Background
Dolby Digital surround sound refers a sound compression system created by Dolby Laboratories. This technology, initially known as Dolby Stereo Digital until 1994, is an intricate audio coding that enables the storage and transmission of high quality sound in a better format than was initially possible. It is sometimes called AC-3 (audio coding 3) and enables users to experience a “rich, enveloping surround sound experience by delivering up to 5.1 discrete audio channels” (Dolby Laboratories). Dolby Digital was first used in film theaters in 1992 to provide digital sound, but has found applicability in various products such as TV broadcasts, DVD discs, and Home Theatre systems. These systems are normally identified with the Dolby Digital logo, a double D symbol.
Dolby Digital produces sound in AC3 format, enabling one to enjoy a surround sound and in its most frequently used form, the Dolby 5.1, contains six distinct sound channels: five channels for normal range sounds (20 to 20,000 Hertz) and a sixth channel for the low-frequency sounds (20 to 120 Hertz). The figure 5 in the 5.1 stands for the five normal-range sound speakers while the ‘.1’ represents the low-frequency speaker and is regularly referred to as the ‘subwoofer’ channel. This simply means that Dolby 5.1 uses six speakers. The AC3 sound format supports sound frequencies of up to 48 kHz. However, in an attempt to improve the quality of surround sound further, Dolby Digital has created Dolby 6.1 and Dolby 7.1 sound systems.
Although the 5.1 format is the most frequently used channel configuration, Dolby Digital technology can be used with the following channel choices:
- Mono (one speaker placed at the center);
- 2-channel stereo.
- 3-channel stereo.
- 2-channel stereo with mono surround.
- 3-channel stereo with mono surround.
- 4-channel quadraphonic.
- 5-channel surround (Dolby 5.1).
- 6- channel surround (Dolby 6.1).
- 7- channel surround (Dolby 7.1).
Dolby 5.1
This is the most commonly used surround audio system. It uses five full-range audio channels with varied frequencies and a sixth channel for capturing low-frequency sounds. The arrangement of the six audio channels is shown below:
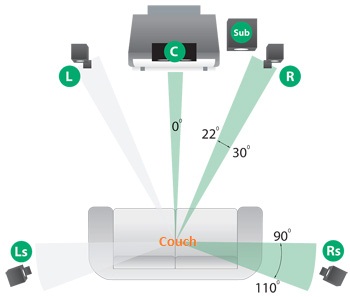
If the user is positioned at the center of the couch, facing the television screen and the center-channel speaker (C) at 0 degrees, then Ls represents the left surround speaker, Rs represents the right surround speaker, Sub represents the subwoofer, while L and R represent the left main speaker and the right main speaker respectively. The left and right main speakers should be within an angle of between and 30 degrees on each side from the user.
The left and right surround speakers should be on both sides of the listening region, and probably above the user’s ear level, or 2 feet or more above the ground and placed at an angle of between 90 and 110 degrees (Lofft, para. 3). The center-front speaker should be placed perpendicular to the television, then placed halfway between the right and left speakers. The subwoofer audio channel should be placed at floor level, around 12 feet from the television.
Except the subwoofer speaker, the other five speakers cover a frequency from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. This is the range for human hearing. The subwoofer speaker captures low frequency effects (LFE). The LFE speaker gives it the “.1” label, this indicates that the sixth audio channel is not complete as it only captures low frequencies (below 120 Hz).
Dolby 5.1 is surround sound and is aimed at giving a high-quality sound output for a home theatre system. This sound format is encoded to a majority of DVDs and Bluray discs as a means of improving the listening experience of an audience by creating a “theater-like conditions at home” (Vaux, para. 1). Instead of just hearing one or two sound channels coming from the TV, the Dolby 5.1 enables a viewer to hear multiple audio channels crated specifically to enhance the listening experience.
