Introduction
The job of an aircraft operator is incredibly demanding and responsible. Without these people it is difficult to imagine life in modern aviation, where much is tied up in the experience and correctness of everyone’s small actions, much less those of these heroes, whose actions few people think about. They are the ones who manage the sky, oversee all the little nuances and enable people to conquer the sky.
The Primary Roles of Aircraft Operators
Their main duties are to obtain the relevant certificates for the vehicle, keep it in good working order, notify special authorities of the slightest change, both in design and appearance, as well as to have a document of radio on board. All these factors taken together are important when preparing for a flight. Without the required certificates, the aircraft is not authorized to take off. Without maintaining a working condition, there is a significant risk of a crash and consequent loss of life. Sending notifications to flight authorities gives them a complete picture of what is going on and allows them to adjust the flight schedule to the appropriate aircraft model, knowing its distinctive features and technical capabilities. Equally important is the radio receiver, which allows one to tune in to the radio controller’s frequency and keep in constant contact with them, thus reducing the risk of a crash to a minimum. All of the above factors are, for the most part, technical aspects of aircraft life and, accordingly, the people involved are responsible for the health of the aircraft and the lives of pilots and passengers.
Many countries are concerned about the safety of their passengers by implementing an air safety protocol for their aircraft. They are all elaborate and include many action points for various emergencies. Studying the aircraft safety manuals of different countries in Europe, such as Germany and the UK, will prove that they all differ. For example, the German authority’s manual does not have a paragraph on what to do when operating gliders. These are essentially the same aircraft that can interfere with an aircraft’s take-off and landing. Such details need to be thought through to prevent consequences in any emergency.
International and National Laws in New Zealand
Having gone through a massive number of documents related to the safety of New Zealand’s airspace, one can conclude that this instruction is very elaborate and consists of many details. In addition to the glider example above, this document includes information on required certificates, parachuting, and even civilian aircraft. In general, it can be seen that the guide itself consists of many sections, each of which is described in detail and has a significant impact on airspace safety. Each of the 175 points is unique and explains the requirements for any given situation. For example, Clause 146, namely the Aircraft Design Certificate contains detailed instructions, requirements, and recommendations. The section itself is divided into paragraphs which one can easily find information on and see amendments to this part. This service is convenient both on the part of the user who is involved in aircraft construction and the state in tracking down infringements.
It is not easy to foresee all circumstances and be prepared for every event in the sky. Although there is a set of rules on behaving in an emergency, one must consider that even a human factor, such as fear, can override all the rules, and a person will not be able to pull themselves together. If an emergency does occur, its reasons must be understood to prevent it from happening again in the future. In order to do this, there are some steps that need to be followed in building the investigation process.
The Procedural Steps for the Conduct of an Aviation Safety Investigation
The first step is selecting a competent team that can assist in the investigation. The most crucial criterion is experience in dealing with similar incidents. The team should consist of specialists who can confidently help finding evidence and interpreting it in the future. There is no guideline on the number of people who should be involved in an investigation. However, the larger the incident, the more people may be needed to form a successful investigation team.
The next step is to gather the necessary information. This can be both physical and intangible eyewitness and logbook records. The collection of relevant information is an essential step as it allows for a reconstruction of what happened. Care must be taken when searching for clues, as the minor details can help piece together the incident and destroy some of the theories made in the first analysis.
The following steps are reconstructing the events and analyzing the information collected. If these points are constructed correctly, a vital breakthrough can be made in the investigation of one case and securing others of a similar nature. If the data collection is thorough and the team is experienced, the reconstruction of the events must be accurate and swift. The analysis, in turn, is already based on a preliminary reconstruction and adequately drawn conclusions from the collection and interpretation of information help to secure future flights.
The Aircraft Performance, Structures and the Flight Environment
Speaking generally about all the nuances and subtleties of safety protocols, it should be understood that, although it is impossible to foresee all emergencies, the risk of their occurrence should be reduced as much as possible. The work on air safety in New Zealand demonstrates that while the list of restrictions and certifications that a pilot, air traffic controller, or even an aircraft engineer must adhere to may be extensive, they are all important and can save many lives.
