Introduction
Examination of the latest trends in the sphere of development of manufacturing processes indicates significant growth in the interest in the practical use of artificial intelligence (AI). However, globalization conceives concerns associated with the implementation of AI in processes that are currently done by employees. The first ethical implication is unemployment or, in other words, the possibility of a reduction in the number of workplaces and even extinction of some jobs. The second ethical implication is humanity, or potential changes in people’s behavior because of the spread of the use of machines in most spheres. It is likely that AI used for the optimization of processes makes humans addicted to technologies widely utilized in sales and customer service roles. Further research on the way integrating AI in daily routine, provision of services, and manufacturing of products will affect society is necessary to ensure the safety of such interventions. This work will address unemployment and humanity’s ethical dilemmas, conceived because of the rise of artificial intelligence as a globalization consequence, by proposing the change in industrial technique to maintain it being capital consuming and promoting corporate social responsibility to make it ethically inappropriate to replace workers with AI-driven robots fully.
Background
AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes enabled by advanced computer systems. It has numerous applications that include but are not limited to speech recognition, navigation assistance, search algorithms improvement, chatting with clients, and text editing. The rapid development of AI and its gradual integration into different spheres such as healthcare, banking and finance, social media, education, entertainment, and others (Lindgreen and Swaen). This tendency is potentially highly beneficial for business owners and stakeholders. The reason for this is the profit companies can obtain by minimizing the number of workplaces, reducing work hours, or completely renouncing some types of jobs currently done by employees. However, the rapid development of AI, negative consequences of which considered a global societal issue, conceives a number of concerns and ethical implications, which should be discussed and addressed before proceeding to integrate smart algorithms into all the industries.
The first ethical implication that is of great importance and is closely associated with some of the worst effects of the use of AI is the probability of unemployment for a significant percentage of workers. Globalization and large-scale industrialization have always been known for focusing on replacing human workplaces with robots to benefit manufacturers by optimizing expenses (Subhabrata Bobby Banerjee). Analogically, the concern that AI would make workers obsolete exists.
It is possible to list a number of jobs that are likely to be partly or fully replaced by AI-driven bots or apps to outline the severity of the issue. Chatbots can replace customer service executives answering FAQs and customer support questions. Bookkeeping and data entry jobs are likely to be done by systems incorporating machine learning more effectively and at a lower cost. Receptionists are not necessary for hotels with auto check-ins. Proofreading, which is a less complex job than editing, is also can be done by a number of apps. Manufacturing can be automated, making the fewer number of workers needed to manage the same amount of work. In retail services, AI-driven both can assist customers in self-ordering while evaluating customers’ patterns.
Then, courier services can be fully provided by drones and robots. Even the number of doctors can be reduced significantly due to robot surgeons and other AI-based bots and apps. Armies may incorporate robots for participating in the battlefield. Market research analysts may be replaced with AI-enabled robots, processing high amounts of data. Finally, with the growth in cars with autopilots, taxi drivers may become obsolete. It is possible to see that the listed job are ones that do not require social or emotional intelligence to perform, while they can be considered routine, which require a high amount of workforce, both educated/ trained and educated. It makes it evident that millions of people can lose their jobs in the nearest future without some regulations and intervention.
The second ethical implication associated with negative consequences of AI development and integration considered a global societal issue is a change in people’s behavior because of the use of machines or “humanity” issue. As AI-driven bots become better at modeling human conversations, such positions as sales and customer service roles which, as mentioned above, are at risk of being replaced, can become a source of damage to people’s humanity (Korinek and Stiglitz). It implies that while interacting with machines, humans tend to become robotic-like because of the absence of the necessity of maintaining regular social contact. While it may be beneficial to introverts, it is a destructive force that makes people less socialized and more addicted to their electronic devices.
The complementary difficulty is the already well-established algorithmic optimization methods that tend to find the most optimal approach to people while completely neglecting their individuality. It is known that devices trigger the reward centers in humans’ brains by attention-grabbing headings (automatically generated by AI based on search engine inquiries) and other methods to make an application more addictive (Lindgreen and Swaen). It is intended to make humans more dependent on machines while optimizing algorithms and simultaneously making people adapt to AI-based devices. It is deteriorative for brains, which are intended to be rather socially driven than AI-approached. The apparent consequence of the uncontrolled integration of AI into all the industries and spheres is the loss of humanity and natural abilities to interact with each other, as it would be replaced with AI-based bots and applications. Therefore, the two mentioned ethical implications have the solid ground that makes finding solutions to the global societal issue extremely important.
