Executive Summary
Zero Trust Architecture is an innovative way of providing cybersecurity, which is beneficial for companies who have confidential information and, at the same time, outsource employees who do not work from the office computers. It is focused on protecting diverse resources such as databases, network accounts, and different services. The term comes from the system’s fundamental principle that each access to the source has to be verified (Rose et al., 2019). There is no option of using the same device and “saving” the possibility of information availability. Regardless of the computer and the human location, the verification procedure is repeated regularly according to the traffic workload.
The main advantage of this system, in comparison to others, is the opportunity to give access to the worker without taking into consideration his or her location. The crucial aspect of Zero Trust Architecture is the principle “never trust, always verify” (Katyal, 2019). The system is concentrated on controlling the traffic, its sustainability, and frequency of use (Kerman et al., 2020). Another significant benefit that should not be underestimated is the automatization of the processes (Eidle et al., 2017). The computing and processing power of the program is much more efficient than human capacities.
The problem of verifying a smartphone or a laptop is also a crucial topic in the sphere of cybersecurity. Zero Trust Architecture provides an innovative solution that controls only the traffic and does not provide access to the information according to location or personal ID of the device (Rose et al., 2019). For example, some organizations prefer using the method of two-factor authentication to decrease data security risks (Katyal, 2019). The reason for creating Zero Trust Architecture is that there does not exist a place where the confidential information would be safe (Zimmer, 2018). Even 20 or 30 years ago, the corporation’s building was the most secure place because only the employees had access to working computers. With the advancement of technologies, it is possible to hack into the system without physical presence. That is why the Zero Trust Architecture program is beneficial for corporations working with private and confidential data or intellectual property (Zimmer, 2018). The purpose of this paper is to investigate the particularities of the program, the role of its innovative approach, and its impact on the cybersecurity of companies’ databases.
Introduction
Zero Trust Architecture changed the understanding of the notion of “security” in the corporate sphere. It is an illustration that the responsibility for the data safety lies not only with the staff members of the organization but also with the company’s leaders. The process of automatization of verification procedure helps to save the time of computer specialists. Moreover, it is more efficient than the work of a professional as there is no human factor in the program.
It is crucial to mention that the system provides both the security of the data and the inside communication of the coworkers. What is more, it is beneficial for establishing the hierarchy in the organization. Zero Trust Architecture provides access not to the full database but to the specific information that correlates with the specialization of the employee (Samaniego & Deters, 2018). It has a positive impact on establishing the company’s structure and controlling the functioning of the separate devices. In order to define the particular characteristics of Zero Trust Architecture, it is necessary, to begin with, the analysis of the previous systems used before its invention.
Previous Approaches
With the invention of the Internet, people were concerned about their privacy and data integrity. The creators of social networks introduced the authentication system to the mass audience, which is still one of the most popular approaches to saving personal data. The original method includes creating a password and a login that no one knows except the particular user. However, the experience of the last decade is an illustration of the insecurity of this methodology. The number of cyber-attacks has increased dramatically during the last years. There are automatic systems that help the criminals in this sphere find ways to log in quickly and easily.
On a personal level, the problem is solved by introducing more complicated passwords that contain numbers, letters of diverse languages, and specific signs. Nevertheless, on a corporate level, the issue requires a more complex solution as the price of the mistake is much higher. The computer specialists introduced the methodology of two-factor authentication, which increased the level of safety and reduced the number of cyber-attacks on the computers of the company (Katyal, 2019). This approach is beneficial as there are two steps that have to be overcome in order to get access to the system. What is more, it is crucial to highlight that many organizations decided to make their own password systems. The set of letters in these passcodes is random and is created automatically. Moreover, it changes regularly: once in a minute or a day, depending on the leaders’ decision. This approach was a revolution in the field of data safety and is used all over the world nowadays. The usage of the Zero Trust Architecture system implies the possibility of making the two-factor authentication a part of this program.
