Introduction
Data is analyzed in various ways. Analyzing and forecasting data is essential because of its applicability. Data analysis involves various measures, such as central tendency and dispersion measures. The measures include mean, mode, median, range, and standard deviation. The study aims to give insight into the measures of central tendency and standard deviation. The study also covers data forecasting.
Data Analysis
Table 1: Wind speed data collected for 10 days in the UK
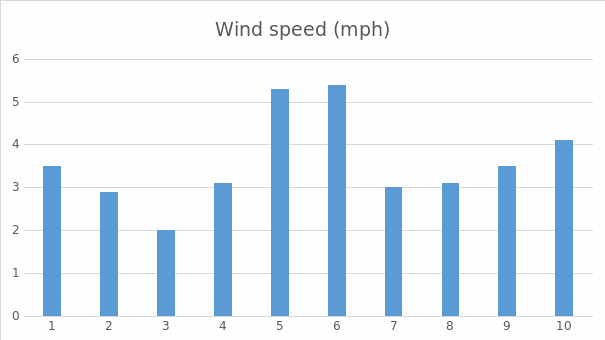
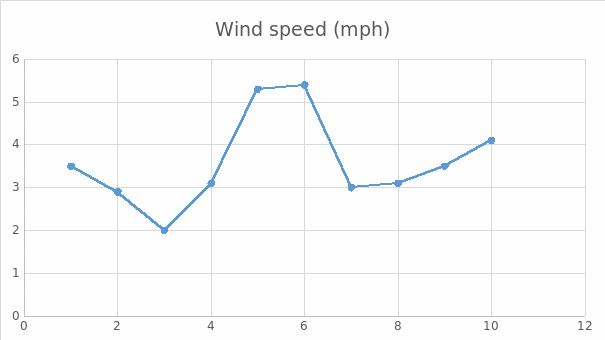
Mean
Mean refers to the average number of a population or a sample. The mean is obtained from quantitative data (Khan, 2019). The mean is the central number of a set of numbers. In this case, the mean will represent the average of the data set, including the wind speed data collected in the UK. To calculate the mean, all values in the data set are summed up and divided by the number of data points.
Steps involved in calculating the mean include:
- Summing up all the values in the data set. Values of wind speed are summed up. We find 3.5 + 2.9+2.0+3.1+5.3+5.4+3.0+3.1+3.5+4.1.
- The sum of the data obtained is divided by the number of values. In this case, data is collected for a period of 10 days; hence, the sum obtained is divided by 10.
The mean of the data set obtained is 3.59. From the value obtained, a conclusion is made that 3.59 represents the center of the data.
Median
The median refers to the middle number of a data set arranged in descending or ascending order (BYJU’S, 2022). The median is obtained from a series of steps, namely:
- Arrange the data in order. Data is arranged from the greatest to the least value or from the least to the most significant value. After arranging the data, it becomes 2.0, 2.9, 3.0, 3.1, 3.1, 3.5, 3.5, 4.1, 5.3, 5.4.
- The number that separates the higher half and the lower half is the median. In the case of multiple numbers, the average of the middle numbers acts as the median.
From the data collected on wind speed in the UK, the median is 3.3. The middle number of the data set, therefore, is 3.3.
Mode
Mode represents the value that occurs most frequently in a data set. A data set can contain more than one mode. Mode is a highly advantageous measure of central tendency because it is applied to data (Trinidad, 2022). Mode is not affected by extreme values in datasets with quantitative data. Obtaining the mode includes some simple steps:
- Data collection and organization from a data set. The collected data on wind speed is organized in a table, as indicated earlier.
- The next step is the determination of distinct values in the data set.
- After the determination of distinct values, the frequency of occurrence of each value in the data set is counted.
- The data that appears more frequently becomes the mode.
From the data obtained, 2.0, 2.9, 3.0, 4.1, 5.3, and 5.4 appear once. The values 3.1 and 3.5 appear twice, making them the most frequent data. The model is used to identify problems in a data set and to characterize data distribution. The data provides two modes; a conclusion is made that the data distribution is bimodal.
Range
The range statistically represents the difference between a data set’s maximum and minimum values. To determine the range, the highest and lowest values in a dataset must be found (Taylor, 2019). The range of a dataset is interpreted as the difference between the maximum and minimum values.
The data collected shows the maximum value is 5.4, and the minimum is 2.0 (Calzo, 2023). The difference between the values is 3.4, which is the range. Determining the range involves measuring how spread out the data is. A larger range indicates greater dispersion, while a smaller range indicates that the data is more closely clustered.
Standard Deviation
The standard deviation is a statistical measure used to calculate the amount of variation or dispersion in a dataset. Measuring the standard deviation is imperative because it gives more information about the level of uncertainty in a dataset (Arshad, 2023). Unlike other measures, the steps involved in calculating the standard deviation are pretty complex. The steps involve:
- Calculating the mean of collected data on wind speed in the UK. The mean in the data is 3.59.
- Subtract the mean from each value in the dataset. Values (2.0, 2.9, 3.0, 4.1, 5.3, 5.4) are subtracted from the mean of 3.59. The obtained values are ( -1.59, -0.69, -0.59, 0.51, 1.71, 1.81).
- Square each difference and add them. The value becomes 11.454436.
- Divide the value obtained by several values, which is 10.
- Take the square of the result, which represents the standard deviation. The standard deviation, therefore, is 1.070254.
Here are the steps for calculating m in the forecasting formula y = mx + c.
The value m refers to the gradient of the equation. It shows the steepness of the line. To calculate the value of m:
- Calculate the value of x2 and xy for each point.
- Find the sum of all x, y, x2, and xy to obtain the values of ∑x, ∑y, ∑ x2, and ∑xy. From the data collected on wind speed values, the obtained values are ∑x = 55, ∑y = 35.9, ∑ x2 = 385, and ∑xy = 204.
- A formula is applied to calculate the value of m.
![]()
The value of m in this case is 0.079.
Value of c in the forecasting model:
c is an intercept and its value is calculated using a formula.
![]()
The value of c from the formula becomes 3.155.
Forecasting wind speed on day 12 and day 14:
To forecast, the value is just applied in the formula hence calculating the wind speed. From the previously obtained value, the equation is
y = 0.079x + 3.155.
On day 12, the wind speed is 4.103 mph.
On day 14, the wind speed is 4.135 mph.
Conclusion
The mean, median, and mode are measures of central tendency that go hand in hand. The mean and median are restricted to quantitative data, while the mode is more advantageous because it is not affected by extreme values in the database with quantitative data. From the discussion, the standard deviation and range are standard deviation measures. The steps for obtaining the median are easy, while the ones for obtaining the standard deviation are complex. Data collected from the field is presented in various charts.
Reference List
Arshad, M. (2023) “Standard Deviation: Understanding and Calculating,” Decoding Data Science [Preprint]. Web.
BYJU’S (2022) “Median in Statistics – Median Formula, How to Find & Solved Examples,” BYJUS [Preprint]. Web.
Calzon, B. (2023). “What Is Data Analysis? Methods, Techniques, Types & How-To.” BI Blog | Data Visualization & Analytics Blog | Datapine. Web.
Khan, A. (2019) Calculation and Interpretation of Mean and Median – Toppr Bytes. Web.
Taylor, C. (2019) “What Is a Range in Statistics?” ThoughtCo [Preprint]. Web.
Trinidad, C. (2022) “Mode,” Corporate Finance Institute [Preprint]. Web.