road accidents as they blatantly disregard traffic rules (Al-Turki & Moha 67).
Traffic laws enhance the regulation of the transportation system in Saudi Arabia. However, some element of reluctance on the traffic rules impairs the efficiency of traffic rules in curbing some avoidable road accidents. Drivers implicated with reckless driving behaviors go scot-free instead of fully facing the charges associated with reckless driving. This encourages more reckless driving, hence an increased number of road accidents recorded in Saudi Arabia.
The public is not full conversant with different traffic laws and some end up violating them for lack of knowledge. Corruption has influenced enforcement of traffic laws for instance drivers implicated in violation of traffic rules just bribe traffic officers then go scot-free.
Violation of the law that prohibits the use of mobile phones while driving accounted for yet another reason that leads to road accidents in Saudi Arabia. Phone calls can cause a distraction while driving. Traffic police are at times reluctant in punishing drivers found guilty of this crime. Traffic officials have gadgets to measure the speed of moving vehicles to check incidences of overspeeding. Drivers implicated with overspeeding do not face charges associated with this crime and they are likely to repeat this crime on several occasions (Al-Zahrani 155).
Even with the implication of the perfect road rules, the complete elimination of road accidents is far from reality. However, observation of different safety driving measures would significantly reduce the number of accidents recorded in Saudi Arabia. The practice of safety measures from the early stages of driving resulted in mature drivers with less likelihood of causing accidents. This involved road construction, which entails planning, design, and maintenance procedures.
Properly developed and maintained roads also cause fewer accidents compared to poorly designed and maintained roads. Safety measures also involve the installation of safety devices such as road signs and streetlights to provide clear instructions to the drivers. Some roads in Saudi Arabia lacked these safety devices and more accidents occurred on these roads than on roads with all these installations. Safer drivers’ habits of reckless driving account for a significant number of accidents recorded in Saudi Arabia. Following Road Safety rules such as avoiding drugs and reducing the usage of mobile phones on the road will help curb the increase in the number of accidents.
Not exceeding the speed limit and use of safety belts for both passengers and the driver reduces the fatality of accidents if they do occur. Research showed that passengers who fasten their safety belts sustain minor injuries when accidents occur (Ghani and Elshabani 89).
The use of road safety signs; Saudi Arabia’s transportation sector has installed traffic signals to guide drivers to control the increasing trend of road accidents in the country. Road signs identified include street signs used to show named roads that do not meet the criteria of highways. In one particular study, signs mounted at the elevated places in road intersections helped drivers to observe speed limits, hence avoiding accidents.
On the other hand, drivers who found restrictions of speed on highways with no road sign elevated ignored the signs on the road at normal positions. The study used signs installed on the road to mark all turning points, schools, hospitals children, and zebra crossing. Similarly, signs to mark junctions and sharp corners placed on the roads could easily capture the attention of the drivers and pedestrians. However, most of the drivers chose either to obey the rules or not depending on their driving convenience. Generally, if important traffic road signs were in place most incidences of accidents could be because of ignorance of traffic signs (Jannadi 63).
Safety education compliance: Drivers in Saudi Arabia received training on traffic safety education to equip them with proper driving habits. A survey conducted showed that most of the institutions met the required standards in offering traffic safety education. Essentially traffic safety education should address the concerns of drivers and the entire public using the roads. However, the study showed that most institutions concentrated on informing the drivers at the expense of the entire public. The public did not understand some of the road signs, they were found to confuse drivers and this led to the occurrence of accidents.
Compliance with traffic safety education was found to be poor whereby most drivers understood traffic regulation but they did not practice them in their driving job. In most cases, drivers involved in accidents in avoidable circumstances admitted ignorance of the law as the main reason for this fault. In order o control the number of accidents recorded in Saudi Arabia minimum qualifications of drivers were constantly regulated and closely monitored to ensure that the required standards. Every practicing driver was required to have a valid driving license whose annual renewal requires the driver to undergo the Most drivers met these requirements with only about 25% of them failing the required standards (Ministry of Communication 58).
Immediate first aid care after a car crash reduces the adverse effects of the accident on the victims. Immediate attention of accident victims aid in the control of excessive bleeding hence controls the risks of death. Saudi Arabians have a history of natural rapid response to accidents. When coupled with training their response to victims of road accidents usually contributes to more survivors as opposed to dead casualties. The Ministry of communication has also developed an emergency line in which individuals can ask for assistance, for instance, an ambulance in case of a road accident. However, these services are not adequate.
For example, seven ambulance stations in Riyadh served by fourteen ambulances serve nearly all tragedies in the city. This number of technicians and ambulances attends to a population of at least four million, which is significantly inadequate. In Saudi Arabia, most of the victims find rescue in the hands of well-wishers or police from the accident scenes to various hospitals where they can obtain appropriate healthcare. Saudi Red Crescent (SRC) is unreliable because of the diminished confidence of the response team and poor management of the services (Alaska, McDonald, and Hassounah 52).
Role of King Fahd University in Traffic Safety
King Fahd University is one of the research institutions in Saudi Arabia; the university researches traffic concerns of the country. Analysis of these studies gives a clear picture of traffic issues on the ground and triggers the government and individuals to act to control the situation. This assist policymaker to develop policies that would ensure improvement of the transportation sector for policies that require strict observation of traffic rules and heavy penalties on those who violate these rules.
The institution also offers training on engineering professional who qualifies from this university making them competent enough to design and construct the safe road. They also act as technical advisors to the government and other stakeholders in the transportation sector. Some of the fundamental courses offered in the university include; the principle of safety management, individual knowledge on safety, the proneness of accidents theory, initiation of safety, and stress theory (Area and Saleem 85).