It is necessary to pay attention to the security of intellectual property. On the one hand, it is the most critical part of the company’s data as it contains information about potential innovations and new developments (Zimmer, 2018). On the other hand, these facts are often hard to be understood by an ordinary person that is why it is not the primary purpose of the criminals. The security of intellectual property is a significant issue in modern society as the majority of the world market is concentrated in the sphere of technologies and the optimization of the processes. The solution to this issue is the integration of cloud services with restricted access (Rose et al., 2019). It means that this information does not exist on a personal computer or in a particular folder. At the same, the employees can access this data from any location using a specific authentication system.
New Findings
Zero Trust Architecture changed the understanding of data security. First of all, it became an illustration that remote availability of the company’s database has the same level of safety as the possibility to find the information from the stationary computer in the building of the organization. It can be observed that the approach of Zero Trust Architecture helps the employees get access regardless of their location (Figure 1). The position of the computer does not change the security parameters (Zimmer, 2018). It is especially beneficial in the current circumstances of the pandemic. The majority of employees work from home and cannot reach their office buildings.
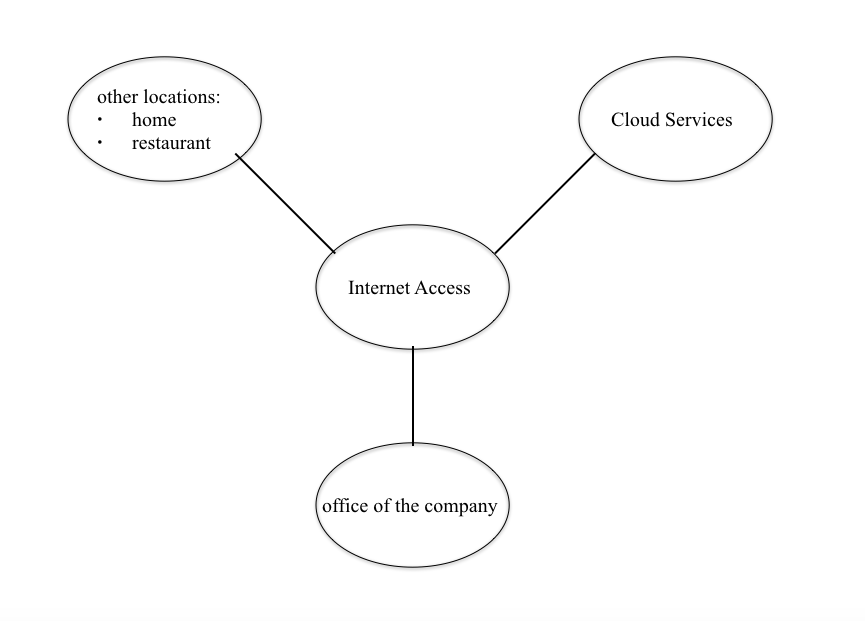
Another significant innovation that is used thanks to Zero Trust Architecture nowadays is the automatized system of authentication of the device and its user. This system decreases the possibility of the mistake and works much faster than a verification procedure made by a particular human. Based on the data from the computer, the program “makes a decision” if this person is worth trusting (Figure 2). Moreover, it is possible to provide access to specific parts of the information according to the level of the worker’s position and area of specialization (Samaniego & Deters, 2018). What is more, not only the data is secured but also the communication among the employees of the company (Rose et al., 2019). It helps to provide more freedom in discussion and replaces messengers and social networks. This feature is crucial in the situation of remote work. It is also important to mention that cloud services give an opportunity for document and file exchange among colleagues in a safe way.
