The Hispanic community is one of the rapidly growing populations in the American community. Although they are non-natives in the country, their presence is slowly being recognized not only in democratic processes but also in the social order. One of the states with significant populations of the Hispanic community in California. This study will focus on alcohol and substance abuse among the female gender population proportion (12-20 years and 25-45 years).
Alcohol and substance abuse is a common practice in many parts of the American community. Statistics indicate that there is a variation of behavior among adolescents from different ethnic backgrounds in California. There are rising concerns on substance use disorders as portrayed by different individuals. The two independent factors involve drug and substance abuse prevalence in Hispanics and Whites from California (Barrera et al., 2019). The following hypothesis is applicable in this case:
H1: Alcohol and substance abuse are more prevalent among the Hispanic female adolescent and the youth (12- 20 years) than among Hispanic women of the working group (25-45 years) in California.
Ideally, alcohol and substance abuse have multiple effects on human health. The practice can lead to use disorder, addiction, and mental health concerns. At the same time, the adolescents may become vulnerable to different social ills while women in productive age may affect the fetus’ health. These problems seem to vary across the population age groups and may have imperative impacts on economic growth. There are more than 40 million Hispanics living in the US, out of which half are concentrated in California and Texas. Problems of mental illness and drug/substance-induced death are common among this group. Data from California indicate that between 2014 and 2017, 1 in every 13 women used alcohol while pregnant and exposed their fetus to danger. Likewise, there are co-occurring substance use disorders and other mental illnesses among adolescents and adult women. To solve these challenges, the government should initiate public awareness and health education programs to help girls and women understand the implications of alcohol and substance abuse.
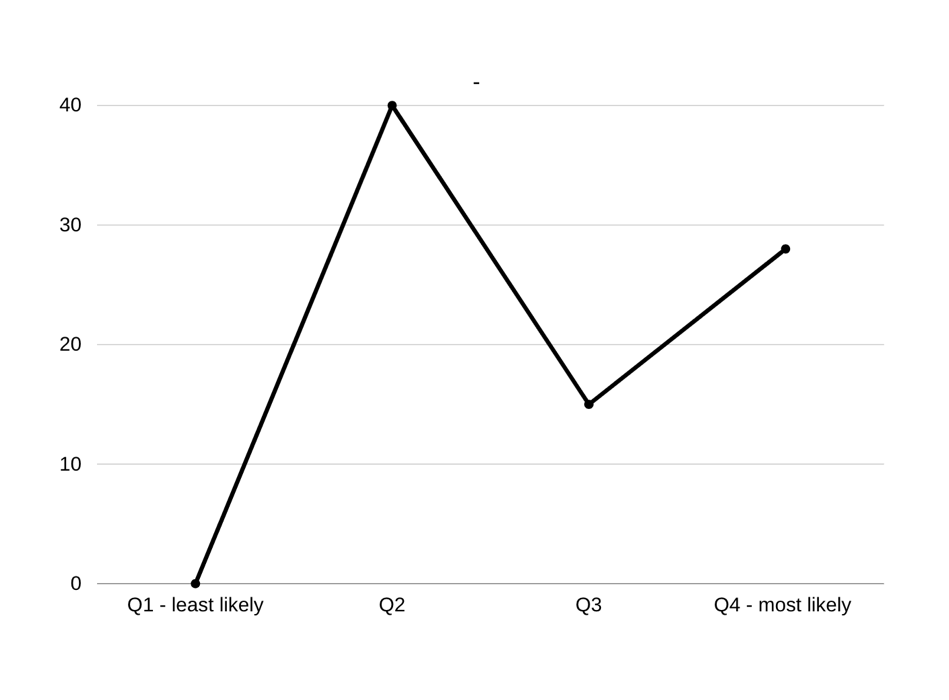
To clarify the existence of the following hypothesis, a confidence interval of the sample might be calculated with the help of a basic formula, which includes the consideration of the sample mean (M), sample size (n), standard deviation (s), and the desired confidence level (Kim et al., 2017). Thus, when taking a population variance of approximately 1000 people, the sample size of the study will be 157 people. Given that the hypothesis is based upon the age between 12 to 45 years, the sample mean will be 28, 5 with a standard deviation of 2. With a confidence level of 95%, it can be estimated that the index will constitute [28.187, 28,813], i.e., the true mean of the peak age of substance and drug abuse among the Hispanic population claims to be approximately 28 years.
The pattern of the following interval might be observed in the following graph, where the x-axis depicts the likelihood of substance abuse, and the y-axis defines the approximate age:
References
Barrera, I., Sharma, V., & Aratani, Y. (2019). The prevalence of mental illness and substance abuse among rural Latino adults with multiple adverse childhood experiences in California. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 21(5), 971-976.
Kim, H. J., Luo, J., Chen, H. S., Green, D., Buckman, D., Byrne, J., & Feuer, E. J. (2017). Improved confidence interval for average annual percent change in trend analysis. Statistics in Medicine, 36(19), 3059-3074.