Background of the Company
The purpose of this report is to prepare a global marketing plan for the Chinese company Zhejiang Gonow Automobile Ltd (ZGA), which started its operation in the domestic market in 2003. This company is producing pickup and sport-utility vehicles (SUV) for the local market but it would like to enter the Indian market with its eco-friendly cars named “A car for megacities” for the customers who are conscious about the environment.
ZGA is the market leader in pickups, and SUV segments in the Chinese market and it can manufacture 320,000 pickups and SUV per year and it will increase its production capacity to produce 100,000 small cars for the Indian market. However, the marketer of ZGA has chosen the Indian market because the Wall Street Journal (2010) reported that India is the second fastest-rising vehicle market due to the availability of financial support and other facilities.
PESTEL analysis
Political factors
Peter, Kerr & Thorpe (2002) stated that India has experienced huge economic growth due to a flexible taxation policy. On the other hand, the government of India has to concentrate on the unification of the country and to protect terrorist trends of communist groups and liberation activists, which reflects a negative impact on the foreign companies.
Economic factors
IndexMundi (2011) reported that India is now the perfect market for multinational companies to do business because the government reduced controls on foreign trade and decreased tariffs to help the country to experience a 7% annual growth rate. As a result, overall economic condition is favorable for the automobile manufacturers though GDP down 6.8%, and increase the unemployment rate can reduce aggregate sales. On the other hand, Prabhudesai (2010) stated that the economic development of India highly depends on the economic position of the US market; for instance, India’s market has faced the adverse impact of the global financial crisis but this situation changed because of the quick recovery of the US economy. However, the following table would help the company to make a decision –
According to the above table, India’s negative trade balance has grown gradually due to increasing dependency on import products. Therefore, ZGA has the opportunity to enter the Indian car market using export and it would be an alternative business entry strategy for the company;
Socio-cultural factors
Many social factors influence the automobile industry in India, such as purchasing power of the people, increase demand for changing lifestyle, customer behavior, educational background, awareness, social mobility, religious backgrounds, religious festivals, and so on. However, the people of India would like to purchase new products at the time of Durga Puja, Diwali, Holi, and other occasions; therefore, ZGA Company should offer special discounts to increase sales in the Indian market.
Technological factors
According to the report of the Library of Congress (2006) and IndexMundi (2011), India has experienced huge success in the case of technological development. To sustain in this market, ZGA would integrate advance technology to produce eco-friendly cars, which need low fuel consumption; as a result, carbon emission from this brand would expected level. On the other hand, it must consider India’s technological structure to offer safe products to the customers;
Environmental Factors
India had participated in Stockholm Conference 1972 to protect the environment and the government of this country passed several laws including the Environment Protection Act 1986 after the Bhopal Gas Tragedy. Barley (2009) stated that the emission of CO2 in India presently accounts for approximately 6% of the total emission in the world, so, the regulation is strict for the foreign company. As a result, the marketer of ZGA has to ensure that they will meet the terms of the regulation regarding air pollution and environmental safety provisions. Johnson (1997) argued that automobiles should have ISO 14000 certificates, which involves the use of a strict environmental management system; however, ZGA Company has already obtained ISO 9001 Certificate and it is trying to get ISO 14000 certificate by meeting all criteria.
Legal Factors
According to the report of Narayanan & Vashisht (2008), the regulation after 1996 is more flexible for the automobile industry, which makes the market more competitive. The government tries to ensure the highest possible business-friendly environment for the multinationals and new entrants, as a result, local auto manufacturers have involved price war and Tata offered the cheapest car in the world because foreign companies captured the market for flexible entry provisions.
