Statistical Technique
The statistical techniques refer to the control and design frameworks used to analyze various aspects at different company levels. Some standards determine the effectiveness of control and quality measures. For Apple, there are several choices, such as Total Quality Management, Continuous Quality Improvement, and Six Sigma form a competitive and efficient structure for analyzing and producing relevant data during production (Khan & Yun, 2019). It consequently aids the various leaders and shareholders in making well-informed decisions, thus forming error mitigation promptly.
In the case of Apple, the total quality control management approach is the most viable, as it is easy to use and manage. These include Pareto charts, control charts, Flow Charts, and scatter plots. Apple’s approach incorporates measures of central tendency, variance and ranges, and distributions to estimate change efficacy. Tree, affinity, and process decision charts improve management and transformation. Different degrees of measurement analysis create statistical insight from qualitative and quantitative Apple data.
Apples Location Analysis
The various aspects can be used to analyze Apple’s current location and the need for relocation strategies to meet project development needs. Proximity to customers is crucial to consider when conducting an analysis. It centers on the savings in transportation costs and time that can be realized by being closer to the customers (Vinodh et al., 2020). A facility establishment process is facilitated when similar business organizations already exist in the market. Another thing to think about when doing the location analysis is the accessibility of skilled labor. When assessing the site, we also thought about how easily reachable our potential vendors would be. Increasing globalization has far-reaching consequences for societies, making environmental policies crucial in analyzing facility location. It would be necessary to relocate the facility if any of the criteria mentioned earlier could not be satisfied by the current site.
In determining the new location, steps that should be followed include hazard identification, risk assessment, and review. The three main planning horizons of the short-range, medium-range, and long-range should be included in sustainability in both the capacity planning process and the location planning process. Short-term capacity planning prioritizes scheduling issues, labor shifts, and the best distribution of available resources. Strategic issues involving the company’s primary production facilities are the main focus of long-term capacity planning.
Work System Design
Work System Design entails conducting an in-depth investigation into the processes used to get things done, with the objectives of determining how to make the most productive and economical use of available resources and determining acceptable levels of output for the work being done. In the Apple company case, there are work system design elements, including processes and activities, participants, information, and technology (Vinodh et al., 2020). The other five elements of significance in the case of Apple are customers, strategies, infrastructure, and the environment.
The work system design makes it easier to determine how to complete a task in project development. It helps managers split responsibilities among individuals. Meticulous preparation reduces potential threats during task performance. It also helps people involved, the market, and the government coordinates their efforts, leading to a higher success rate. The work system design makes it easier to determine how to complete a task. It helps managers split responsibilities more effectively. Meticulous preparation reduces potential threats during task performance. It also helps people involved, the market, and the government coordinates their efforts, leading to a higher success rate.
Phases of Project Life Cycle
The enactment and implementation of changes in the Apple case aspect involve various stages and cycle steps. The various phases of the project life cycle include initiation, planning, controlling and execution, and closure. Initiation is the first stage of the project life cycle. It is essential to specify the project’s scope and the approach that will be taken to achieve the desired results during the project’s “initiation” phase. Every task completed throughout the project must be organized and given to specific people during the planning phase (Manzoor et al., 2021). Making sure that all activities are adequately controlled and carried out is the most crucial thing one can do when it comes to the controlling and execution stage. The stage of closure marks the end of the project’s life cycle. The project manager ensures the project is completed successfully during this last stage.
The project lifecycle provides a structured and systematic approach to completing the project’s delivery. Everyone on the team will be able to track the project’s development, see where it is headed, and pinpoint where there may be issues with the final products. Each stage has its own set of responsibilities and activities spelled out. Because of this, all groups now have a standardized plan of action to follow.
Communication within the project organization and the definition of roles within the project are improved by having a framework for the project that is clear to all participants and can be easily understood by them. In addition, tasks can be split up depending on where the project is in its life cycle. Understanding what is expected of them at each stage will be much simpler. It aids in resource planning, reducing waste, and guaranteeing that essential materials will be on hand when required. The implementation stage will require the bulk of available resources.
