Introduction
The success of any business enterprise whether it is a small scale, medium or large enterprise depends on how well its management department works. According to Lonergan (2010), project management is the process by which the management department of an organization plans, organizes, and manages resources of the organization with an aim of achieving a specific goals and improving the efficiency of service delivery. In most cases, the project management process is not a short time but a long-term process that involves planning and implementation of the projects. Before the project, management process is laid out, data analysis and sampling has to be done to establish the area that the project will focus on.
The purpose of this research paper is to critically analyze the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) that many organizations adapt to when implementing their project management plans. The paper will look at how the project team will communicate, where the project information will be stored and methods in which the information will be accessed. The paper will describe how the project issues will be tracked and how any outstanding issues will be escalated for resolution and finally the paper will briefly describe how the project team will resolve disagreements and conflicts including the appropriate escalation path you would like the team to use.
In addition to the above stated points, the paper will look at the main risks that are involved during the project management plan and implementation and how tan organization can reduce such risks. As such, it is important Optimizing innovative capacity for small enterprises is a vital ingredient for successful execution of strategy, especially in project management related models. Methods and systems of addressing operations-related optimization in the context of small business enterprise draw effectiveness by facilitating optimizing of innovative capacity.
Work Breakdown Structure
The purpose of the Work Breakdown Structure in an organization is to ensure that the decisions implemented by the company meets the needs of the clients. The WBS structure is divided into three different segments and each of them contributes differently to the project management process. There is the WBS development, time and cost estimation and finally the schedule development.
The figure below shows a sample of a Work Breakdown Structure
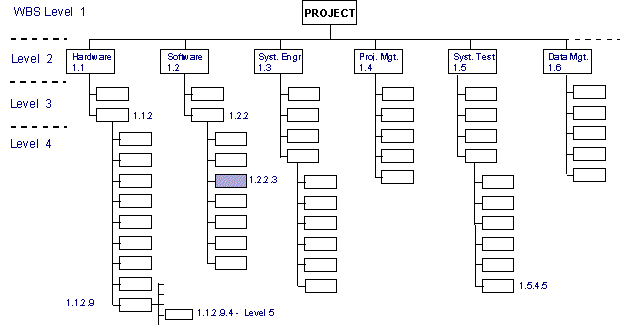
Introduction to the Work Breakdown Structure
There are different stages that are covered in the WBS process and in each level, the project implementers carry out different tasks. From the sample above a normal WBS have four main levels with the top level being reserved for the project managers. The second level of the WBC consists of different departments in the organization and under each department; there are different levels for the project implementation. The different departments have managers who oversee the activities of the department and report to the chief project coordinator.
WBC Development Stage
In the WBC development stage, the project designers identify tasks and work on the breakdown of how the tasks will be carries out; other important things that are taken into consideration during these initial stages of WBC development are the time the assignment will be completed and the project schedule.
The figure below gives a summary of the WBC development stage:
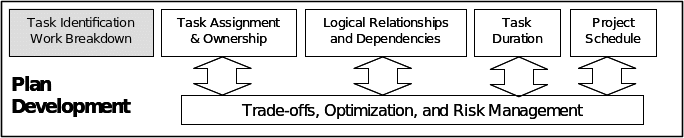
Time and Cost Estimation Stage
In project management and implementation, time of essence. The lesser time that an organization spends on a project, the less money it is likely to spend on its implementation. In this stage, the WBC planners give a rough estimate of time that they are likely to take on the project, however this depends on the nature of assignment given to them. If the assignment is complicated, they are more likely to spend more time as when the project is simple.
The amount of money spent also varies depending on the budget drawn. In this stage, the project life cycle is also taken into consideration and this has a great impact on the time and cost estimation. The project life cycle covers three main steps; the initial phase (part of which is covered in the WBC development), the intermediate phase and final phase (which is covered in the schedule development)
Schedule Development
After the project has been designed and it is ready for implementation, then it is time for the final phase of WBC lifecycle that is schedule development. Under this stage, the project managers come up with a “time table” or plan of action on how the project will be rolled out. In most cases, the project is rolled out in phases to enable the organization monitor the performance of the project (Kerner 2009). In addition to that, they will be able to monitor the input that the new project generates for the company. The schedule development will also help the project managers manage the project easily and be able to re-evaluate and improve on the viability of the project.
Project managers have immense delegated power but lack the teeth to manage the business process they are creating. This draws out the difference in project management and functional management practices. The project manager is inclined to put efforts in scheduling, controlling and planning. His role is rather confined to execution of strategy rather than management of the process that oversees the creation, funding, and facilitation of this plan or project. The project manager has a greater role to play apart from foreseeing the implementation of strategies and smooth rollout of a project. Funding and facilitations are among other major roles he has to look into.
Project Management Risks
Many risks are involved when it comes project management. The risks that face the project managers need to be analyzed carefully by the management to determine whether they will derail the process of project s implementation. Each department faces different risks, which should be addressed separately. PMBOK states that, the conflict over resources is one of the major risks that face the organization especially in the intermediate stage; this is because of the demand for more capital by various departments to complete the tasks given to them (PMBOK 2009). Project management is the science of managing a strategic plan, the objective being, and a measure of success.
This measure of success is through a project manager’s ability to negotiate, well, with both upper levels and functional management in an organization. These levels draw functionality from resources set aside for the project objective. In some situations, the management my withdraw funds / resources allocated to one department and allocate them to another department because of new demands that may arise. The management of the organization therefore needs to plan well to ensure that the funds available are well budgeted for to avoid such conflict. In addition to that, the management needs to balance the human capital in the various departments to ensure that there is no shortage of human capital.
Summation
Project management in an organization is a vital task in an organization, however if not well planned for it can cause many losses to the company, both financial loss and loss of resource. Project management should be viewed from a broader perspective whereby the process should be viewed as central in facilitating strategic plans. Organizations use project management to rollout various projects, as such the project management aspect of rolling out is critically important.
Project managers have a greater role to play though their roles differ with mainstream management practices. Their role is to facilitate the development of brainchildren to reality and once this is accomplished, they move into another project. The challenging aspects of project management is the every changing roles, especially in the funding and budgeting for the project and equitably distributing funds to all parts of the project.
The human resource department of an organization which in most cases is mandated with the responsibility of implementing new projects in an organization should be well equipped financially and personnel to ensure that the projects that are implemented are beneficial not only to the organization but to the clients as well. However, human resources managers have been blamed for prejudicing project managers and often faulting them in their duties and forcing them out for the fear of these managers replacing them. However, this only makes project management more challenging and essential in modern management practices. It offers a broad view of how resources and strategy should be used to bring change and development.
References
Chapman J.R (2007). Introduction to the Work Breakdown Structure. Web.
Emprend Inc (2002 – 2006). INTRODUCTION: Plan and Schedule Development– Task Identification and Work Breakdown Structure. Web.
Kerzner H (2009) Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling10th. Edition. John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
PMBOK (2009) A Guide to The Project Management Body of Knowledge 4th Edition. Project Management Institute.
Lonergan K (2010), Project Management. Web.