Argument
With respect to the above-mentioned concerns, contemporary society has, because of the rise in the potential of the use of AI, two solutions can be outlined. First, the change in industrial technique that would focus on capital-intensive technologies may address both the ethical implications (Korinek and Stiglitz; Subhabrata Bobby Banerjee). It would enable to prevent the reduction in the number of jobs while not depriving AI of its usefulness as the complementary tool for some processes’ facilitation. Moreover, continue enabling people to provide some services AI can also do not only limits the negative influence on human behavior but may be beneficial for companies that intend to show their superior care to customers (Matjaz et al.; Au-Yong-Oliveira). Therefore, such a decision can immediately and successfully respond to any associated concerns.
The second solution is the rise in corporations’ social responsibility done by the promotion of global stakeholders to establish ethical guidelines to ensure the protection of employees from unemployment regardless of the level of AI’s development (Lindgreen and Swaen). This intervention is less likely to show direct influence on prevention the deterioration of behavior that AI might cause, but it is rather beneficial for the sense of humanity overall (Ke and Wang). Business ethics is a crucial part of the functioning of both society and corporations.
With respect to the parts of the society that will benefit from the implementation of the outlined solutions, the mentioned above types of hired employees would not lose their jobs because their employers considered the integration of AI-driven bots more cost-effective. However, business owners still can apply marketing and manufacturing techniques to stand out from numerous competitors by allowing humans working on the listed above positions to provide some VIP services or adopting some AI-based solutions that would make employees more effective (Korinek and Stiglitz). Moreover, every human being would be mentally benefited from the opportunity to communicate with a living worker rather than with a robot (Lindgreen and Swaen). It is hard to overestimate the potential of the united contribution of the two proposed solutions to addressing the ethical issues raised from the integration of AI in different spheres.
Interpretation of Statistical Data
It is possible to interpret relevant statistical data to support the two proposed, within the argument, solutions. Thus, Guangsu et al. (2019) analyzed the rate of digitalization of industries in China and found a high risk of automation. The incorporated data for AI adoption rate by industry is presented in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Ai Adoption Rate by Occupation in China
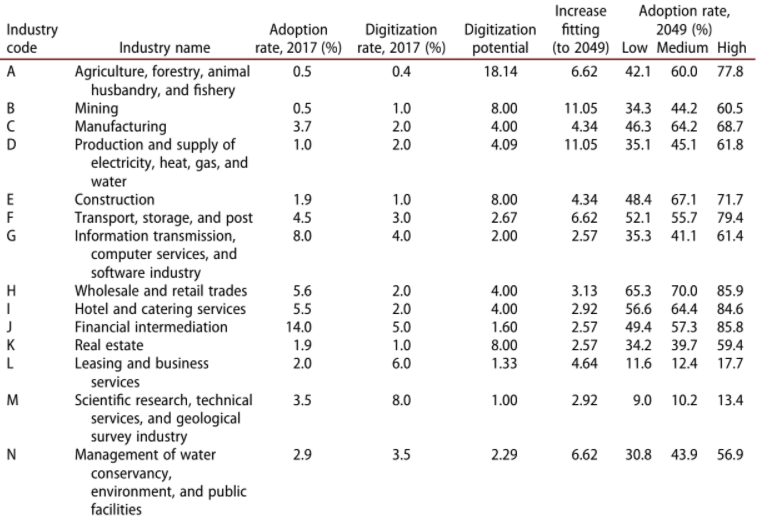
This study can provide an appropriate insight into how significantly the number of opportunities for people to be hired can be deteriorated by the integration of AI into most industries. The research is highly reliable and valid for the China region. It reflects the latest tendencies, provides a forecast, and enables to emphasize the significance of the issue and prove the viability of ethical implication outlined above. The research provides a similar table of adoption rates by occupation but does not include some types of jobs; thus, writers, editors, emergency workers, translators, politicians, and many others were omitted that can be considered a bias. There are also no factual statistics for the current AI adoption rate by occupation. There is a significant need for the authors to deepen their research by including the lacking positions and, potentially, to research the global statistics.
In another peer-reviewed source, the authors indicate the discrepancy between the efforts put in the profitability of companies of Chine and the success of CSR interventions intended to address social and ethical issues. The results can be seen in Table 2 below.