By dividing the project into phases per the Apple company analysis, the project manager may more readily track and celebrate accomplishments. The Concept Stage includes creating the business case, where the project manager can quickly connect the stages and celebrate their completion. In the definition phase, a risk management strategy and quality assurance strategy are created together with the project management plan. During the project’s execution stage, the pieces of the final product are designed and built (Collier & Evans, 2020). The project lifecycle’s stages reveal the project’s development over time, illuminating the need to pay more attention to certain aspects, such as risk management in the beginning and Project Evaluation Reviews in the middle. With each passing step, the project’s particulars are fine-tuned to perfection. Detail is being added to the plans, and cost estimates are being updated.
Project Management
The initiating stage gives the green light to the rest of the project’s operations by describing its scope, parties, and deliverables. Planning determines the optimum project strategy. It also includes facilitation and core planning, which include planning of scope, development of schedule, planning of resources, and budgeting. Personnel and materials are assembled to implement the plan in a project’s “execute” phase. In “monitor and control,” progress and risk-mitigation measures are reported (Manzoor et al., 2021). The close stage element relies heavily on contract closeout as the final stage.
Every initiative the company takes is driven by a desire to serve the company’s needs and desires better while also expanding the company’s potential customer base. To accomplish the goals that prompted the project’s implementation, the organization needs to complete the work it has started and improve its capabilities. The project management team helps the business make a case for the ideas that will ultimately fund the project, which is essential given the high stakes involved in any endeavor. The company would be unable to reach its objectives if its leaders did not participate actively in the project’s management.
Implementation of Change Process
Analysis of change process implementation involves a series of stages, especially for a company like Apple. Implementing the change process involves identifying errors and issues, the component aspects that need change, the management cycle for the process, process mapping overview, tools, and solution analysis (Manzoor et al., 2021). After finding problems with the project, the organization, Apple in the case, needs to change how it manages projects so that it can continue to get the benefits and realize the full scope of the project within the organization.
PERT/CPM development
Several stages are involved in the development of project frameworks in the PERT/CPM framework.
- Determine the necessary activities for the project.
- Trace the chain of events and establish the correct sequence of actions.
- Determine how much time will be required for each task.
- Construct a diagram that shows the activities, represented by arrows, and the events, shown as nodes, which are depicted as overlapping circles to indicate their relative importance.
- Determine the earliest possible and latest possible start and end times for the event stages
- Find the fastest way to complete the task by finding the critical path.
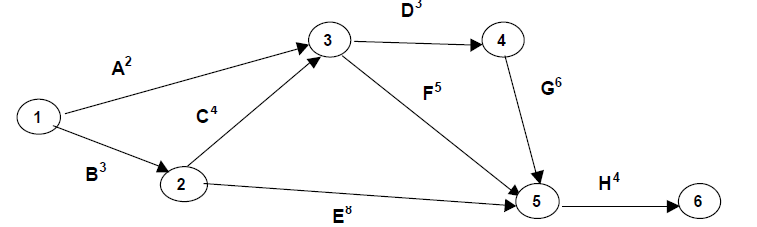
Path B-C-D-G-H is the critical one having 20 weeks.
References
Collier, D. A., & Evans, J. R. (2020). Operations and supply chain management. Cengage Learning.
Khan, S. A. R., & Yu, Z. (2019). Strategic supply chain management. AG: Springer International Publishing.
Manzoor, U., Baig, S. A., Hashim, M., Sami, A., Rehman, H. U., & Sajjad, I. (2021). The effect of supply chain agility and lean practices on operational performance: a resource-based view and dynamic capabilities perspective. The TQM Journal. Web.
Vinodh, S., Antony, J., Agrawal, R., & Douglas, J. A. (2020). Integration of continuous improvement strategies with Industry 4.0: a systematic review and agenda for further research. The TQM Journal. Web.