Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this research paper was to determine how political factors affect the construction industry in Dubai and what can be done to lower these costs.
Design: The research used both primary and secondary sources of data to collect the needed information. Primary data were analyzed both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Findings: The study reveals that political factors have significant impacts on the cost of construction in Dubai. The involvement of the government as a customer, a policymaker, and enforcement authority significantly affects the costs.
Research limitations: The area of study was limited to the city of Dubai.
Practical implications: The outcome of this research shows that although the Dubai government has tried to lower the cost of construction in the city, more remains to be done to further lower these costs.
Introduction
Background
The United Arab Emirates has one of the fastest developing construction sectors in the world. The city of Dubai is currently one of the top global business hubs and tourists’ destination centers. The growing relevance of this city has played a significant role in boosting the growth of its construction sector. Currently, Dubai is home to the world’s tallest building and the world’s largest man-made island, thanks to the public-private partnership in the sector of construction. The government has been keen on diversifying the economy of this country as a way of reducing its overreliance on oil and gas exports. Massive infrastructural development, especially in housing, transport, healthcare, education, and other sectors has been witnessed over the recent past.
These developments have completely transformed the country’s economy and Dubai is now viewed as one of the best destinations for not only tourists but also foreign investors from North America and Europe. The construction industry has particularly attracted massive attention from both the local and foreign investors as the real estate market continues to become more attractive. When it was announced that Dubai had secured the right to host World Expo in 2010, the construction industry received a major boost. It was good news for the construction sector as both the public and private sectors started developing new strategies to make the expo a success (Mollaoglu et al. 19). The government has focused on transport, healthcare, and social amenities sectors as it prepares to receive the world. On the other hand, the private sector has been focusing on the real estate and entertainment industries to tap into the expected market.
It is important to note that as the country experienced massive growth in its construction industry, the political forces significantly affect it. As Motaleb and Kishk note, the political environment defines a country’s business environment (61). One of the main areas where the political environment affects the construction industry is in the field of security. The real estate heavily relies on the political stability of a country. People cannot live in a city where there is instability. For instance, the city of Aleppo currently cannot support the construction industry because of the ongoing armed conflicts. The political class can also get so much involved in the industry because of personal or national interests that it becomes impossible for the local or foreign private players to operate effectively.
Issues such as corruption and favoritism, which have serious negative impacts on the construction industry, are also related to a country’s political environment. Some of these political forces may have significant impacts on the cost of construction within a given region. As Scholiro says, for any business to survive, the additional costs must always be passed to the customers (235). If the additional costs are too high to be passed to the customers, then such a firm may not survive in that particular market. It is important to investigate how the political environment in the United Arab Emirates affects the cost of construction in the city of Dubai. In this paper, the researcher seeks to identify and analyze the effects of political forces on construction costs in Dubai.
Problem Statement
The construction industry is currently one of the industries in the United Arab Emirates that is experiencing rapid growth. This industry has helped put the city of Dubai on the global map as one of the fastest developing cities in the world in terms of infrastructure and economy. These developments convinced the world that Dubai is the best city to host the 2020 World Expo. However, Schwab warns that this industry will still be relied upon to help in preparing for the expected expo (18). As the city prepares to receive the world in 2020, the transport infrastructure must be developed further. Roads, rail, air, and sea transport will need improvements to meet the expected high population of visitors in the city. The hospitality industry will also need a major boost. All these developmental needs rely on the construction industry. Even after the expo, Dubai city will need to continue on its growth path, and it means that the construction industry is going to be very important in this city for a very long time. The growth in the construction industry in Dubai will define future infrastructural development in the city of Dubai and other emirates within the country. It is, therefore, important to look at the problems that the construction industry may face currently and shortly.
In the macro-environmental analysis, one of the factors known to affect the growth of an industry is the political environment. The political forces within a given city or country at large may paralyze the operations of firms in a given industry. The construction industry is very sensitive and can be vastly affected by negative political forces. The United Arab Emirates has indeed experienced a long period of political stability since 1974 and that is why the city of Dubai has experienced massive growth after the country gained its independence. However, it is known that the government of Dubai has been specifically focused on investing in various sectors of the economy to reduce the country’s overreliance on oil and gas production.
Some of the largest Dubai-based companies are owned either by the government or by the royal family. Widén et al say that when the government is heavily involved in specific industries, then it may affect the ability of the private players to operate successfully (88). It creates an uneven playing ground where the government-owned companies get several favors such as tax heavens while the private-owned companies do not. It means that when it comes to pricing, government entities can afford to give their customers discounts because of their low cost of production. Political influence on an industry can be both positive and negative depending on the approach that the government has taken. The coming world expo and the need to ensure that the city experiences continuous infrastructural development require a positive impact of the political class on the construction industry. That is why this study is very important.
Aim
In their study, Turner and Riding observed that any major research costs time and money, and as such it is important to define the aim (180). At the end of the study, it will be necessary to determine if the desired goal was achieved. This can only happen if the aim of the research was clearly defined before the onset of the research. That is why in this study, the researcher set up the aim that should be achieved. The following is the aim of this research.