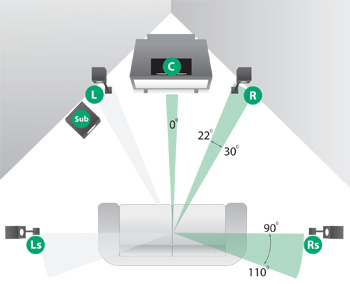
When the TV is placed in a corner, the subwoofer speaker can be placed next to the left or right main speaker as shown below:
Dolby 6.1
Dolby 6.1 surround sound is a system that gives a 6-channel audio output. It is almost similar to the 5.1, however, it incorporates an additional center channel speaker placed behind the user to improve the sound effects. The configuration of speakers in the Dolby 6.1 is shown below:
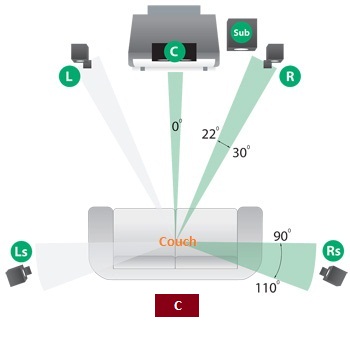
The 6.1 format was only a fad and is not common as an audio output system. In fact, very little material is available on DVDs or Bluray discs that exploit this speaker configuration (Getprice, para. 5).
Dolby 7.1
Dolby 7.1- surround audio system comprises of seven distinct, full frequency sound channels and an additional subwoofer that outputs low frequency sounds. This configuration is known as Dolby Digital EX and uses an additional mono audio channel at the rear end. Although a mono channel, the output of this additional audio channel is improved by incorporating two of the speakers as shown below.
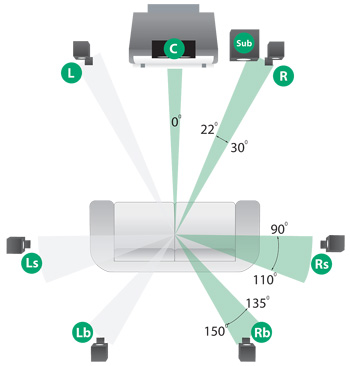
This speaker configuration differs from the Dolby 6.1 in that the mono speakers are not placed directly behind the user (hence180 degrees to the centre channel speaker), this dual arrangement is important because the brain interprets sounds coming directly behind us as coming from the front. The arrangement also helps in synthesizing the discrete sounds from the Left back and Right back mono speakers and therefore increases realism in sound effects. The advantages attributed to this configuration are factors that have contributed to the lack of popularity of the Dolby 6.1, in which the sixth audio channel is placed directly behind the audience (Lofft, para. 10).
Dolby 7.1 is sometimes referred to as HD sound since it is supported by the latest gadgets such as HD televisions and modern video game consoles (Kay, para. 3). This technology is, however, not limited to these gadgets, it finds application in numerous audio and audiovisual media.
Similar to other Dolby systems, the 7.1 arrangement works by decoding all seven audio channels originating from only the left and right speakers. However, the mono speakers work in a different way as they require the sound signals received from the left and right speakers to be phase shifted through an angle of 90 degrees. Even though the 5.1 audio channel is currently the most popular, it will soon be replaced by the 7.1 system that delivers a richer and deeper sound (Lofft, para. 3).
Subwoofer Placement
Since low frequency sounds of below 80 Hz is non-directional, the subwoofer can be placed anywhere in the room, however, corners will give the greatest LFE experience, though, the risk of getting a booming sound increases (Lofft, para. 10). Placing a subwoofer further from any intersecting room boundary will lower the likelihood of a booming sound, or excessive bass. This emanates from the fact that bass sound waves are large and easily affected by walls and ceilings, leading to poor sound output. The best position for a woofer is one in which the bass sound does not originate from any one particular position, instead, it smoothly ‘disappears’ into the sounds produced by the other speakers. The usual positions for placing subwoofers include the area behind the sofa, or directly next to or below the TV.
In order to achieve the best bass output, a user has to try out different positions since bass output depends on the dimensions of the room. However, it is recommended that one should use two smaller subwoofers rather than one large subwoofer, in this way, the bass sound easily synchronizes with the other sounds for a richer, high-quality sound.
Works Cited
Dolby Laboratories. Dolby Digital Details: Experience Stunning Audio Quality. 2011. Web.
Getprice. HDTV Setup Guide – Surround Sound Speaker Placement. No date. Web.
Kay, Douglas. 7.1 Computer Speakers – What is Dolby 7.1? 2009. Web.
Lofft, Alan. An Essential Guide to Home Theater Speaker Placement. 2006. Web.
Vaux, Robert. What Is Dolby 5.1 Surround Sound? 2011. Web.