Introduction
Natural disasters are various natural phenomena that cause sudden interruptions in the normal functioning of the population, as well as the destruction and damage to property. They often have a negative impact on the natural environment. Natural disasters typically include landslides, earthquakes, mudflows, floods, snowdrifts, volcanoes, hurricanes, landslides, droughts, and storms. Fires, and especially forest burnings, are also an example of a natural disasters. Forest fires are one of the dangerous cases that are spread throughout the world. Every year, uncontrolled fire kills a large number of people and animals and also has a long-term effect on the environment.
Forest Fire
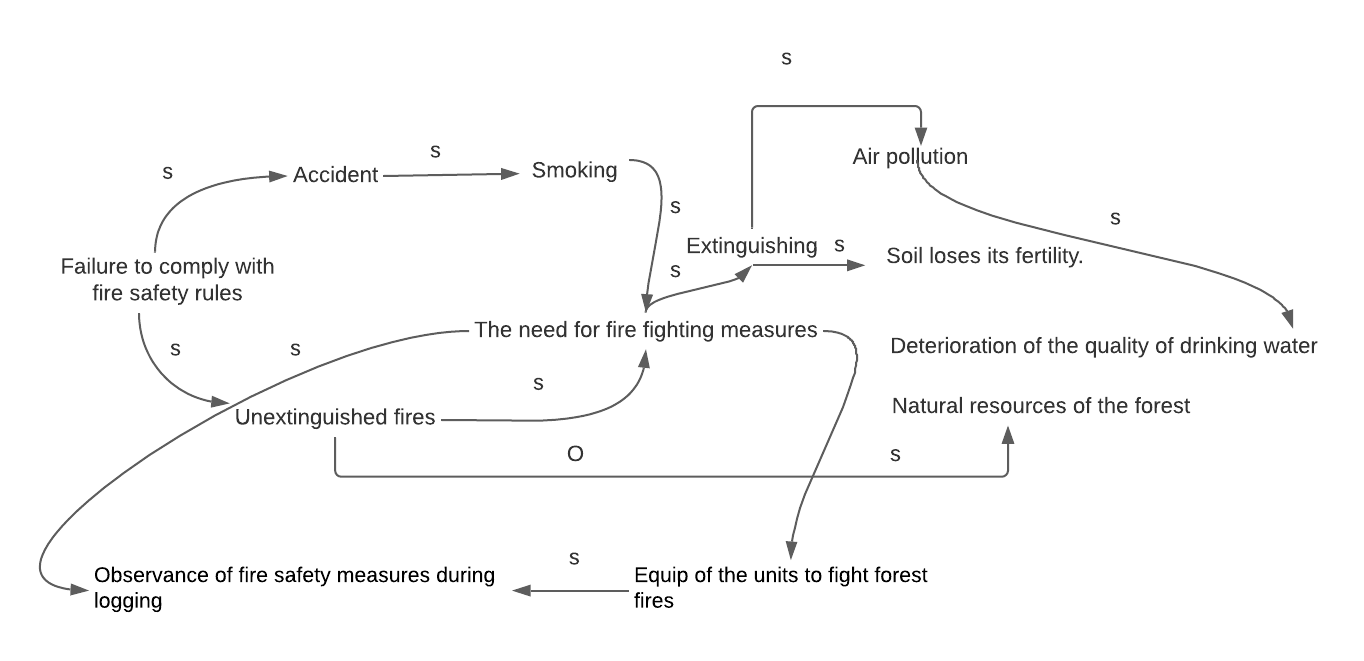
Forest fire is a natural, uncontrolled spread of fire through forest areas. The causes of forest fires are usually divided into natural and anthropogenic. The most common natural causes of large forest fires on earth are usually lightning strikes. The size of the fires makes it possible to observe them visually, even from space. Additionally, during fires, grass, shrubs, mosses and lichens burn out, soil, and trees are damaged, and microorganisms die (Martinho, 2019). Moreover, one of the main negative environmental consequences of fires is smoke and air pollution, which affects the lives of people and animals in the long term.
In young forests, where there is a lot of greenery, the likelihood of sunbathing due to lightning is much lower than in old forests, where there are many dry and diseased trees. The Dixie Fire in California, which has not stopped for a month, has become the second-largest wildfire in the history of the state (Jensen, 2021). The fire started on January 13, after which the wind drove it toward the ocean. About 30 thousand people were evacuated from the state due to a threat to safety and life. In recent years, large forest fires have often devastated vast areas in different states of America. In the summer of 2021, in northern California, 740 arches were engulfed in flames (Billings et al., 2021). The fire brought natural and economic destruction, as well as an impact on the mental state of the inhabitants.
The main causes of forest fires include the thrown unextinguished match or cigarettes, bottles and glass fragments, not completely extinguished fires, deliberate arson, and thunderstorms. The primary damaging factors for the forests include fire and high air temperature. Secondary damaging factors include vast areas of smoke, poisonous gases, and the collapse of trees (Sevinc et al., 2020). The consequences of large forest fires include the cessation of flights, climate change, stopping traffic on roads and railways, a sharp deterioration in the environmental situation and much more (Gates, 2021). While the ecological role of forest fires can be the natural renewal of forests, the consequences of the large fires bring an extensive number of negative effects for the population.
Conclusion
In conclusion, to reduce the incidence of fires, limiting visits to forests during the dry summer is important. Moreover, it is important to observe fire safety measures during logging and other work using technical means and by the population and educate the population in the basic techniques of extinguishing forest fires. In addition, it is important to properly equip the units to fight forest fires and to clean the logging site from harvested wood, branches, wood chips and forests from dry trees and debris in a timely manner. With precautions and preparations in place, the risk of fire over a wide area can be minimized.
References
Billings, M., Carroll, M., Paveglio, T., & Whitman, K. (2021). “Us versus Them;” local social fragmentation and its potential effects on building pathways to adapting to wildfire. Fire, 4(4), 96. Web.
Jensen, D. (2021). Multi-dimensional Disaster Response for Older Adults. Humboldt Journal of Social Relations, (43), 10-18. Web.
Gates, L. (2021). Undergraduate research and climate change. Scholarship and Practice of Undergraduate Research, 5(1), 3-3. Web.
Sevinc, V., Kucuk, O., & Goltas, M. (2020). A Bayesian network model for prediction and analysis of possible forest fire causes. Forest Ecology and Management, 457, 117723. Web.
Martinho, V. J. P. D. (2019). Socioeconomic impacts of forest fires upon Portugal: An analysis for the agricultural and forestry sectors. Sustainability, 11(2), 374. Web.