To determine the effect of political factors on the cost of construction in Dubai
It is expected that after identifying these political factors, the study will come up with several recommendations that will help in ensuring that the government policies do not affect the construction sector negatively.
Scope of the Study
When conducting research, the primary aim of a researcher should often be to produce new knowledge that will enhance the existing knowledge of a given field. Research should expand on the existing knowledge so that the stakeholders will have a better view of a given problem being investigated. In this study, the focus is on determining the political influence on the construction industry. Scholars, policymakers, and experts may find this document important in their respective fields. However, care should be taken when applying the recommendations made or using this document to define policies. This study was primarily based on the city of Dubai. Although some of the secondary sources of data focused on this city and other regions around the world, the primary data collected specifically focused on the city of Dubai. The scope of this study is, therefore, limited to the city of Dubai. Anyone who uses this document outside the context of Dubai should do so with care. The document may be successfully used when the political environment of the city is very close to that of Dubai.
Research Question and Hypotheses
Research is a very complex process, especially when it comes to collecting specific data needed for the study (Rahman and Alhassan 2). It is easy for one to sway from the main topic and collect data that does not narrowly focus on what is being investigated. It is, therefore, important for a researcher to come up with specific research questions that would help in gathering the relevant data from both primary and secondary sources. The research questions narrow the focus when collecting data, ensuring that only relevant information is collected from the field. The following is the primary research question that was used in this study.
What is the effect of political factors on the cost of construction in Dubai?
The above primary question was supported by several questions to help in gathering the needed data. Below are the supportive questions that were used.
How involved is the political class in the construction industry in Dubai?
What is the relationship between players in the construction industry and the political class in Dubai?
How are the activities and decisions of the political class affecting the cost of construction in Dubai?
Based on the above three questions, the researcher came up with the following hypotheses.
H1o: The political class is not deeply involved in the construction industry in Dubai
H1a: The political class is deeply involved in the construction industry in Dubai
H2o: The political class has no cordial relationship with the players in the construction industry
H2a: The political class has a cordial relationship with the players in the construction industry
H3o: The decisions and activities of the political class have not helped in lowering the cost of construction in Dubai
H3a: The decisions and activities of the political class have helped in lowering the cost of construction in Dubai
The data that will be collected from both primary and secondary sources will help in determining the above hypotheses.
Literature Review
The Construction Industry in Dubai
A report by Miniaoui and Schilirò shows that “during the last real estate boom in 2006, Dubai was home to 30,000 cranes, 24% of the world’s total” (229). It was considered the world’s crane capital because no other city could match it in terms of construction activities that were going on at that time. When Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed al Nahyan was elected as the president of the United Arab Emirates, he initiated several ambitious projects that were meant to transform the economy of the country from that which relies primarily on oil and gas production to that which relies on a diversified economy. After consultation with various leaders from other emirates, they came up with a plan that would help in this transformation. In this plan, one of the main decisions that were made was that the government had to invest heavily in its infrastructure. The construction industry was to become a major area that the government and private sector would be vastly interested in as a way of ensuring that the economy was transformed. At that time, Dubai city had not come to limelight as a major destination for tourists (Grose 41). It was struggling to become one of the regional business hubs. It was, therefore, not easy for the government to convince the private sectors to make significant investments in the construction industry. However, the government was interested in boosting the growth of the construction sector, and as such, most of the initial investments were made by the government. The following are some of the sectors where the construction sector became very relevant.
Construction in the transport sector
The transport sector in Dubai has experienced phenomenal growth over the last 15 years. According to Ozorhon, the road, rail, air, and sea transport has completely changed from what it used to be in the 1970s and 1980s in Dubai (460). Rail transport, for instance, is completely different from what it used to be in the past. The government has invested heavily in the construction of modern railway lines that can be used by electric trains, making transport within the city very affordable and less time-consuming. Figure 1 below shows one of the many modern railway lines that have been constructed in this city.

Road transport has also been a major area where construction companies have benefited a lot in the recent past. When the current regime took power, they initiated an ambitious project to improve roads within the country. This was necessary, as a way of making this city become a global business hub and tourist destination. The government knew that moving from one place to another was very important. New modern roads have since been constructed to ensure that movement from one part of the city is swift and very convenient. A report by Randeree classifies roads and rail transport in Dubai as some of the best in the world (4). The road and rail transport in Dubai currently matches that in developed nations such as Germany and Japan. Figure 2 below shows a section of the modern roads that have since been constructed in this city to ease traffic.

These two areas of transport clearly show the growth that has been experienced in the construction industry. Most of these roads were designed and constructed by foreign companies. They were fully funded by the government. The sea and air transport have also benefited a lot in the government’s effort to improve the transport sector in the country. As the government continued to channel money to the transport sector, the construction industry became very lucrative. New foreign and local construction companies emerged to take advantage of the growing opportunity. The involvement of the government in the transport sector created a demand for construction services. Today, the government is still heavily investing in the transport sector. Some new roads are being constructed others are being expanded while some need maintenance. The players in the construction industry still have a growing market that they can tap into because of the government’s commitment to the transport sector.