Porter Five forces analysis
This paper will use Porter’s five forces model of competition to assess the competitive environment for ZGA in the Indian market. However, the following figure shows these forces for ZGA –
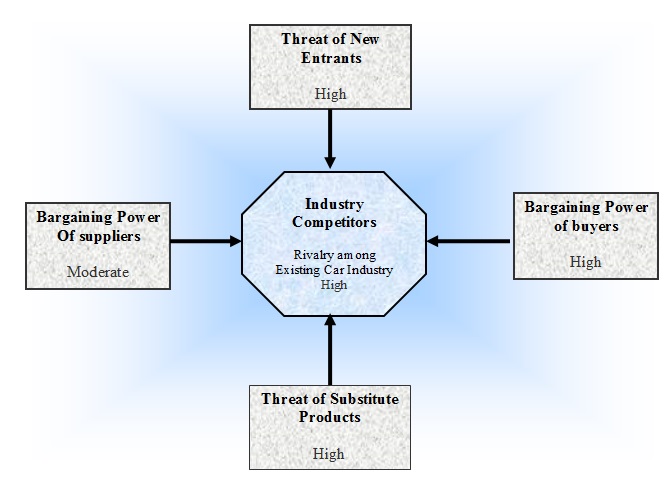
Threats from new entrants
Narayanan & Vashisht (2008, p.9) reported that Chinese car producers need to pay 17% taxes to enter the Indian car market. They further added that taxation policies also vary by the decision of State ministry, Maharashtra government offers some flexible provisions for the foreign companies. On the other hand, Gopal (2006) stated that it is easy for the large US and Japanese automobiles to enter this market as they have a strong brand image but small firms need to struggle to start operation and compete with these companies;
Bargaining power of suppliers
ZGA would intend to joint venture with Tata Motors, the market leader of the Indian Automobile industry. However, the bargaining power of the supplier would be low for ZGA if it can joint venture with Tata Motors as Tata has own steel mill and the relationship of this company with other suppliers are outstanding; otherwise, the power of suppliers would be high;
Bargaining power of buyers
According to the view of Gopal (2006, p.23), the bargaining power of buyers is high due to low switching off costs, and availability of cars at a lower price. Here, it is important to mention that Indian Banks are more willing to pay car loans with flexible payback conditions; therefore, the buyers have the purchasing power to purchase cars from several brands. On the other hand, middle-class target customers drive to purchase cars of foreign companies and low earners rely on the public transportation system increase the bargaining power of buyers;
Threats of substitute products
ZGA must face hard competition from some other alternative transportation besides different products of direct competitors, such as Indian people who would like to use the train, tram, and another public transportation system. On the other hand, large numbers of two wheels and three wheels particularly Honda, Rickshaw and taxi are available and popular transports in every state of India;
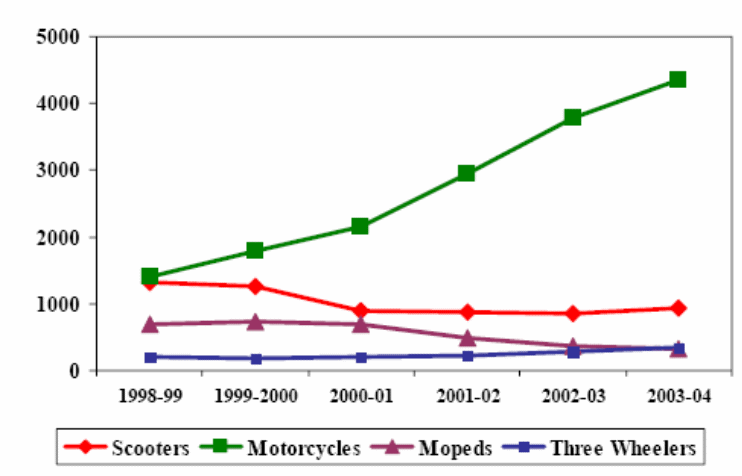
The above figure shows that the use of Motorcycle in India is increasing day-by-day and the use of three wheels is in a stable position; on the other hand, the use of Scooters and Mopeds are decreasing.
Rivalry among existing firms
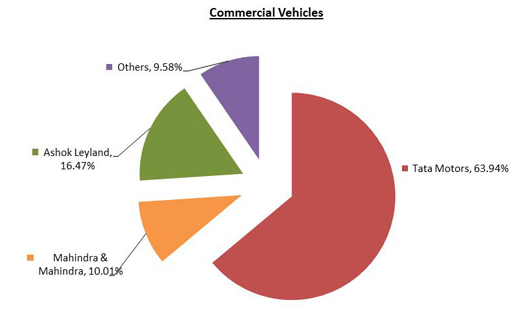
ZGA has to face intense competition from both domestic and international automakers. However, domestic car maker such as Tata Motors holds the largest market share of Indian small and commercial car markets and this company produced more than 4 million cars for the local market and generated $14 billion sales revenue in the fiscal year 2008-09. This company has already taken several measures to sustain itself as a market leader, for instance, it enlisted in NSE, introduced the cheapest car in the world and so on. At the same time, some other auto manufactures like Maruti Suzuki, Bajaj Auto, Mahindra & Mahindra, Eicher Motors, Ashok Leyland, Hindustan Motors, Ford India, Hyundai Motors offer several brands with new features to attract the customers.
