Macroeconomic Variables Affecting the Amusement Park Industry
Products and services offered by the Walt Disney Parks and Resorts Worldwide, Inc. include theme parks, hotel lodging, cruises, and tours. Therefore, the company belongs to the amusement park industry, which is a subcategory of the travel and leisure industry. Consequently, macroeconomic variables affecting this segment will have a direct impact on the performance of the Walt Disney Parks and Resorts.
Primary variables influencing consumer behavior and demand are consumer disposable income and inflation rate. As the average consumer income grows, more and more people can afford to travel for leisure and to attend theme parks (Daedal Research, 2014). The rate of inflation is another major determinant of growth and profitability of a particular industry because it impacts consumer purchasing power: other variables being constant, high inflation decreases the amount of products and services consumers can afford (Daedal Research, 2014).
On the supply side, investment is crucial for the theme park industry, especially in the Middle East and Asia where amusement parks have not yet significantly penetrated the local markets (Rubin, 2015). Therefore, changing interest rates directly impact investment, as they can either attract or drive away potential investors (Brue, McConnell, & Flynn, 2013).
Macroeconomic Changes in China
With one theme park in Hong Kong, a special administrative region of China, and one park under construction in Shanghai, China is one of the countries where the Walt Disney Parks and Resorts has a major presence. These parks’ strategic location in economically and demographically thriving Asia can be of great benefit to the company. In fact, economic data suggests that the abovementioned macroeconomic variables in the region have been highly favorable to the company in the past three years.
Personal disposable income has experienced steady growth since 2012, and the 2014 average income was higher by more than 4,000 Chinese yuan (Trading Economics, n.d.).
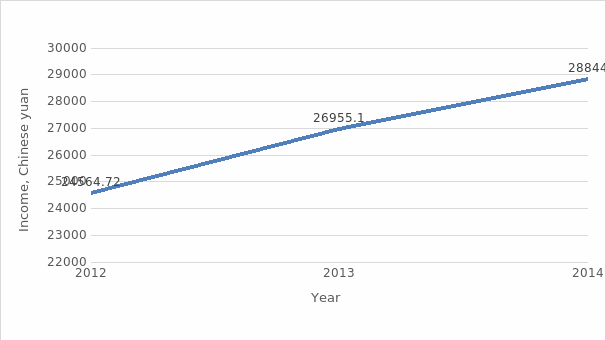
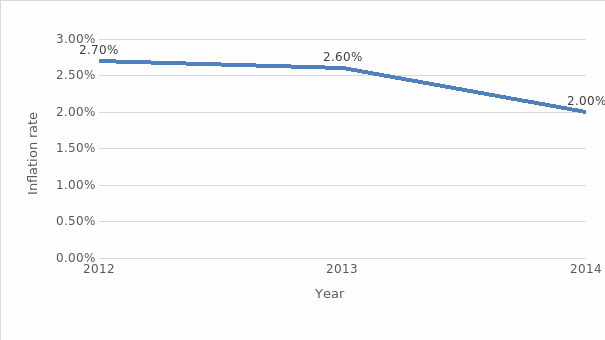
The inflation rate, on the other hand, went down by 0.7% since 2012, which is a significant decline since the rate was already quite low in 2012 (Trading Economics, n.d.). The consequence of changes in disposable income and inflation rate is that the population of China can afford more products and services in 2014 compared to 2012.
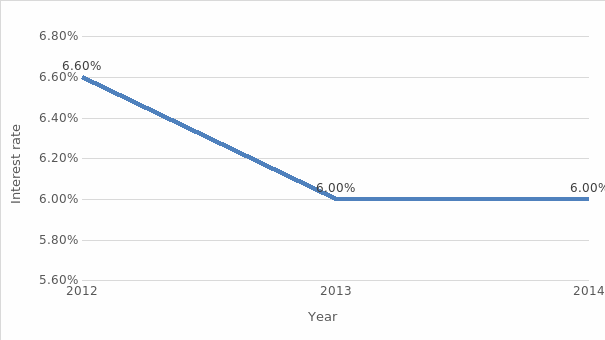
Finally, the interest rate decreased from 6.6% in 2012 to 6% in 2013 and 2014, attracting more investors to China, which is especially important for the Shanghai construction project (Trading Economics, n.d.).
Impact of Macroeconomic Variables on the Company’s Performance
As revealed in the previous analysis, the financial performance of the Walt Disney Parks and Resorts has been steadily improving over the past three years, with sales growing by approximately 30% and gross profits nearly doubling from 2012 to 2014. Both internal and external economic and non-economic factors have contributed to the company’s success. The oligopolistic structure of the market hinders the entrance of new players, and the company’s product differentiation strategy allows it to stand out among its current competitors. Technological advances ensure smooth flow of the company’s operations, and high seasonality of demand allows it to charge premium prices.
The movements of macroeconomic variables over the past three years also contributed to the performance of the Walt Disney Parks and Resorts, as the company’s customers have more disposable income and its investors receive more favorable interest rates, compared to 2012.
References
Brue, S., McConnell, C., & Flynn, S. (2013). Essentials of economics (3rd ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
Daedal Research. (2014). Global theme park market: trends & opportunities (2014-2019). Web.
Rubin, J. (2015). The global attractions attendance report. Web.
Trading Economics. (n.d.) China | Economic indicators. Web.