Construction in the social amenities sector
The city of Dubai is currently one of the leading tourists destinations in the world. This is attributed to the consistent investments that the government has been making in the social amenities sector in the recent past. When the United Arab Emirates gained its independence in 1974, it could not attract tourists, especially from countries such as Europe and North America. It had extreme temperatures, poor infrastructure, and lacked social amenities that could attract tourists. However, the major construction projects initiated by the government have changed everything in this country. It is unbelievable that the city of Dubai has become one of the world’s top destination centers despite the extreme temperatures. The government has invested in the construction industry creating beautiful amenities that attract both regional and international tourists. For instance, many tourists come from the United States, Canada, Europe, Australia, and China to see the world’s tallest building. Many other social amenities in the country have been attracting the attention of regional and international tourists all over the world. Palm Tree Island (see fig. 3), is one of the largest man-made islands in the world. Its unique design and location have made it one of the sceneries attracting tourists all over the world.

Construction in the social amenities sector has been booming over the recent past, attracting both the regional and international sectors. Hospitals and schools have also been experiencing massive expansion as the government tries to expand its operations. In a report given by Schilirò, the United Arab Emirates has invested heavily in the institution of higher learning (5). Some of the local institutions have been heavily funded so that they can accommodate more students from the region.
Construction in the real estate sector
The real estate is one of the sectors that have also received a massive boost through government-sponsored projects. However, Alam says that most of the players in the real estate market are private companies (6). The massive infrastructural development in this city has made it very attractive to regional and international visitors and business people. The smooth flow of traffic improved security, and emerging job opportunities has seen many people immigrate from all over the world to Dubai. The majority of those currently living in this city are non-Emirati nationals. The real estate market has been the biggest beneficiary of this massive growth. The housing market has remained attractive over the last decade. The global economic recession slightly slowed this growth. However, the planned FIFA 2022 World Cup in neighboring Qatar and 2020 World Expo has created a new demand for office and housing units.
According to Pamuk et al., some of the top global construction companies have set their bases in Dubai (236). The market has remained very lucrative despite the prediction by some economists that the real estate market was nearing a stage of the bubble burst. In this study, the steady growth of this housing market is attributed to the growing relevance of Dubai as a strategic business hub. Companies from the Far East and parts of Europe use this city as their strategic centers from where they can distribute their products to the emerging economies in Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. It is currently considered the main gateway to the Middle East and African markets. Used products like clothes and electronics from developed countries find their way into the African and Indian markets through Dubai. This is so because planning logistics in Dubai is very easy. The road and rail infrastructure are in excellent condition. Labor is also relatively cheap as people from developing countries travel to the city in search of jobs. The growing human population is putting pressure on the existing housing units. As such, the construction industry is assured of the growing real estate market in this city.
Foreign Investors in Dubai’s Real Estate Industry
According to Name, one of the areas in which the political class can influence construction costs in a country is by creating bottlenecks for foreign investors (281). As such, it is important to analyze the foreign investment in Dubai’s construction industry. In a report published by Miniaoui and Schilirò, the city of Dubai has attracted a high number of foreign investors from Europe, North America, Japan, and China who are keen on tapping into the construction market (233). Most of the state-of-the-art structures in this city were designed and constructed by foreign companies. For instance, Burj Khalifa, which is the tallest building in the world, was designed by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill LLP, an American company. The actual construction was done by Samsung C&T Corporation, a South Korean company that has also set its bases in this city. Several Chinese and Japanese construction companies were also sub-contracted to perform other tasks when constructing this massive structure. The city now hosts numerous foreign construction companies, which have come to tap into the growing construction sector in this city. Samsung C&T Corporation, Skidmore, and Owings & Merrill LLP, AECOM are some of the international companies, which are currently operating in this city. Some regional companies such as ACCL International from Afghanistan have also set their bases in Dubai (Akintoye et al. 67). The city has also attracted construction firms from developing countries such as the ALAMA Group of Companies from Uganda.
In their report, Abd et al. argue that Dubai is currently one of the most attractive markets for construction companies (2095). This is so because the government has been positively involved in the construction industry. The government has been spending many resources to construct roads, rail, schools, hospitals, houses, among others. The government has not restricted foreign players from tapping into the local economy. The government has always insisted on maintaining high quality in the products of this country. Most of the foreign companies have created competition in the market, leading to the production of high-quality products. It is easy for foreign firms to register and get a permit to operate in Dubai. The competition in the local market has had direct impacts on the cost of construction. Both the local and foreign firms know that the government is keen on quality. They are forced to use quality management models to help them cut down on the cost of production while still focused on producing high-quality products at the same time.
