Introduction
History of Batteries (Types – Production – Consumption) in Europe, the USA and China
One of the most revolutionary ideas at the time of the invention was the battery. A battery is defined as a device where energy is stored and delivered through electrical means. Alessandro Volta invented the first electric battery in the early 1800s. Based on his theory of the Voltaic pile, Volta was able to produce a steady supply of electricity. The unit of measurement, Volt, is named after him in honor of his work that largely contributed to the field of electricity. The metals used in his first battery were copper and zinc. Volta noted that there was electrical interaction when two different plates of metal were submerged in an acidic solution and in close proximity to each other.
Further work was carried out by John Fredrick Danielle who constructed a multiple plate battery that was made up of both copper and zinc plates in combination with copper and zinc sulfates. This battery was used in the early days in the operation of many devices such as the telegraph and doorbells. This was later followed by the invention of another type of battery in 1859, the lead-acid battery. Early batteries could not supply enough voltage for a continuous period. This led to fluctuations in the level of voltages supplied and the use of batteries had to be limited to small-scale electric devices. Currently, the number of battery types has significantly increased. Modern people use zinc-carbon, silver oxide, nickel-metal hydride, alkaline, zinc-air, small sealed lead acid, and many other types of batteries. More generally, two basic types of batteries are primary (these can be used only once) and secondary (these ones can be reused).
The production of batteries was intensified during and after the World War I where the batteries were used to power small devices such as torches and radios. The development of radio and TV Broadcasting also helped to accelerate the production of the batteries as battery-operated televisions could be operated from home. At present, batteries are produced all over the world and consumed by a large number of people. China is the leader in batteries manufacturing, whereas the United States and the countries of the European Union have the highest rates of batteries consumption.
What Is a Battery?
Composition
The battery is composed of plates made of lead and lead dioxide. The two plates are both immersed in concentrated sulfuric acid. The reactions that take place in the battery are completely reversible, which makes it possible to reuse some batteries. The reactions involve the combination of sulfate that leads to the creation of lead sulfate whereby one electron is added. When the battery discharges, there is a build-up of PBso4 plus water in the acid giving out a characteristic voltage of about 2V. By combining six cells, one is able to harness the characteristic 12V that one normally finds in the Lead acid battery. When compared to the Zinc Carbon battery, recharge is easy as the reactions are completely reversible. The reaction in a zinc carbon battery involves no giving back of hydrogen into the electrolyte; thus, the recharging becomes difficult.
Design
Any battery, irrespective of its type or kind, has a case the main function of which is to protect electrolyte and all the battery components. Each cell in the battery has a separate reservoir separated by the walls in the case. All battery cases are different: “Some battery cases are made from translucent plastic and the electrolyte level is visible through the case, which allows the electrolyte level to be checked without removing the cell vent caps.” When the case is made from another material, the lifetime of a battery can be defined based on the work of the device.
Lifetime
The lifetime of non-rechargeable batteries varies depending on the type of battery. When it comes to estimating the lifetime of rechargeable batteries, it should be remembered that these batteries are prone to faster discharge than their primary counterparts. The lifetime of such batteries is measured in lifecycles which is the rate of charging and discharging that the battery can undergo. Degradation of the cell normally happens when the electrolyte that is contained within the battery shifts away from the electrodes or in some other cases where the electrode is eaten away or becomes corroded. In the case of most of the batteries, the thicker the plates that make up the electrode, the longer lifespan the battery will enjoy. The lifetime of batteries can be extended if they are exposed to a lower temperature; this tends to slow the chemical reactions that the battery undergoes.
Size
Among the most common battery sizes, there are AA, AAAA, C, D, N, and 9-volt batteries. They all have a cylindrical shape but differ in height and diameter. Thus, AA battery is 50.5 mm in height and 14.5 mm in diameter; AAAA is 42.5 mm in height and 8.3 mm in diameter; C battery has a height of 50.0 mm and diameter of 26.2 mm, while D battery’s height is 61.5 mm and its diameter is 34.2 mm. The smallest of all is the N battery the height of which is 29.35 mm and the diameter is 11.95 mm. Finally, 9-volt battery is 48.5 mm in height and 26 by 17.5 mm in diameter.