However, if an unforeseen situation occurs, one should not get lost and follow the steps to investigate the incident. As already mentioned, team selection is the first and essential step. It makes sure that the collection of evidence will be detailed and allow for the reconstruction of the disaster. Once all the materials have been gathered, it is equally important that they are appropriately interpreted and examined. This process can take a long time, but it is essential. It is the way to establish the cause of the accident and prevent it from happening again. The analysis must be clear and structured, using graphs and the history of the flight itself and the vehicle on which it took place.
If all the steps have been taken correctly, there should be no problem improving the airspace. There are several examples of investigations that, although lengthy, have resulted in the correct interpretation and saved the lives of future pilots and passengers, one of them being investigation number 19/6687, dated 29 September 2019.
Review of the Air Accident Report
First of all, I would like to note the structure of the crash report. Everything is structured and divided into chapters for easy reference to the document, which cannot but help when researching the crash. A small team of specialists was involved, as the aircraft itself was not significant, and the crash location was known approximately. It did not take long to collect materials because of the number of casualties and the size of the aircraft. After a thorough investigation, a report was compiled that describes the beginning of the flight, its process, the moment of impact, and the aftermath. It is fascinating as it is difficult to reconstruct a picture of the crash without witnessing it. Still, it is immediately apparent that the people involved in this investigation are first-class professionals.
The beginning of the report gives a brief description of what happened and why. Thus, it is not necessary to look for the conclusion at the end of the document but briefly read the experts’ findings, which is incredibly convenient (Stevenson-Wright, 2019). Following the paper, there is a description of the beginning of the flight, in what condition the pilots were, their psychological and physical health, the weather at the moment of departure and throughout the flight, as well as the state of the aircraft. In addition, graphs describing the course and altitude of the flight have been provided below. This enables a more detailed analysis of the causes of the crash. After examining the personal information of the crew members, it can be concluded that the instructor was a certified pilot and entirely responsible for the flight. In contrast, the pilot himself was a novice who had just bought a new aircraft, which subsequently became one of the causes of the crash. The human factor played a crucial role in the crash, which will be discussed further in the article.
Judging by the information on the aircraft, it had been undergoing a technical inspection only a couple of days before the crash, and there were no defects, which may indicate that the cause of the crash was not a technical malfunction. The weather forecast graphs also indicate that the weather did not affect the outcome of the flight. Only a tiny area of turbulence occurred in the path of the aircraft, but an experienced instructor should have been able to help the pilot deal with it. The GPS tracker and radio station were also in good working order. This rules out that the pilot went off course or failed to contact the control room to request assistance.
A photograph from the scene shows the gruesome aftermath of the aircraft’s collision with the ground. It appears from the image to have fallen at a tremendous speed and brought instant death to the entire crew, consisting of the instructor and the pilot himself. Post-accident inspections concluded that there were no visible defects in the aircraft on take-off, showing that the plane itself was in good working order. Medical personnel documented the deaths of the two men due to their injuries. Despite the delay of the rescue team due to the failure to locate the exact position of the aircraft, the deaths occurred instantly. There was also found to be a small fire at the crash site, but medical records show that this did not affect the outcome of the crash of the two people.
Further examination of the engine showed it to be fully operational, which is also supported by the investigation results and the tests carried out, which are also found in this research paper. This once again proves that the airplane was in perfect working order and suggests that the cause of the crash was something else. It later turns out that the main problem was the pilot’s inexperience and a slight change in weather conditions.