Comparing Construction Cost in Dubai and That of Major Regional Cities
Several factors determine the cost of construction within a given city. When the demand for construction is high in a region, the price tends to increase. The Middle East and North Africa regions have witnessed massive infrastructural development, which has directly affected the cost of construction. Doha, Riyadh, Jeddah, and Cairo are some of the top regional cities that can be compared with Dubai. These are cities, which have emerged as major trade centers and tourist destinations. According to Erogul, the cost of construction in these cities varies due to differences in socio-political and economic forces (2175). In the 2016 International Construction Cost Index study that was conducted by Arcadis, several cities in the Middle East were ranked high in this list (Miniaoui and Schilirò 54). Doha, Qatar was ranked the 12th most expensive city for construction in the world. It is ranked higher than Jeddah in Saudi Arabia, which is the second most expensive in the region and 18th in the world. The city of Dubai was ranked third in the region and 18th in the world.
It is important to note that of the three most expensive cities for construction in the Middle East, Dubai came in third. However, in terms of demand for construction projects, Dubai tops the other regional cities. It means that there are efforts by stakeholders to try to regulate the cost of construction despite the growing demand. As Hallam et al. suggest, the government is always one of the major regulators of the cost of a product, besides the forces of demand and supply (55). The Dubai government has influenced the cost of production in the construction directly and indirectly. Directly investments made by the Dubai government in the construction industry have helped in regulating the costs. The Dubai government is the top client of most of the leading construction companies. As such, these companies are keen not to exploit the government. The improved infrastructure means that the cost of moving supplies from one place to another has been significantly slashed. It is more convenient to transport the construction materials from the suppliers to the construction sites either through road or rail transport.
Involvement of the Political Class in Construction Industry
The United Arab Emirates has a unique political system that integrates the traditional monarch and modern democratic system of governance in what is referred to as the Federal monarch (Castellani et al. 671). The current president of the country is Khalifa bin Zayed who is the ruler of Abu Dhabi, while the prime minister is Mohammed bin Rashid who is the ruler of Dubai. The country has 40 members of the Federal National Council, out of which 20 are appointed by the president while the other twenty are directly elected in the emirates they represent. The work of these members of the national council is to advise the president and the Supreme Council. It is important to note that these representatives do not have the direct power to influence the business climate in the country.
It is the president of the country and the ruler of Dubai who has a direct influence on the construction industry. It is the responsibility of the leader of Dubai to define the business climate in this emirate. Mohammed bin Rashid, the ruler of Dubai, has always avoided meddling in the business environment in negative ways. His government has enacted policies to help improve the business environment for both the local and international construction companies. That is why several construction firms have come to this country to tap into the existing opportunities. The business environment is free from any negative political involvement. Local and foreign firms that stick to the set rules and regulations about construction standards and procedures, pricing, raw material sourcing, employment laws, taxation, and other legal requirements are assured of operating without interference. Just like in any other part of the world, corruption may be an issue, but the government has been working tirelessly to eliminate this vice. Many firms admit that corruption is not a major problem in Dubai’s construction industry. The current political climate in the city is likely going to attract more investors.
Conceptual Framework
In this study, the researcher will look at how political factors (independent variables) affect the cost of construction in the city of Dubai (dependent variable). Developing a conceptual framework will help in determining how these variables are related. In the review of the literature conducted above, several political forces have been identified to have either direct or indirect impacts on the cost of construction. It is not important to develop a conceptual product at this stage, demonstrating the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. It will help in visualizing these variables, making it easy for someone using this report to understand the focus of this study. The following is the conceptual framework for the study based on the variables used (see fig. 4).
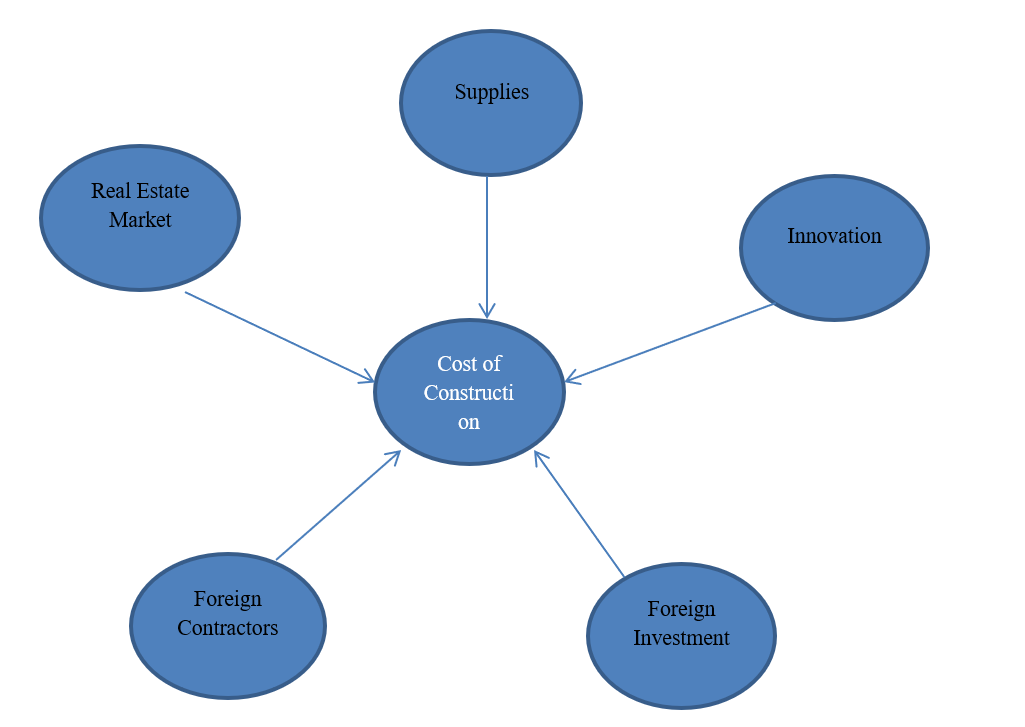
As shown in the above conceptual framework, there are five factors, which have direct impacts on the cost of construction in the city of Dubai. These five factors are directly influenced by the country’s political environment. These factors are discussed in detail in this paper.