Limitations
Some road accidents in Saudi Arabia go unreported and the data collected may not be an accurate representation of traffic concerns on the ground. Individuals involved in road accidents may opt to resolve the matter from the road on their own without involving the authorities. Data collection through mailed questionnaires may be inadequate and may not meet the expectations of the research. Not many people would respond to the online filling of questionnaires as most people consider it as a waste of time (Khalid, Michael and Mazen 48-58).
System failure may lead to loss of some data and research may take longer than expected since respondents have to mail the questionnaires back. Future researches will provide more tangible solutions to the traffic concern in Saudi Arabia based on the current trends. For instance, research that makes use of the traffic conflict model, data collection that allows immediate response and analysis would make future research less tasking (Oxford Business Group 76).
Conclusion
Incidences of traffic road accidents have been on the rise in Saudi Arabia because of the increased rate of economic development. A significant form of development has been recorded in the transportation sector leading to the increased number of vehicles and hence increased congestion which leads to increased risks of accidents. Many traffic road accidents have been attributing to reckless driving, failure to observe traffic rules and regulations, overspeeding, driving under influence of alcohol or other drugs, and lack of enforcement of traffic laws.
Though complete elimination of road accidents may be ideal, in practice many challenges inhibit this possibility since humans would often get out of some traffic rules. Conversely, the implementation of traffic safety measures would significantly reduce the number of road accidents recorded in Saudi Arabia. For instance, drivers should adopt safer driving habits, comply with safety road signs and traffic safety education. Finally, simple safety precautions such as first aids should always accompany all traffic expeditions. Having such preliminary medical services at an arm’s length critically alleviates the conditions of road accident victims by relieving them of their pain while awaiting the doctor’s interventions.
All drivers should meet the minimum qualification before they obtain a driving license. Ultimately, the government should endeavor to ensure all institutions that offer training services to drivers meet certain minimum criteria. This would then go along away in producing qualified drivers who may not cause accidents frequently, since they score public road safety credibility. Enforcement of traffic laws needs to be improved, all drivers who violate traffic rules should face full charges.
Recommendation
To reduce the number of accidents on the roads in Saudi Arabia, several measures ought to be instituted. The following are just the recommendations that I think could work out to curb this phenomenon.
Proper vigilance of the roads
The local authorities need to increase their vigilance on the roads to be able to control the traffic adequately. A high presence of traffic control officers will instill fear in several reckless drivers. This way, the drivers will be sure to follow the roads to avoid arrests and prosecution.
High penalties for traffic offenders
Instituting high court penalties for traffic offenders may also be very effective in reducing traffic accidents and thereby reducing deaths and injuries sustained in these accidents. For example, a driver who causes deaths of passengers and other road users through reckless driving ought to face murder charges. This way road users will be cautioned on the reckless use of the roads, and this will go a long way in reducing accidents. Penalties such as banning drivers and withdrawing their licenses will also help ensure that drivers obey the set traffic rules.
Licensing
The authority responsible for licensing vehicles as well as public transport workers also need to be very keen on the issuance of licenses. Licensed vehicles need to undergo checkups after a specified period to check their roadworthiness. Some public transport vehicles get too worn out and repairs are inevitable. Such vehicles should be withdrawn from the public transport system to reduce the chances of them causing accidents.
Proper training road marking
Institutions responsible for training drivers should also improve on their training to make sure that they uphold professionalism. This will ensure that licensed drivers meet professional standards and therefore reduce cases of accidents. Roads should also be properly marked. This may also be effective in reducing accidents
Works Cited
Al-Ankara, Khalid and El-Bushra, El-Sayed. A Profile of Transport in Saudi Arabian Cities. Urban and Rural Profiles. Berlin: Stuttgart-Gebr, Borntraeger, 2006. Print.
Al-Oteibi, Saheed, Noble, Al-Fazahd, and Costa, Ferdich. The Impact of Planning On Growth and Development in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1970–1990. New York: GeoJournal Springer. 1998. Print.
Al-Sayed, Mohammad. Problems Road Traffic Issues in Saudi Arabia. n.d. Web.
Alskait, Khalid, McDonald Michael and Hassounah Mazen. The Impact of Urban Arterial Cross Section on Abutting Property Values: The Case of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Transport Policy. Elsevier, 2008. Web.
Al-Turki, Mohamed and Moha, Said. Saudi Manual for Traffic Studies. Final Report. King Abdul-Aziz City for Science and Technology General Directorate of Research Grants Programs. 2008. Print.
Al-Zahrani, Ahmed and Jadaan, Bener. Current Traffic Safety Issues In Saudi Arabia. J.King Fahd University. Eng Sci, L 7.11. 998. n.d. Web.
Aree, Mohamed and Saleem, Farred. Effects of Increasing Axle Loading. Saudi Engineers Conference. Dhahran Saudi Arabia: University of Petroleum and Minerals, 1995.
Ghani, Ghani and Abdulla El-Shabani, A. A Profile of Transport in Saudi Arabian Cities. Urban and Rural Profiles. 2006. Berlin: Stuttgart-Gebr, Borntraeger. Print.
Jannadi, Mohamed and Al-Sudairi, Aziz. Traffic Safety Management in the In Saudi Arabia. Building Research Information, 23.1. 1995. Web.
King Abdul-Aziz City for Science and Technology. National Traffic Safety Committee: An Information Report. Riyadh: King Abdul-Aziz City for Science and Technology, 2008. Print.
Ministry of Communication. Roads Data Bank. Riyadh: Ministry of Communication Saudi Arabia, 2008. Print.
Ministry of interior. General Directorate of Traffic. Saudi Arabia: ministry of interior, 1990. Print.
Oxford Business Group. The Report Saudi Arabia. New York: Oxford Business Group, 2008. Print.
Appendix 1.0