Re-Think for Batteries
The Importance of Batteries
In the operation of devices, such as laptops, mobile phones and other devices, the battery has become our friend as we cannot operate these devices without power supply. The case is especially true when we are talking about portable devices. The use of batteries is not limited to portable devices only, but also to large scale forms of engineering such as ships, airplanes and automotive cars. The batteries are also used as back up when the power from the national grid cuts off or becomes messed due to other factors. The research has shown that the battery industry contributed about $ 48 billion in America alone; this shows how enormous this field is.
Choose the best one (quality)
Among all the types of batteries, there are only several ones that can be called the best. Among these, there are lithium-ion, nickel-metal-hydride, and lead-acid batteries. Lithium-ion battery has the lowest weight and high-energy density. It is most often used in medical devices owing to its durability. Nickel-metal-hydride battery also has high energy density; this type of battery does not contain any toxic metals. Lastly, lead-acid battery is the most widespread; its weight is low and it is quite economical. The choice of the battery should depend on its application and the time which a device is expected to serve.
Recharge (Reuse)
Rechargeable batteries are used in portable devices and in tools that require uninterruptible power supply. When compared to primary batteries, rechargeable batteries undergo low self discharge rate. This means that the battery is able to sustain up to 70% of the said rated capacity. Rechargeable batteries are used not only in devices, but also in different applications, such as the power grid energy storage. In this application, rechargeable batteries are used for load leveling where the energy is collected by various energy sources; those can be solar panels used at night. Their use helps to reduce costs and is considered to be more environmentally friendly.
The Effect on Environment (Toxicity)
Batteries have come under fire from environmental activists as one of the major contributors into pollution. It has been found out that the metals used in the production of the batteries, such as lead, are toxic. Another factor is that used batteries contain electronic waste the recycling of which is extremely difficult. Several laws have been put in place to govern the recycling and disposal of the batteries. With a vast majority of citizens of all the countries using batteries, it has become a major concern to take care of the environment with the numerous amounts of batteries that are being disposed of all the time.
Recycling of batteries
Collection (Methods of Collection in the UK and the USA)
Collection of used batteries takes place according to different schemes. The matter is that recycling of the batteries has to take place in a way that would be not harmful for the environment. In addition, some of the batteries may discharge toxins if they are not properly recycled. This is why in the UK, for instance, “a number of local authorities now collect waste household batteries as part of multi-material kerbside collections, such as the well-publicized Bristol scheme.” As far as the USA is concerned, the country also implements a number of Battery Collection programs (quite often cooperating with Canada at this). Apart from this, used rechargeable batteries and old cell phones are collected in frames of free programs and then shipped for recycling.
Most Common Processes in Battery Recycling
The processes in battery recycling are numerous. Most of them are aimed at discovering different toxic materials in the used batteries. Among these materials, there is lead, mercury, plastics, nickel, metal content, acid, etc. One of the most common processes is heat treatment. This process is used for discovering lead, acid, and plastics in the used batteries. Similar thermal techniques are used for the discovery of cadmium in Nickel-cadmium batteries. Moreover, vacuum-thermal treatment is also one of the widely used processes for battery recycling. It is mostly used for recycling batteries that contain mercury. Finally, some of the batteries are reprocessed mechanically, by means of smelting, or thermal-metallurgical processes.