Methodology
In every research project, there must be a clear method of collecting data from various sources and analyzing it to come up with findings. Describing the methodology enables the users to understand the process that was used to collect data and to arrive at a specific conclusion. In this study, data were collected from both primary and secondary sources. Secondary data was collected from books, journal articles, and reliable online sources. Primary data, on the other hand, was collected from individuals in the construction industry.
Sampling Method
In this paper, players in the construction industry were considered the right people to get the needed information about the effect of political factors on the cost of construction in Dubai. They understand how activities of the government affect the cost of supplies, innovation, foreign investment, the influx of foreign contractors in the country, and the real estate market’s attractiveness. There are so many people in this industry and based on the time constraint it was not possible to interview all of them. As such, the researcher opted to sample some of them. Simple random sampling was done to select twenty participants for the study. These are people who understand the construction market in Dubai and forces that affect the cost of construction.
Primary Data Collection
After identifying the participants for the study, the researcher prepared them for the process of data collection. A formal letter was written to these individuals explaining the purpose of the study and the role of the participants. The participants were informed that this was scholarly research and that the information collected is not going to be commercialized in any way. A day before the day of data collection, the participants were reminded through a phone call about the impending interview. The researcher physically visited the participants in their offices within the city and conducted the interview. This approach of data collection was chosen because most of the respondents are very busy individuals who cannot easily spare time to visit this institution of learning to be interviewed by the researcher. A face-to-face interview was also important for the researcher because it made it possible to ask the participants to clarify issues that were not clear.
Instrument Used in Data Collection
The researcher used a questionnaire to gather data from the respondents. The questionnaire was developed before the day of data collection. As Ozorhon et al. note, the use of questionnaires in the interviews helps in guiding the process of collecting relevant data (259). The interviewer becomes more organized having questions written. It ensures that all the important issues are covered in the interview. The interview used in this research is in the appendix of this paper.
Data Analysis
Data collected from the primary sources were analyzed using both qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative methods make it possible for the researcher to use mathematical tools to conduct analysis. Some of the factors are believed to be more significant in influencing the cost of construction than others. The quantitative analysis makes it possible to determine the magnitude of the variables hence ranking them in terms of their significance in influencing the cost of construction. The qualitative analysis makes it possible to describe different phenomena. It will enable the researcher to describe how different variables affect the cost of construction based on the information collected from the respondents.
Ethical Issues in Data Collection and Analysis
It is important to observe ethics when collecting and analyzing data from the respondents. In this study, the researcher observed ethical issues when collecting and analyzing data. The respondents were informed about the purpose of the study and their role in it. Their identity was protected to ensure that other people who may have contrary opinions do not subject them to unfair criticism. To hide the participants’ identity, they were assigned letters of the alphabet instead of using their actual names. The researcher observed ethics during the interview, asking questions that were in the questionnaire used. In the analysis, the researcher remained ethical by resisting the temptation to ignore responses that were contrary to the opinion of the researcher or the majority. All the responses received from the participants were analyzed to have a clear understanding of the issue under investigation.
Analysis and Discussion
Analysis of the Primary Data
The Dubai construction industry is booming and the current forecasts show that the industry is likely going to experience continued growth in the industry. The primary data collected was analyzed both qualitatively and quantitatively. The aim of collecting and analyzing the primary data was to respond to the primary research questions and to confirm the set hypotheses. In this section, the researcher will analyze each question based on the responses obtained during the interview.
How involved is the political class in the construction industry in Dubai?
The first question was focused on determining the extent to which the political class is involved in the construction industry. The respondents were asked to rate the level of involvement on a scale of one to five. One represents the least level of involvement and five represents a very high level of involvement. Figure 5 shows the results obtained.