SMART Objectives
- ZGA will reset its marketing objectives to enter the Indian market and it hopes to enter within 2012 by joint venturing with renowned car marker like Tata Motors;
- It will increase its integrate profit by 40% with the next 4 years;
- However, ZGA will spend 5% of its net sales revenue of 2011 for the market research to enter the Indian market;
- ZGA must increase the budget by 35% within 2013 for promotional activities as it helps to increase sales;
- This company will arrange an IMC campaign within the next 2 years to attract large customers;
- Finally, ZGA will open at least 140 new showrooms in different states within 2015.
Global Market Entry Strategy
Joint venture
The marketer of ZGA has decided to enter the Indian market using a joint venture strategy because this strategy will help the company to strengthen its position in a new market, utilize the brand image and share the technology of local partners. At the same time, this strategy has some other positive issues, for instance, low cost for business expansion, low-risk factors, local partner’s influence government policy, and development of accessing monetary assets, the achievement of economies of scale, offering pre-emptive competition, greater flexibility and diversification opportunity to meet the objectives.
Franchise
Blair & Lafontaine (2005) stated that franchise is equivalent to licensing but it focuses on long- term contractual agreement and Johansson (2008) argued that this method provides a significant form of vertical integration with an effective combination of centralization of skills and decentralization of operation. However, this strategy would not be effective for ZGA company to enter Indian market because ZGA has domestically marketed and have no presence in the global market; therefore, investors may not be interested for its eco-friendly products.
The risks and opportunities of other strategies
Risks
Export would not be an effective strategy for the company because ZGA has not strong supply chain management system in India and the company has to comply rules and regulations strictly through WTO accession makes it easy to enter this market. On the other hand, ZGA has no practical experience and knowledge about the Indian market as well as socio-cultural factors of the country, which will create hindrance for the operation of ZGA.
On the other hand, franchise strategy would not be effective for ZGA Company to enter the Indian market because ZGA has domestically marketed and have no presence in the global market; therefore, investors may not be interested in its eco-friendly products. At the same time, the problems of the franchise are – the company could lose control over the management of the business, ZGA needs to depend on the franchise supply network, this process might damage the reputation and need large funds to conduct franchise agreement.
Opportunities
Johansson (2008) pointed out that export is a comparatively low-cost action to enter a foreign market to increase its annual profit level and this process reduces the risk of large start-up business costs. ZGA could follow franchise strategy considering the advantages, such as the investors are more willing to invest in established business as it offers a higher opportunity for making a capital investment with adequate control throughout the process, and it has low-risk factors with advance security system for the investors.
Global marketing strategies and tactics
In this case, the marketers of ZGA observed the market and decided that pricing strategy would be the most appropriate global marketing strategies and tactics for ZGA because the low price product suppliers mainly captured the Indian Vehicle industry. However, many large companies entered this market with innovative product line but due to the high price of the product, they failed to attract the target customers while Tata Motors is the market leader mainly for low price products, therefore, ZGA will consider this strategy.
The fact that India is the second-fastest-growing car market with 17.5% of the global population and magnificent economic growth makes India a quite attractive market to enter. However, what is more, important to think about before this penetration could be a success is that India is the nation that has estimated to have one-third of the earth’s poor people – as per a 2005 World Bank report, 41.6 percent of the total Indian population is under the global poverty line of USD 1 – making the market quite unattractive.
Although India’s economy is booming, but the new wealth does not go equally to the entire population – only a very few number of them are getting benefited with massive wealth; while others live in unpleasant, deprived and obnoxious conditions, where the demand for the car is hard to come by. This inequality in wealth is clearly visible in Mumbai, which is getting bigger as India’s commercial capital, but is still the home for the largest slum in Asia – which creates a great panic for the country’s economy and the operations of foreign businesses; therefore, after penetrating the market this can prove to be a huge trouble for ZGA.
In a situation, it is by no means wise for a business like ZGA to enter the market only for a very few number of rich people. This is because this can hardly to something to increase the profit level of the company, and rather can cause substantial losses for reason that the costs associated with entering the market is far greater than the sales that would occur.
This indicates the fact that to succeed in India, ZGA should consider that it is completely inappropriate to settle a high pricing that is affordable for only by a small number of rich families. It should focus on the growing middle-class group of the country, which can buy a car after saving their income for years – and perhaps decades.