Hydrometallurgy Process (Description and Process Diagram)
Hydrometallurgy process is also widely used for recycling the batteries. It is used for battery crashing with the purpose of extracting some components (especially from the lead-acid batteries). This process is carried out in several phases (crushing and powdering ones). First, the battery is crushed and then powdered; after this, dry process is used to separate grains with the help of the screening or magnetic methods. This all takes place without water and under low temperature, which minimizes the possibility of the toxins getting into the sewer or air. The following diagram presents the hydrometallurgy process of recycling the batteries:
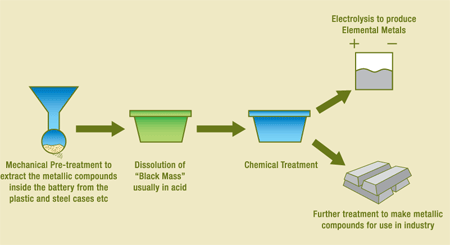
Pyrometallurgy Process (Description and Process Diagram)
Pyrometallurgical process for battery recycling is based on thermal treatment of batteries for separating certain components from them. A definite metal can be discovered from a battery if the latter is heated to a definite temperature at which the desired metal vaporizes. Basically, this is a mere distillation process. After the recovery of necessary metals from the used battery, hydrometallurgical process takes place. The following diagram presents pyrometallurgical process:
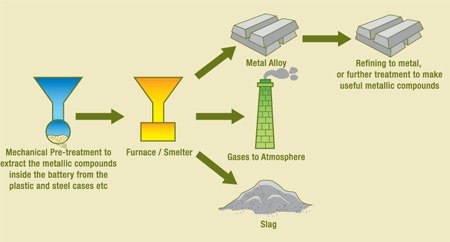
Classification of Battery Recycling Technologies around the World
There are three main recycling technologies used around the world. One of them is artificial separation technology. It consists in cutting the used battery and separating the components of this battery from each other. The remnants are then put into a chemical solution which allows separating some other materials. Another technology is the pyro-cycling one. As in case with the pyrometallurgy process, the battery is first broken and then heated to a rather high temperature at which certain metals and substances vaporize. Finally, the third technology used is the wet-recycling technology. This technology involves leaching to which the used batteries are exposed. This is the least expensive technology for battery recycling.
Battery legislation, collection and recycling in other developed countries
In the United States, the Mercury-Containing and Rechargeable Battery Management Act is used to regulate and enforce the ban of sale of mercury batteries or batteries that contain mercury as electrolyte. Disposal of batteries is also regulated in states using different legislatures. For example, in New York, batteries cannot be disposed in a form of solid waste.
The countries of the EU are also quite active in issuing legislation as for battery recycling. Already in 1991the Union has introduced a Directive on Batteries and Accumulators which required all the “batteries containing more than 25mg of mercury (except alkaline manganese batteries), 0.025% of cadmium by weight and 0.4% lead by weight to be collected separately from household waste for recycling or special disposal.”12 In 1998, this directive has been amended; this time the permissible heavy metal limits were reduced and marketing of the batteries that contained definite levels of mercury was prohibited. Currently, the directive is also experiencing amendments; the EU and the Member States are trying to reduce the permissible heavy metal limits even more, to make the recycling of the batteries more effective, and to place a ban on incineration of any industrial batteries. This shows how much the countries of the EU strive to preserve the environment and make the recycling of the used batteries safe. Moreover, this increases the contribution of each of these countries into preservation of the environment and health of the world’s population.
Application of Batteries
Electrically Powered Vehicles
These are vehicles that do not use the conventional fuel for power. Such vehicles use batteries that are in the form of hydrogen cells. Electrically powered vehicles are touted as cars of the future due to the low carbon emission that is emitted to the ozone and their being environmentally friendly. The other cars generate their power from fossil fuel. Electrically powered vehicles run on the lead-acid batteries. This type of batteries is the most convenient in case with these vehicles due to its low cost and high availability. Besides, lately re-engineered lead-acid batteries have higher power density and increased longevity.
Mobile phones
Batteries are used in mobile phones and other mobile devices due to the portability factor. In mobile phones, the most widely used batteries are Lithium-ion ones; this is due to their weight to power ratio. Several years ago, nickel metal-hydride batteries were the most popular in case with the mobile phones owing to their low weight and small size. However, due to high voltage depression, they were replaced by the Lithium-ion ones which, in addition, are even lighter. At present, the majority of the mobile-phone manufacturers prefer using lithium-polymer batteries the shape of which can be changed in accordance with the shape of the mobile phone.
