Internal Analysis
The performance of Uber is heavily dependent on its strengths and weaknesses. These parameters are inbuilt into the company operations and nature and are entirely controllable from within. Strengths are exploited from within to gain better market share and increase productivity and profitability. Uber is a global brand name, with advanced technology and a large customer base. However, the company is also subject to regulatory challenges with high operational costs, dependence on drivers, and safety concerns which greatly hinder its progress. In this section, the strengths and weaknesses are discussed in detail.
Key Competencies
Innovative Technology
Uber’s app-based platform is its key competency, which allows passengers to hail a ride from any location and drivers to find passengers easily. The technology also enables payment processing, real-time tracking, and analytics (Seidl, 2022). The business uses technology to reward customers with incentives and promotions during regular service, which makes them more amiable and competitive in the cutthroat industry.
Market Dominance
Uber has a significant market share in many regions worldwide, which makes it challenging for new competitors to enter the market. As a result, it may use the advantages of having a huge client base to sell its products, keep current users, and draw in new ones (Seidl, 2022). The substantial customer base suggests enormous income for the business to meet its objectives, turn a profit, and expand into new markets and services.
Customer-Centric Approach
Uber’s customer-centric approach, which focuses on providing safe, reliable, and affordable rides, has been a key to its success. The competency places the company in a competitive edge to serve its customers in a satisfying manner (Seidl, 2022). Uber uses data analytics to make informed decisions, such as determining pricing and identifying areas with high demand. This helps the company to optimize its operations and provide better services to its customers
Scalability
Uber’s business model allows for rapid expansion to new markets and regions, which has contributed to its growth. The company introduced. Over the years, the model has been expanded to encompass food delivery, ride-sharing, and cab services. By providing a range of products and services, the corporation can increase its revenue sources. A different chain of enterprises may be able to make up the difference if a company underperforms or fails to meet its revenue targets (Seidl, 2022). Also, the promotion of various services is aided by one another. For instance, once users of ride-hailing services are satisfied, they are likely to sign up for the other services as well. In this sense, the diversification of services will benefit the business operations and the ability to generate revenue.
Weaknesses
Regulatory Challenges
Uber has faced significant regulatory challenges in many countries due to concerns over safety, insurance, and labor laws. The difference in laws and regulations makes it difficult for the company to employ a discrete or dynamic business model (Seidl, 2022). For instance, inside the U.S., different states may enact different laws for business establishment, affecting the welfare and performance of the drivers. The company should chip in and lobby for a fair operational ground for its drivers and services.
High Operational Costs
Uber’s business model requires a large fleet of drivers and vehicles, which can lead to high operational costs, especially during peak hours. As a result, the company has struggled to make profits due to its business model. The company is yet to make profits, despite many years of market dominance and global recognition (Young & Farber, 2019). The losses are attributed to the company costs of doing business which cannot be avoided.
Dependence On Drivers
Uber’s business model is heavily reliant on drivers, which can lead to issues with driver retention and recruitment. Over the years, drivers have protested the terms and conditions for work, staging demonstrations around the world. Such demonstrations and downing of tools have paralyzed the company’s services, resulting in losses and damaging the company’s reputation. The dependence on drivers increases the cost of doing business, company reputation, and customer satisfaction (Young & Farber, 2019). The challenge seems ingrained in the company’s business model and hard to tackle.
Safety Concerns
Uber has faced criticism for its safety practices, including incidents of assault and harassment. On most occasions, customer reports of assault are treated with urgency with the intention of retaining the company’s reputation (Giddy, 2022). However, cases of driver assault are treated with laxity, affecting the drivers’ morale and raising questions about their welfare (Giddy, 2022). The safety concerns affecting the company are primarily raised by customers and drivers, and the company has failed in taming such incidents (Giddy, 2022). While it is important to satisfy customer needs and experience, the welfare of the drivers must be prioritized.
Financial Ration Analysis
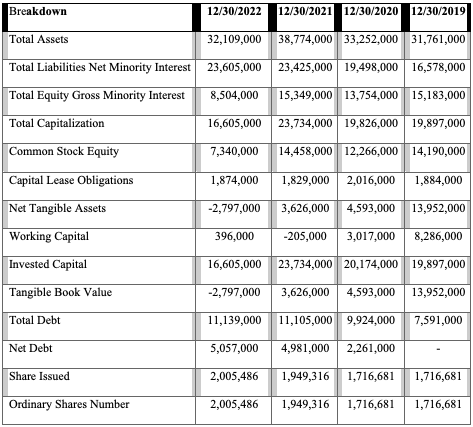
Table 1 summarized the company balance sheet for the last four years (2019-2022). The currency values are in United States Dollars. The total company assets were on a steady rise from 2019 to 2021 but declined in 2022. The Total Liabilities Net Minority Interest increased over the specified period from $16,578,000 in 2019 to $23,605,000 in 2022. The company’s equity and total capitalization declined in value, an indication the company is performing poorly. The net tangible assets, working capital, and invested capital also declined as shown in Table 1. The total company debt increased from $7,591,000 in 2019 to $11,139,000 in 2022. The net debt also registered a significant hike, putting pressure on the company’s financials and operations. Despite the company’s poor performance, the number of shares issued increased to 2,005,486 in 2022. The original number of shares in 2019 was 1,716,681.
Implications
The company has never been profitable since its inception, making it difficult for investors and managers to formulate a reliable way forward. However, the company must make profits for the investors to gain from their outlays. First, the company must increase its number of tangible assets and reduce liabilities. Increasing assets promote revenue generation platforms, resulting in higher proceeds. Liabilities result in undue costs that must be avoided or eliminated for sustainable performance.
The company must also change the trend in its non-tangible assets as they play a significant role in its balance sheet. The number of shares issued should be increased and their prices harmonized accordingly for market stabilization. Further, the company should also consider buying back its shares to increase its value and competitive advantage. The adoption of the above-stated recommendations will ensure the company attains profitability and sustainability in its operations.
References
Giddy, J. K. (2022). Uber and employment in the Global South–not-so-decent work. Tourism Geographies, 24(6-7), 1022-1039. Web.
NYSE. (2023). Uber Technologies, Inc. (UBER), Yahoo! Finance. Web.
Seidl, T. (2022). The politics of platform capitalism: A case study on the regulation of Uber in New York. Regulation & Governance, 16(2), 357-374. Web.
Young, M., & Farber, S. (2019). The who, why, and when of Uber and other ride-hailing trips: An examination of a large sample household travel survey. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 119, 383-392. Web.