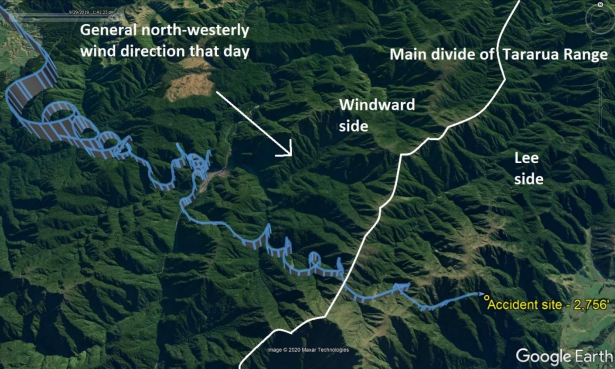
Investigations showed that there was an area of turbulence in the place where they were flying over, which caused the plane to stagger and head for the nearby mountains. It was also found that there was a device in the cockpit to measure changes in weather conditions during the flight, to which the instructor should have paid attention. In addition, it became apparent that many pilots of other aircraft had decided not to fly in that area because of the unstable weather situation. Notwithstanding the above reasons, the instructor, who was experienced in flying in mountainous terrain, was overconfident and allowed the flight to occur even in such an unstable time.
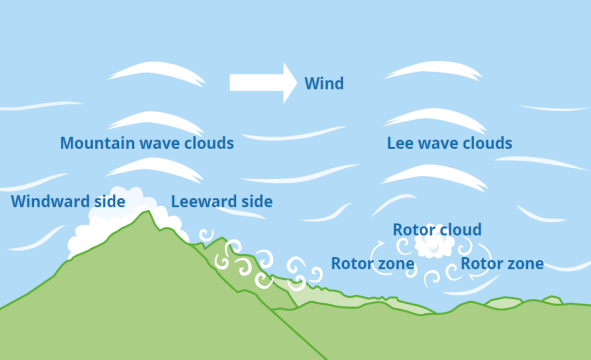
This was the leading cause of the crash and loss of life and the inexperience, as mentioned earlier, of the pilot himself and the turbulence zone. According to the map in the study, the aircraft should have circled the mountain peak and spun it from the other side. However, the plane could not be stabilized due to turbulence spikes and went straight into the mountainside, with fatal consequences.
The conclusion to the article describes all the above aspects, which theoretically and practically influenced this flight. The airplane was in good technical condition. The crew members were aware of the upcoming flight, the weather conditions, the route and had the necessary tests and certificates to fly on that day.
However, having collected all data, the investigators concluded that the cause of the accident was the overconfidence of the instructor responsible for the flight, changes in weather conditions, to which the pilot did not pay attention due to inexperience, as well as the turbulence zone, which the instructor was not able to cope. Following the listed factors, it is possible to conclude that the cause of death was the human factor and irresponsibility in decision making.
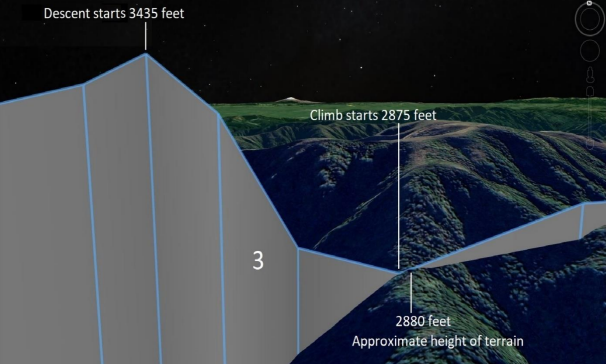
As a whole, the investigation was carried out following all rules and recommendations, and thorough work on searching for proof of crew members’ guilt was carried out. If I were the research team, I would have done the same and investigated every detail that could have influenced the outcome. An enormous amount of information was gathered, and the order of events was reconstructed to the exact minute.
Conclusion
Although the disaster took people’s lives, it clearly shows the problems in today’s airspace safety. People are not robots, and they tend to make mistakes and make wrong decisions. This example demonstrates the professionalism of working in the search for evidence to reconstruct the events of the crash and the involvement of third parties. It is not known how long it took and how many resources were called upon, but one can say that the work done makes it possible to protect future pilots from repeating the mistakes that occurred in this case. This work is constructive for people who are just getting involved in the investigation process and shows how important it is to gather and interpret all the details during analysis and interpreting.
Reference
Stevenson-Wright, P. (2019). CAA Occurrence 19/6687 TECNAM P2002 SIERRA RG ZK-SGO Collision With Terrain Tararua Range, 8NM West of Eekethuna.