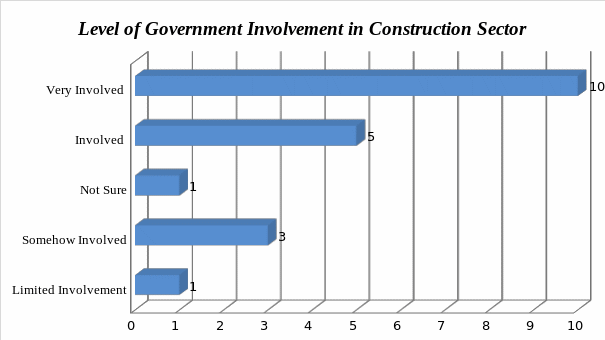
As shown in the outcome of the analysis of primary data, it is clear that majority of the respondents are convinced that the government is highly involved in the construction industry in Dubai. The above results mean that the null hypothesis below is rejected.
The political class is not deeply involved in the construction industry in Dubai
The data collected confirms the alternative hypothesis that was set based on the preliminary information collected from the secondary sources. It is true that the political class in this country is deeply involved in the construction industry in the city.
The political class is deeply involved in the construction industry in Dubai
They are involved as regulators, investors and clients. Their involvement ensures that there is law and order in this industry.
What is the relationship between players in the construction industry and the political class in Dubai?
The second question focused on determining the relationship between players in the construction industry and the political class. This question was based on the premise that if the relationship between the players in this industry and the political class is not cordial, then there might be a deliberate attempt by those in the political leadership to frustrate the industry. One of the ways of doing this is to increase the cost of doing business locally for these players. When asked this question, their response was statistically computed and the following figure 6 shows the results.
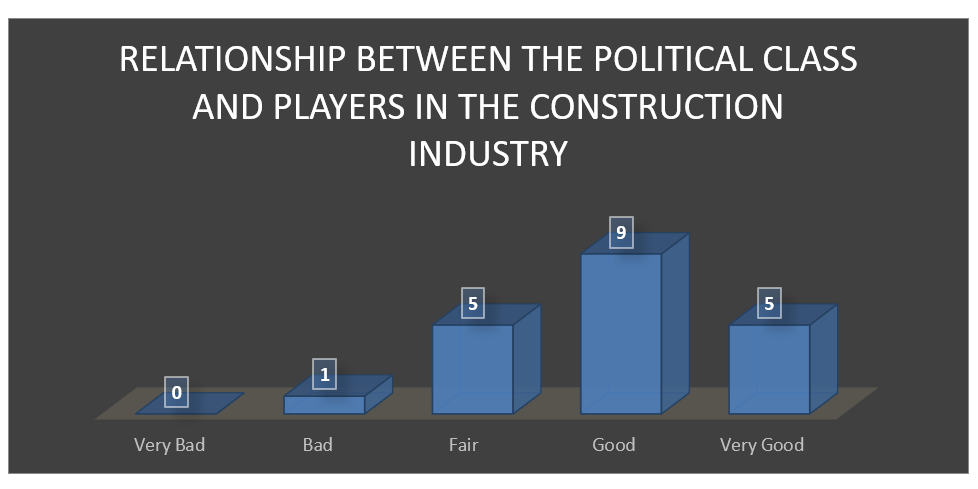
It is clear from the above figure that the relationship between the players and the political class has been cordial. It means that the null hypothesis below was rejected.
The political class has no cordial relationship with the players in the construction industry
Majority of the respondents feel that there is a good relationship between the players in the construction industry and the political class. It confirms the alternative hypothesis below.
The political class has a cordial relationship with the players in the construction industry
The good relationship makes it possible for the political class and players in the construction industry to work closely in an effort to help develop the city’s infrastructure.
How are the activities and decisions of the political class affecting the cost of construction in Dubai?
The third question focused on determining how the decisions and activities of the political class affect the cost of construction in Dubai. The responses obtained from the participants refute the following null hypothesis.
The decisions and activities of the political class have not helped in lowering the cost of construction in Dubai
When asked this question, the respondents identified a number of decisions and actions of the political class that may have a direct influence on the cost of construction in the city of Dubai. The policies that the politicians make about taxation and presence of foreign workers in the country directly influence the cost of construction. When the government comes up with policies that allow free movement of labor from other parts of the world into the country, it lowers the cost of production. Similarly, lowering tax on some of the imports helps in lowering the cost of construction in the city. It means that the results obtained from the respondents confirm the null hypothesis below.
The decisions and activities of the political class have helped in lowering the cost of construction in Dubai.
The analyses of the three research questions reveal that the political class’s actions and decisions have significant impacts on the cost of construction in the city of Dubai. The respondents are fully aware of the impact the government may have on determining the cost of construction of various projects.
Discussion
The city of Dubai is currently one of the top global business hubs and tourists’ destination because of the massive infrastructural development witnessed over the recent past. The government has committed massive resources in the construction sector, a move that has transformed an otherwise desert town into a modern city that attracts regional and international visitors. The construction sector is likely going to experience further growth in the near future. However, the stakeholders are always concerned about the cost.
When the cost of construction increases, the players in this industry may be forced to transfer the additional cost to the clients in order to remain operational. The analysis of primary data and the review of the existing literatures clearly reveal that political factors influence the cost of production. It is necessary to look at the specific areas where political climate may have direct impacts on the overall cost of construction in this city.