For such a middle-class group, buying a car may mean forgoing the investment that it should make in buying meat or milk in the next five years, and merely depending on plain rice. Even though this sounds weird, but that is, what the reality is in every second family in India. Also, the more alarming thing is that even the rich people of India have a psychology that suggests not to invest money in bad ways – they teach their children such that investments should be made where it is highly necessary; so buying two cars where one would suffice is completely unwise.
In such a circumstance, is very important for ZGA to construct an appropriate pricing strategy for such a poor nation, as an inability to do so might push it out of the market. Moreover, a clever pricing strategy, above all, can help a business to succeed even in such an unfriendly consumer attitude. When Yum! Brands and McDonald’s, for example, entered the Indian market with a joint venture with some local businesses; they offer very low prices as compared to their pricing in the US, UK, and other western European countries. This resulted in a huge number of Indians visiting the Yum and McDonald’s stores, generating substantial profits. Now, these two brands are operating at a huge success in India just because of excellent pricing strategy. Consequently, ZGA should construct a pricing that should be right above the production costs, but still quite low to be afforded by the middle class.
Control and evaluation methods
The management of ZGA should evaluate business operation and performance of the new market by comparing the profit margin of two terms of the company to evade any accumulative losses and to take preventive or corrective actions. However, ZGA should have five departments to control five major sides of the business and they will arrange quarterly meetings to coordinate the works of all departments.
This strategy would help to reduce the effort of the employees as financial managers would be responsible for financial activities, the sales department would be liable for aggregate sales and the production department would be accountable for the quality of the products. However, the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) would control and co-ordinate the activities of the five departments and take all important decisions considering the external and internal business environment. At the same time, the CEO must instruct the managers to implement the present strategies for prospects and he must attain annual general meetings and quarterly meetings to discuss the present financial position of ZGA in the Indian market.
The performance of the managers and marketers need to evaluate in order to develop the position of the company in the Indian market and the top-level management would design an evaluation criteria before entering this market. In this context, the marketers will compare the sales of the Chinese market and the Indian market to take the necessary steps to develop a weak market and to avoid unexpected losses in the future.
However, the marketers should measure the performance and profitability level of all the showrooms in India and they should try to implement new strategies to develop the position of weak outlets by finding out the cause of low-profit margin. At the same time, the top-level management needs to consider that many large companies have collapsed due to a lack of corporate governance practice and conduct accounting fraud in the financial statement; therefore, they need to concentrate more on the corporate governance and financial reporting system.
As the disclosure rule in India is not too well organized and there is no severe punishment for the disobedience of listing rules, the directors of the ZGA Company can engage with unfair and unethical activities to operate the business in a new market. In this circumstance, they need to realize that entering a new market is the subject of huge investment, so, the directors should not think about personal interest or waste money for unnecessary purposes. Moreover, the top-level management can review the present international strategies, feedback from the customers, and market survey reports to broaden the features of its brands and to develop the performance of the company with innovative and diversified product range.
Reference List
Barley, S. (2009) India’s carbon emissions poised to triple, new report finds. Web.
Blair, R. D. & Lafontaine, F. (2005) The economics of franchising. Web.
Gopal, C. (2006) Global Automobile Industry: Changing with Times. Web.
ImaginMor (2009) Automobile Industry India. Web.
IndexMundi (2011) Exports of India. Web.
IndexMundi (2011) Imports of India. Web.
IndexMundi (2011) India GDP – per capita (PPP).. Web.
Johansson, J. K. (2008) Global Marketing. 4th ed. New Delhi: Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company Limited.
Johnson, P. L. (1997) ISO 14000: the business manager’s complete guide to environmental management. 1st ed. London: John Wiley and Sons.
Library of Congress (2004) Country Profile: India. Web.
Narayanan, G. B. & Vashisht, P. (2008) Determinants of Competitiveness of the Indian Auto Industry. Web.
Peter, V.M. Kerr, I. A. & Thorpe, M. (2002) Tax Policy in India. Asian Journal Of Public Administration, 24(1). Web.
Porter, M. E. (2004) Competitive Strategy. Export Edition. New York: The Free Press.
Prabhudesai, A. (2010) India Economic Survey 2009 – Analysis and Full Report. Web.
The Wall Street Journal (2010) India Car Sales Touch Record High. Web.