Table 2: Comparison of the Success of CSR Practices Implementation
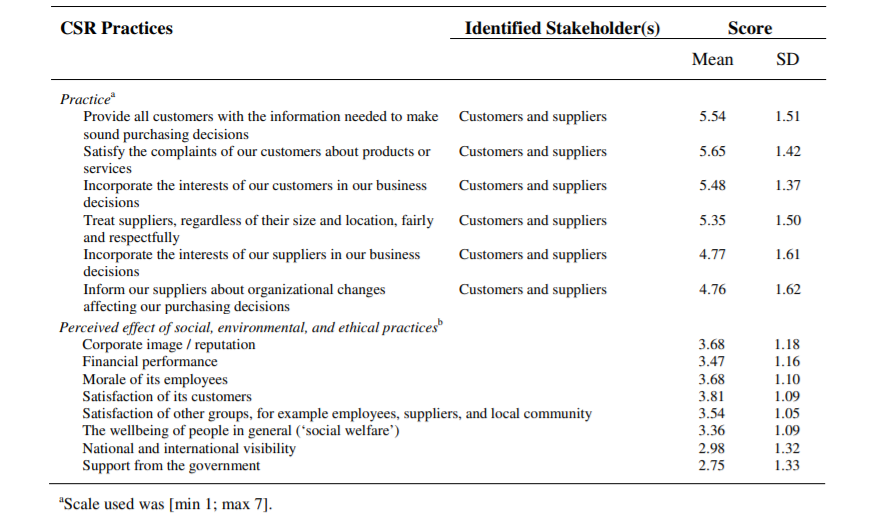
The evidence reveals that social and ethical practices, which are potentially beneficial for employees, are scored low compared to practices directly intended to improve the experience of customers while purchasing a company’s goods. Therefore, there is proof for the need to promote management of corporations to develop ethical guidance that would protect their workers from such danger as job loss from AI development. The source provides constructive survey-based, valid, and reliable recent survey-based critics of the current tendencies for CSR practices implementation. However, it is focused only on one particular region and does not take into consideration features of philosophies and beliefs spread across China, as well as does not outline cultural specificities, which can be considered biased. Thus, there is a need to make this study a less culturally-dependent one and take global data for future research.
The third source aims to reveal how successful apps intended to help people cope with mental health deteriorating events are. Such software is built to be human-like, supportive, and empathetic. While such interventions may seem interesting at first glance, they reveal how good AI-based chatbots and apps can mimic human behavior. The results of the survey conducted by Inkster et al. (2018) are shown in Table 3 below.
Table 3: Coping Major Event-App Experience-Based Feedback Response Distribution
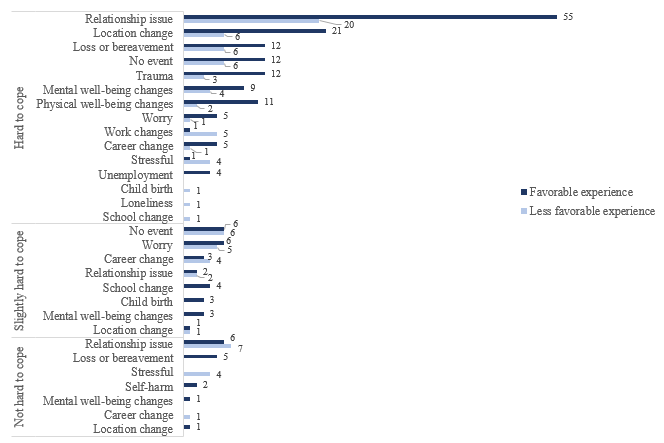
It is shown that users had a favorable experience with AI-driven chatbots even while dealing with hard to cope with events. The research provides a solid, credible, and valid examination of the effectiveness of the AI-based applications based on a slightly outdated survey. It is possible to assume that the number of cases of favorable experience would be higher if the survey were conducted in 2021. However, there is no examination of the long-term influence of support provided by AI-based bots on people’s mental health and behavior. It is hard to imagine the severity of consequences in the event applications became more effective communicators than respective specialists such as psychologists. Thus, there is a need for deepening the research by examining the effect of interactions of AI on human mental health. The provided statistics proves that while the level of adoption of AI is rising and the chatbots and software are becoming more effective, the level of social protection of workers that potentially can be replaced with robots is low.