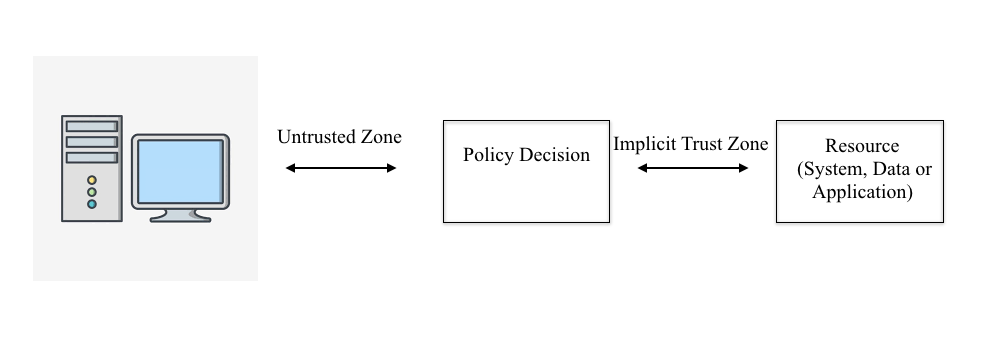
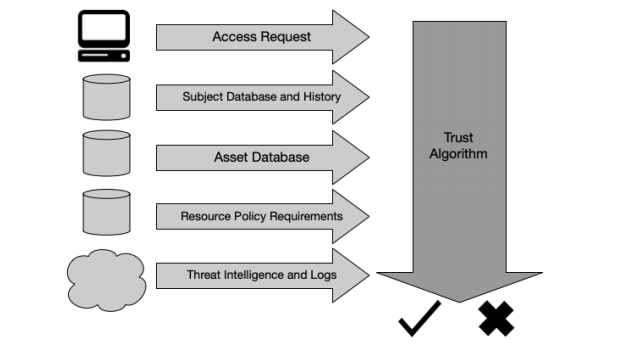
The algorithms used by Zero Trust Architecture also have to be considered as they are innovative for the sphere of cybersecurity. There are several diverse parameters that are used by the system in order to make the verification procedure save for all the participants (Figure 3). It is beneficial in case of theft of the device and the attempt to reach access from the particular computer. The program is based on the principle of “zero trust;” that is why it would not be possible to see the information for an outside user (Rose et al., 2019). The authentication is required regularly regardless of the device’s IP and the parameters of the user experience.
It is important to highlight that the system is completely automatized that makes its implementation easier for the companies which do not have a specific IT-department. The leaders of the organization can hire an expert who would install the necessary programs. If Zero Trust Architecture system functions successfully, there is no need to pay the programmer. However, the process of policy decisions should be organized in a particular way for each firm as there are various scenarios of its functioning. For example, it is possible to give complete access to users from the office without a verification procedure. Zero Trust Architecture is a flexible system that can be adapted to the needs of the company.
Another crucial point is the safety of the program’s database itself; it works on the principles of dynamic policy. It means that there does not exist a unique folder where all the information exchanged and viewed is saved. It is beneficial for the company as it becomes impossible to get access to all data in one attempt. Even if the cyber-attack is committed, there would be a chance to steal only a small part of the information. Moreover, the system collects and shares the data about the traffic and the current state of assets with the head office (Rose et al., 2019). It helps the computer specialists of the company to fix the problem in a short period of time.
Conclusion
Zero Trust Architecture is an innovative approach to saving and controlling corporate data. Its main advantage is the possibility to get access from any location and various devices. It regulates the amount of traffic and requires the verification procedure regularly that helps reduce the risk of cyber-attacks. The option of giving access to information partially is beneficial for data integrity and for organizing the hierarchal system inside the organization.
References
Eidle, D., Ni, S. Y., DeCusatis, C., & Sager, A. (2017). Autonomic security for zero trust networks. IEEE 8th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference, 288–293. Web.
Katyal, N. (2019). Block unauthorized access with Zero Trust Architecture. Dataquest. Web.
Kerman, A., Borchert, O., Rose, S., & Tan, A. (2020). Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture. National Institute of Standards and Technology, 1(2), 20–22.
Rose, S., Borchert, O., Mitchell, S., & Connelly, S. (2019). Zero Trust Architecture. NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-207, 1(1), 1–46, Web.
Samaniego, M., & Deters, R. (2018). Zero-trust hierarchical management in IoT. IEEE International Congress on Internet of Things, 88–95. Web.
Zimmer, B. (2018). {LISA}: A practical Zero Trust Architecture [PowerPoint Slides]. Web.