Political Impact on Supplies
The construction industry in Dubai relies on various materials, some of which are imported from various countries around the world. Some of the materials used in the real estate industry are imported from Japan and China. It is the role of the political class to set policies relating to importing various products into the country. According to Abuelmaatti and Ahmed, the government has avoided coming up with policies that may inflate the cost of supplies in the construction sector (221). Some of the respondents stated that the government is one of the main customers of construction companies.
Increasing the cost of imports in the construction industry may only prove counterproductive, as the additional cost will still be transferred to the government. In fact, some of the respondents explained that the government has been working closely with the players in this industry to help them access materials they need from other countries without incurring unnecessary costs. The locally produced materials are also affordable because the political class has avoided levying high tax as a way of boosting growth in the construction sector.
Political Impact on Innovation in Construction
Innovation is very important when it comes to lowering the cost of construction. Using some of the modern ways of construction helps in cutting costs and improving the quality of the final products. Innovation thrives in an environment where there is highly skilled labor. The government of Dubai has made an effort to ensure that there is sufficient skilled labor force in the country. The ruler of Dubai has financed development of new university and expansion of the existing ones.
The city currently is home to some of the finest universities in the region. It means that the construction industry can easily get skilled labor from the local labor market. The government has also allowed experts from other countries to come and work in the country. These political decisions have enabled the construction industry to have access to highly skilled individuals in the construction industry. These experts have helped in promoting innovation in this industry, hence lowering the cost of construction in Dubai.
Political Impact on Foreign Investment
Foreign investment creates healthy competition in the market. It creates a platform where players get committed to creating higher value for their customers at a lower cost. They are forced to be more efficient and to identify and eliminate weaknesses that may increase costs of operation. Healthy competition in the market is a key driver to lowering the overall cost of construction. The political environment in the country has made it possible for foreign investors to come into the city. Foreign construction companies from Europe, North America, and Far East have moved to Dubai to tap into the growing construction market. Other regional construction companies from neighboring countries have also moved to Dubai.
The competitive environment created by these political policies has improved efficiency in the construction industry, hence lowering the cost in this industry. These foreign investors have introduced some of the best practices into the local construction industry, leading to significant drop in the construction cost. Every player is keen on offering the best prices for their customers in the market. However, they know that they can only lower their prices if they find ways of cutting down the costs.
Political Impact on the Real Estate Market
The real estate market can only flourish if there is a growing population of families in need and capable of purchasing homes. Most of the companies in the construction sector rely on customers who purchase the housing units as opposed to renting them. As Alam notes, when the rate of stock turnover is high, then companies can benefit from economies of scale (6). It means that the construction companies can lower their costs when they purchase goods in bulk as opposed to purchasing them in small quantities. Purchasing the construction items in bulk enables the companies to negotiate for a better price. It also allows the companies to cut down the cost of transportation.
The real estate market heavily relies on how well the local population can afford to purchase the housing units. It depends on the purchasing power of individual citizens. The purchasing power of cities depends on the political policies embraced by the government. A government that owns most of the country’s wealth denies its citizens the ability to improve their purchasing power. A corrupt system of government also reduces the purchasing power of the customers. In Dubai, the political policies have enabled the locals to own wealth, making it possible for them to afford housing units. It explains why the construction industry has been growing rapidly. The net effect is that the cost of construction in the country has come down.
Recommendations
The government of Dubai has done a lot to ensure that the cost of construction in the country is low. The political class has tried to work closely with the private sector to promote the growth of this industry. However, it is important to note that Dubai City, having been ranked 18th most expensive city for construction in the world, is one of the most expensive cities for construction companies at global level. It is costlier than some major cities in the United States, Germany, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, China, and Japan among other developed countries. It is necessary for the political class and private sector to come up with ways of cutting down this cost further. The following are some of the recommendations that should be taken into consideration.
- The government should work closely with the private sector players to eliminate cartels that may inflate prices of raw materials for this industry for personal gains.
- Involvement of government in the construction industry should not create unfair competition between public and private enterprises.
- The government may need to subsidize some of the important materials needed in the construction industry to help lower their costs.
- New policies are needed that will regulate the industry in terms of quality of products delivered by the players in this industry. They must understand that as they cut their costs, they should not compromise on quality.
Conclusion
Dubai is currently one of the leading global business hubs and tourists’ destination because of the massive infrastructural development it has recorded. The construction industry has recorded massive growth over the last one decade. As shown in this paper, this city is currently home to the world’s tallest building and the largest man-made island. As the construction industry continues to grow, one of the main concerns of the players is the increasing cost of doing business. The cost of materials, labor, and other resources has been rising steadily.
In this paper, it has been demonstrated that political factors have significant effects on the cost of construction in Dubai. The study has identified areas where the government has made deliberate efforts to lower costs of production. However, more remains to be done by the political class to further lower down these costs. Currently, Dubai is ranked the 18th most expensive city for the construction companies, a sign that more still remains to be done to cut down costs of operation. The recommendations above identify the areas where the political class should give emphasis.