Evaluation of The Ethical Outcomes
It is possible to provide an evaluation concerning the ethical outcomes and respective ethical issues. Based on the solutions provided, the positive ethical outcome is the limitation of the influence of the negative consequences related to the integration of AI in most industries. In other words, it is avoidance of unemployment and prevention of human mental health and behavior deterioration. The possible ethical issues are the reduction of the profitability of many businesses that overwise could have been benefited, and not facilitating fulfillment of the duties of some types of workers that could have been assisted by AI-based solutions.
The negative ethical outcome is the deceleration of technological and scientific progress globally. The possible ethical issues are limiting the contribution of AI-based technologies in conducting advanced scientific researches and reducing the chance of creation of potentially favorable, for all society, inventions. It is likely that compromising the pace of scientific progress and limiting some businesses’ potential is a small price for ensuring the mental safety of all the society members and protecting many employees from job loss.
Conclusion
The rise of artificial intelligence as a globalization consequence conceives ethical dilemmas, which are deteriorations of humanity and risk of unemployment for many employees from across all the industries. Despite all the benefits AI may bring, an increase in the involvement of robotics in daily routine may cause a negative influence on the social abilities of humans and reduce the number of existing jobs. The potential decision for the problem is a change in industrial technique that would switch the focus from replacing workers with AI-based tools to complementing and facilitating the same quantity of employees’ work. The second solution is influencing owners of businesses and stakeholders to make them develop the ethical codes of corporate social responsibility that would obligate companies to maintain a number of workplaces. Such interventions are beneficial for preventing the risk of unemployment and maintaining a high level of socialization for all the people around the globe, while the necessity to compromise the pace of scientific progress is minor.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence: Annotated Bibliography
Au-Yong-Oliveira, Manuel, et al. “What Can We Expect from the Future? The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Society.” 2020 15th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Web.
The purpose of this work is to examine the impact of the digital revolution on society, which includes the use of AI, along with its advantages and disadvantages. This study covers the influence of AI on firms and services and on community and employment, examines hopes and concerns for AI, and provides points of view on the issue, including optimistic, pessimistic, and pragmatistic ones.
The study is based on 10 interviews and on the survey to which participated 100 respondents. The results are ambivalent as half of the participants indicated the presence of both practical and social concerns, while the other half claimed the possibility of humans always being ahead of AI due to the use of advanced computers. This work contributes to finding solutions to such a global societal issue as potential unemployment and changes in behavior in two ways. It examines the existing points of view determining the attitude of society toward the use of AI. It also reveals that the means of corporate social responsibility should be used to address ethical implications rather than it is the duty of developers of AI. This research is related to other sources utilized to prepare the work due to focusing on the ethical dilemmas raised because of AI usage, which is the other studies’ basis as well.
Ke, Jie, and Greg G. Wang. “China’s Ethical Dilemmas under Globalization and Uncertainty.” Advances in Developing Human Resources, vol. 16, no. 1, 2014, pp. 74–91.
The purpose of this work is to examine how globalization creates economic and social uncertainty while conceiving ethical dilemmas. The study’s aim is also to propose the solution that is to be implemented by human resource development (HRD) practitioners at the national, organizational, and individual levels. The research covers ethical imperatives in the age of globalization while relating them to China’s main ideologies, cultural beliefs, and values.
The authors utilize literature analysis to outline how particular cultural differences and ideologies, including Confucianism, Taoism, and capitalism, impact ethical codes of conduct, training, and other formal rules. The evidence provided indicates that discrepancy in values does affect ethics at all levels, which, with respect to globalization, causes distinct ethical dilemmas related to globalization and the use of AI. Thus, it is stated that it is the duty of HRD practitioners to make efforts to understand Chinese cultural characteristics and establish a contemporary corporate culture that would be more ethically oriented. This study does discuss ethical implications associated with globalization and the use of AI and thus is related to other sources.
Subhabrata Bobby Banerjee. “Corporate Social Responsibility: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly.” Critical Sociology, vol. 34, no. 1, 2007, Web.
The purpose of this work is to examine the contemporary discourse of corporate social responsibility, which is intended to consolidate the power of large corporations and serve narrow business interests rather than employees. With respect to globalization, this issue is of great significance because of ethical implications associated with potential unemployment, the danger of which is conceived by the use of AI. This study covers issues of social responsibility of modern corporations, the concept of sustainable development, politics, and government and international institutions.