Laptops
Laptops are used everywhere and they demand more power than mobile phones. Batteries normally used to power laptops are Lithium-ion batteries. The batteries are much stronger than those that are manufactured for mobile phones. The researchers are also coming up with the ways to reduce the energy that is wasted in batteries. It is known that not all the energy produced by the cell gets used by the device; much of this energy is wasted in form of heat energy. This energy is also a limiting factor when you are operating devices as they will not operate at optimum level. By getting rid of the heat, the devices are able to operate well. Apart from the Lithium-ion batteries, laptop manufacturers also use Nickel-Cadmium and Nickel-Metal-Hydride batteries. As for the Nickel-Cadmium batteries, they are used rather rarely because, due to the problems with memory, the batteries not always get fully recharged. This is why Nickel-Metal Hydride and Lithium-Ion batteries remain the most widely used in the manufacturing of the laptops.
Advancing battery technology
New types of battery
With the development of technologies, new and better forms of the energy started to emerge. New types of batteries are much smaller than the earlier versions, which allows manufacturing smaller and lighter electronic devices. Power that can be derived from these new batteries is ever increasing. The paper battery, for instance, consists of nanotubes and nanowires made up of silver due to its highly conductive nature. Moreover, research labs have come up with the ways to use the bacteria as the source of power. Some new types of batteries are based even on the decay of nuclear power. Such batteries are claimed to be 10 types more powerful than the usual ones; the same is said about the air-fueled battery that is capable of unbelievably large energy storing. All this will soon dictate new ways into how we will be able to store and harness.
Improving battery efficiency
Batteries have long been considered as a storage unit and they have served mankind in the best way possible. Despite the toxic effect caused by the batteries, degradation of the environment can be reduced with better disposal of the batteries and newer forms of technology that can lead to less pollution. With the advancement of technologies, pollution is likely to be reduced. There have been advancements in green energy and we have also seen the rise of solar cell battery that can be found to lead to cleaner energy. Lighter batteries are being developed and the students at MIT have recently come up with battery that is in the form of a paper. The technology used to drive this technology is nanotechnology
New types of power supply
Apart from the batteries, modern manufacturers of electronic devices have invented other types of power supply. AC adapter is one of these types. It is mostly known as an adapter block; it consists of a small transformer (possibly with diodes) surrounded by a constant magnetic field which remains stable unless the adapter is unplugged. One more new type of power supply is uninterruptable power supply that can generate energy from more than two sources at once. The load can hardly ever experience interruption because the storage battery always reserves some power and is ready to work in case of a dropout. Finally, there is also programmable power supply where the output voltage can be easily changed remotely. Some of these power supplies can be board-mounted, while there also exist floor- and wall-mounted ones.
Conclusion
Modern people can hardly imagine their lives without batteries because everything they have at hand has either usual or rechargeable batteries. Types and kinds of batteries are numerous and new varieties of them continue emerging. However, the biggest problem the world is preoccupied with is the recycling of the used batteries. New legislation has to be issued to make the recycling of the used batteries more environmentally friendly and less harmful for the world’s population.
Bibliography
Barak, M, Electrochemical power sources: primary and secondary batteries, IET, Washington DC, 2005.
Call2Recycle, Recycling at work, 2010, Web.
Collins, D, Batteries research and development in non-mechanical electrical power sources: proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium held at Bournemouth, Pergamon, Bournemouth, 2004.
David, H, Recycling of consumer dry cell batteries, William Andrew, Scotland, 2005.
Erjavec, J, TechOne: Basic automotive service and maintenance, Cengage Learning, New York, 2004.
Jennifer, C, Taking out the trash: a no-nonsense guide to recycling, Island Press, Chicago, 2005.
John, S, Your complete guide to renewable energy technologies and sustainable living: Real Goods solar living book, Gaiam Energy Tech, Inc., New York, 2005.
Lamar, L, Storage battery engineering: a practical treatise for engineers, Oxford Publishers, London, 2008.
Linden, D & Reddy, T, Handbook of batteries, McGraw Hill, New York, 2002.
Minami, T, Solid state ionic for batteries, Springer, Michigan, 2005.
Ronald, D. Understanding batteries, Royal Society of Chemistry, Great Britain, 2006.
Rosch, W, Winn L. Rosch hardware bible, Que Publishing, New York, 2003.
Samuel, L, Battery hazards and accident prevention, Springer, Michigan, 2004.
Steven, H, Major industrial products with the greatest environmental pollution levels, Spear Books, Ohio, 2006.
Waste Online, Battery recycling information sheet, 2005, Web.