Works Cited
Abd, Yousif, et al. “Toward Building A National Innovation System in UAE: In 2012 Proceedings of PICMET’12.” Technology Management for Emerging Technologies, vol. 1, no. 4, 2012, pp. 2086-2099.
Abuelmaatti, Aisha, and Vian Ahmed. “Collaborative Technologies for Small and Medium-Sized Architecture, Engineering and Construction Enterprises: Implementation Survey.” Journal of Information Technology in Construction, vol. 19, no. 2, 2014, pp. 210-224.
Akintoye, Akintola, et al. Construction Innovation and Process Improvement. Wiley-Blackwell, 2012.
Alam, Muhammad. “Market Orientation and Innovation: Are They Related Concepts?” International Journal of Trends in Economics Management & Technology, vol. 3, no. 6, 2014, pp. 6-18.
Bygballe, Lena, and Malena Ingemansson. “The Logic of Innovation in Construction.” Industrial Marketing Management, vol. 43, no. 3, 2014, pp. 512-524.
Castellani, Davide, et al. “How Remote Are R&D Labs? Distance Factors and International Innovative Activities.” Journal of International Business Studies, vol. 44, no. 7, 2013, pp. 649-675.
Erogul, Murat. “Entrepreneurial Activity and Attitude in the United Arab Emirates.” Innovation: Management, Policy & Practice, vol. 3, no. 7, 2013, pp. 2159-2186.
Grose, Michael. Construction Law in the United Arab Emirates and the Gulf. Wiley & Sons, 2016.
Hacklin, Fredrik, et al. “Strategic Choices in Converging Industries.” MITSloan Management Review, vol. 55, no. 1, 2013, pp. 64-73.
Hallami, Mirriam, et al. “Technological Innovation in the United Arab Emirates: Process and Challenges.” Transnational Corporations Review, vol. 5, no. 2, 2013, pp. 46-59.
Miniaoui, Hela, and Daniele Schilirò. Innovation and Entrepreneurship for the Growth and Diversification of the GCC Economies. McMillan, 2016.
Mollaoglu, Sinem, et al. “Assessing Key Dimensions to Effective Innovation Implementation in Inter-organizational Project37 Teams: An Integrated Project Delivery case.” Engineering Project Organization Journal, vol. 4, no. 1, 2014, pp. 17-30.
Motaleb, Omayma, and Mohammed Kishk. “An Investigation into the Risk of Construction Projects Delays in the UAE.” International Journal of Information Technology Project Management, vol. 4, no. 3, 2013, pp. 50-65.
Muscio, Alessandro, et al. “Does Government Funding Complement Or Substitute Private Research Funding To Universities?” Research Policy, vol. 42, no. 1, 2013, pp. 63-75.
Neaime, Simon. “The Global Financial Crisis, Financial Linkages and Correlations in Returns and Volatilities in Emerging Mena Stock Markets.” Emerging Markets Review, vol. 13, no. 3, 2012, pp. 268-282.
Ozorhon, Beliz, et al. “Integration and Leadership as Enablers of Innovation in Construction: A Case Study.” J. Manage. Eng., vol. 30, no. 2, 2014, pp. 256–263.
Ozorhon, Beliz. “Analysis of Construction Innovation Process At Project Level.” J. Manage. Eng., vol. 29, no. 4, 2013, pp. 455–463.
Pamuk, Haki, et al. “Do Decentralized Innovation Systems Promote Agricultural Technology Adoption? Experimental Evidence From Africa.” Food Policy, vol. 44, no. 3, 2014, pp. 227-236.
Rahman, Motiar, and Aminu Alhassan. “A contractor’s Perception On Early Contractor Involvement.” Built Environment Project and Asset Management, vol. 2, no. 2, 2012, pp. 2-8.
Randeree, Kasim. “Organisational Justice: Migrant Worker Perceptions in Organisations in the United Arab Emirates.” Journal of Business Systems, Governance & Ethics, vol. 3, no. 4, 2014, pp. 3-11.
Schilirò, Daniele. “Innovation in Small and Medium Enterprises in the United Arab Emirates.” International Journal of Social Science Studies, vol. 3, no. 5, 2015, pp. 4-14.
Scholiro, Daniel. “Diversification and Development of the United Arab Emirates’ Economy.” Journal of Applied Economic Sciences, vol. 2, no. 24, 2013, pp. 228-239.
Schwab, Klaus. The Global Competitiveness Report 2013–2014: Geneva, World Economic Forum. Wiley, 2013.
Turner, Narelle, and Melaine Riding. “Early Contractor Involvement in Australia: Learnings from Transfield Services Projects.” Small Enterprise Research, vol. 22, no. 2, 2015, pp. 173-184.
Widén, Kristian, et al. “Links Between Successful Innovation Diffusion and Stakeholder Engagement.” Journal of Management in Engineering, vol. 4, no. 8, 2013, pp. 81-98.