The author utilizes literature analysis to provide evidence of corporations being focused on profit earning at any cost rather than following ethical codes of conduct. It is revealed that particularly the misuse of the power of corporations may be the primary cause for the ethical implication of “unemployment” and not the possibility of AI fulfilling some duties currently done by employees. This source is related to others due to the comprehensive discussion of the way promotion of corporate social responsibility can be the solution for negative consequences associated with globalization.
“The Dilemmas of Internationalization: Corporate Social Responsibility in Th…: Library OneSearch.” Ashford.edu, 2014, Web.
The purpose of this work is to highlight concerns with empirical and conceptual validity of integration of internationalization strategies in the Multinational Corporation (MNC) operation revealing their unsuitability to resolve global and local corporate social responsibility (CSR) issues. This study covers an investigation of to what extent the development and implementation of MNCs’ CSR policies reflect home or host country perspectives.
The author utilizes literature analysis and semi-structured interviews to discuss important aspects of CSR policies meaning for organizations, employees, culture, and perception of stakeholders’ responses. It is outlined that a wide range of CSR issues are faced at all levels of the corporation, while MNCs tend to ignore local culture. It is questioned if the implementation of integrated strategies is even possible in the contemporary realities, as their outcomes cause both local and global issues, while the tendency to globalization strengthens the complexity of establishing well-functioning CSR policies. The study is related to other sources as it once again indicates the unwillingness of corporations to be rather social than profit-focused, which is the reason for the ethical implication to arise.
Westernization: With the Bad Comes Good. “Westernization: With the Bad Comes Good.” Paragon Language Services, 2016, Web.
The purpose of this work is to examine Westernization as the concept implying the adoption of Western cultures to benefit longstanding practices in various spheres and to reveal it as a valuable attitude toward globalizing the economy. This study covers the methods through which Westernization or modernization is a way to address the ethical implications of unemployment and change in behavior through corporate social responsibility.
The author utilizes literature analysis providing evidence of the usefulness of Westernization for preventing adverse effects of globalization. It is revealed that Westernization creates a world with greater knowledge and the ability to communicate and share ideas globally while accepting cultures from every angle; thus, it prevents cultural devolution. Therefore, this research indicates the methodology that may contribute to developing solid CSR policies through acceptance of Modernization. It would prevent misuse of corporations’ power to gain extra profit from the use of AI rather than ensure the safety of a worker. This work is related to other sources due to confirming other authors’ concerns about the potential danger of globalization for employees in the event corporation does not have established contemporary ethical codes of conduct.
References
Au-Yong-Oliveira, Manuel, et al. “What Can We Expect from the Future? The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Society.” 2020 15th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Web.
Inkster, Becky, Shubhankar Sarda, and Vinod Subramanian. “An empathy-driven, conversational artificial intelligence agent (Wysa) for digital mental well-being: real-world data evaluation mixed-methods study.” JMIR mHealth and uHealth, vol. 6, no. 11, 2018. Web.
Ke, Jie, and Greg G. Wang. “China’s Ethical Dilemmas under Globalization and Uncertainty.” Advances in Developing Human Resources, vol. 16, no. 1, 2014, pp. 74–91.
Korinek, Anton, and Joseph E. Stiglitz. Artificial Intelligence, Globalization, and Strategies for Economic Development. No. w28453. National Bureau of Economic Research, 2021, Web.
Lindgreen, Adam. and Swaen, Valerie. (2009), “Corporate social responsibility”, International Journal of Management Reviews, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1-7. Web.
Perc, Matjaz., Ozer, Mahmut. & Hojnik, Janja. “Social and juristic challenges of artificial intelligence”. Palgrave Commun, vol. 5, no. 61, 2019, Web.
Subhabrata Bobby Banerjee. “Corporate Social Responsibility: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly.” Critical Sociology, vol. 34, no. 1, 2007, Web.
“The Dilemmas of Internationalization: Corporate Social Responsibility in Th…: Library OneSearch.” Ashford.edu, 2014, Web.
Westernization: With the Bad Comes Good. “Westernization: With the Bad Comes Good.” Paragon Language Services, 2016, Web.
Zhou, Guangsu, et al. “The Effect of Artificial Intelligence on China’s Labor Market.” China Economic Journal, vol. 13, no. 1, 2020, pp. 24-41. Web.