Introduction
Nowadays, the development of medicine and medical treatment has experienced a considerable growth, which permitted representatives of health care professions to cure a large number of conditions that would have been lethal and incurable in the past, as well as to alleviate the suffering of patients who have less severe health problems. Nevertheless, numerous systems of alternative medicine still exist and are often quite popular not only among people without any medical education but also among health care professionals. Homeopathy is one of such systems of alternative medicine. It is based on the premise that the causes of some symptoms in healthy people may be utilized in small doses in order to relieve these symptoms in unhealthy people. The current paper investigates the effectiveness of using a homeopathic drug to address headaches. A report on taking such a drug is provided, and evidence available in recent scholarly studies is discussed.
Taking the Remedy
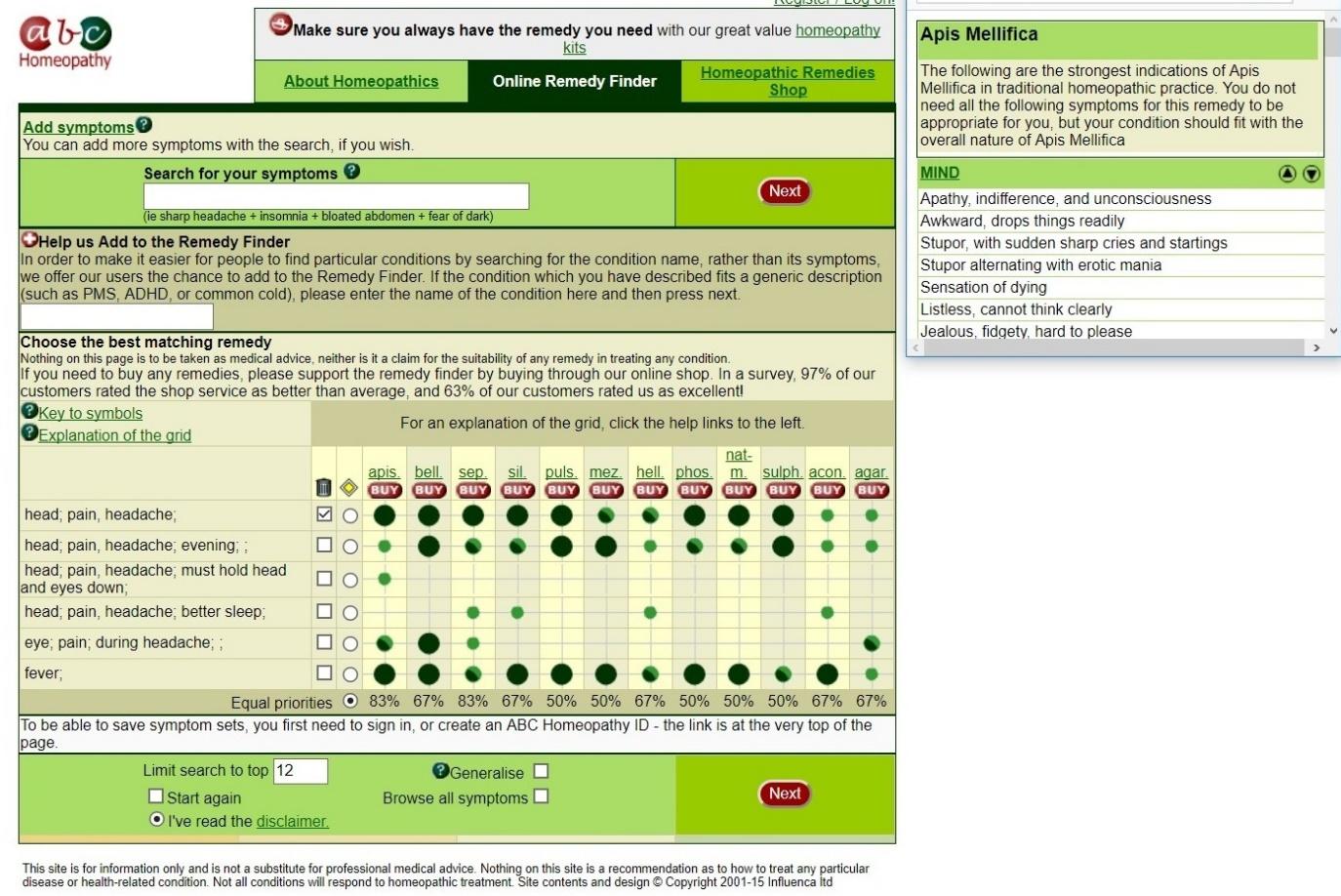
According to the homeopathy grid, which can be found in the Appendix, it was recommended to take Apis Mellifica as a remedy against such a symptom as headaches that occurred regularly, once to thrice a week. After the advice provided in the grid was taken into account, it was decided to purchase Hyland’s Apis Mellifica 30x and to take it according to the recommendations provided, i.e., 4 tablets sublingually 4 times per day. On the whole, when the pack of tablets with Apis Mellifica was used up after taking it for approximately 15 days in the said manner, the headaches still persisted and continued taking place with a similar frequency as before. It should also be observed that when the Apis Mellifica were taken sublingually when the symptom was present, the pain did not subside, and regular medications against pain, such as paracetamol, had to be taken in order to alleviate the suffering. Therefore, it is possible to conclude that the utilization of such a homeopathic drug as Apis Mellifica in the proposed manner (4 tablets sublingually 4 times a day) in order to address headaches appeared to fail to produce any noticeable results.
Further Evidence
On the whole, it was quite impossible to find any recent scholarly evidence about the effectiveness of Apis Mellifica against headache. Search via such engines as Google Scholar for articles no older than 2013 produced no results containing both the words “headache” and “Apis Mellifica”; the same was observed while searching medical databases such as WebMED or CINAHL. Therefore, articles by Kristoffersen, Aaseth, Grande, Lundqvist, and Russell (2013), Schetzek et al. (2013), and Subhranil and Munmun (2013) were reviewed. On the whole, all these studies found that when used as a medication to treat headache, homeopathic remedies displayed poor results; these results tended not to be better than the effects of placebo treatments (Kristoffersen et al., 2013; Schetzek et al., 2013; Subhranil & Munmun, 2013). Therefore, it is possible to state that the evidence which can be found in the recent scholarly, peer-reviewed literature suggests that homeopathic remedies are, generally speaking, an ineffective method for treating headache.
Conclusion
All in all, it should be stressed that the use of Hyland’s Apis Mellifica 30x (4 tablets sublingually 4 times/day) appeared to have no perceptible effect when it came to relieving regularly occurring headaches. Even when the symptom was present, the drug was ineffective, and it was necessary to take other drugs (e.g., paracetamol) instead. Recent evidence from scholarly articles also suggests that homeopathic treatments may have poor effectiveness against headaches, probably not greater than that of placebo treatment.
Appendix
The Homeopathy Grid
References
Kristoffersen, E. S., Aaseth, K., Grande, R. B., Lundqvist, C., & Russell, M. B. (2013). Self-reported efficacy of complementary and alternative medicine: The Akershus study of chronic headache. The Journal of Headache and Pain, 14(1), 36.
Schetzek, S., Heinen, F., Kruse, S., Borggraefe, I., Bonfert, M., Gaul, C.,…Ebinger, F. (2013). Headache in children: Update on complementary treatments. Neuropediatrics, 44(1), 25-33.
Subhranil, S., & Munmun, K. (2013). Homeopathic treatment of headaches & migraine: A meta-analysis of the randomized controlled trials. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 6(3), 194-199.