An electronic health record (EHR) is a digital storage of a patient’s medical information that can be accessed from any location and at any given time. EHR systems facilitate the seamless flow and exchange of information within hospitals and health care settings in order to improve the quality of medical care provided to patients (Bowman, 2013).
There are various types of EHR used by different hospitals and health facilities. The Kendall Regional Medical Center uses Meditech to store information and streamline workflow within the facility. I interviewed multiple users of the system from different departments to find out about the benefits they receive from using it to fulfill their duties. They had different answers regarding their perception of the system’s effect on patient care.
Benefits of using the EHR
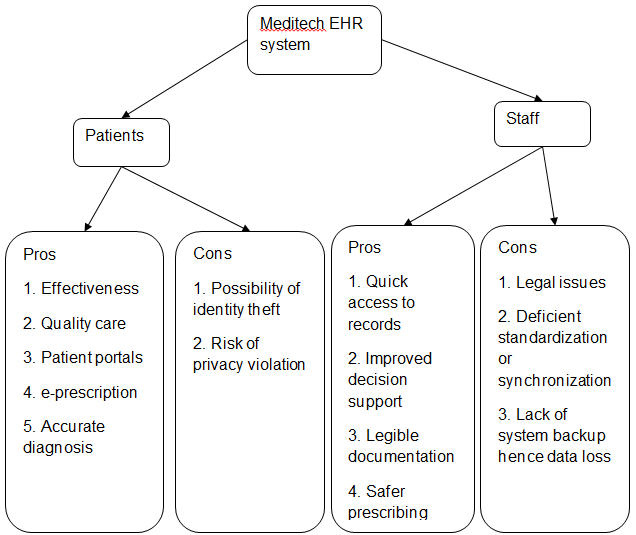
One of the benefits that staff members enjoy from using the system is increased productivity. The system allows them to make better decisions and coordinate patient care. Providers are able to make fast and safe treatment decisions because of the availability of up-to-date and complete patient information on the system. Safety is an important component of patient care that is improved by the use of the Meditech system (Palma, 2013). Other workers cited streamlined workflow as the major benefit of using the system.
This resulted from alerts regarding medical errors, ability to access information from any location and at any time, effective communication with patients, and easy monitoring and tracking of patients’ progress. Other advantages include improved diagnostics and patient outcomes, practice efficiencies, increased patient participation, and cost savings (Menachemi & Collum, 2011). Increased patient participation contributes toward improving the medical care provided because the care giver is able to collect all the information needed to make a correct diagnosis.
EHRs facilitate reliable access to patients’ complete information and as a result, make early diagnosis and prevent the progression of illnesses (Butler & Fox, 2015). In addition, it eradicates the possibility of medical errors that compromise patient safety. EHRs improve safety by identifying complications that arise as a result of new medication, keeping records of a patient’s allergies and medications, and identifying conditions that could endanger the life of a patient in case certain medications are used (Palma, 2013). Moreover, they expose safety problems whenever they occur during the implementation of a treatment plan.
Effects of the system on patient care
According to the staff members that I interviewed, the system has positive effects on patient care because it facilitates safe and reliable prescribing, real time reporting and sharing of information, and complete documentation of records. Care providers can access patient records from any location and as a result, improve the coordination and efficiency of medical care (Butler & Fox, 2015). The system also provides an interface that connects different departments within the facility for easy, safe, and fast dissemination of critical information.
For example, a physician can access test results from the laboratory without any inconveniences or delays. The timely availability of information supports the decision-making process and supplies clinical alerts and reminders to care providers. The Meditech system also plays an important role in quality improvements especially with regard to provision of patient care. The system encourages patient-centered care because physicians can access all information regarding a patient’s medical history and health condition (Electronic Health Records, 2012).
Concept map
References
Bowman, S. (2013). Impact of Electronic Health Record Systems on Information Integrity: Quality and Safety Implications. Perspectives in Health Information Management 10, 1-17.
Butler, J., & Fox, J. (2015). How to Make Electronic Health Records an Asset Instead of A Burden.
Electronic Health Records. (2012).
Menachemi, N., & Collum, T.H. (2011). Benefits and Drawbacks of Electronic Health Record Systems. Risk Management and Healthcare Policy 4, 47-55.
Palma, G. (2013). Electronic Health Records: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly.