Introduction
Contemporary Approaches to Human Resource Management and Development
Human resource management is a factor within the organization that prominently influences the asset value and competency in the marketplace. The department deals in the optimal coordination of employees towards enhancing appraisal exchange. The intensification in digital entrepreneurial practices globally fostered connectivity among consumers hence the rise in the attainment of product and service information (Stone et al., 2020). The advanced communication posed an opportunity and threat to the different companies. The prospect encompasses the emergence of a niche market for dynamic institutions. The ultimatum engulfs establishing critical approaches that effectively attain a competitive market position. Incorporating strategies that boost workers’ performance index led to the profound client’s satisfaction level and the loyalty essence.
There is an interdependent relationship between employees’ performance and customer satisfaction and loyalty. Human resource management practice is significantly attributed to the competence of an organization due to the identification of critical factors that influence the quality of service experience. Research indicates that the integration of dynamic approaches to enhance the engagement of workers fosters a prominent effect towards the intensification of customer loyalty due to the adept consistency on the highly levelled quotient of consumption (Boon et al., 2019). Apart from profitability, another goal to enhance the value of an institution enshrines empowering the laborers with apt knowledge, experience, and skills. Therefore, it is the responsibility of the managerial team in the human resource department to integrate approaches that intensify the interchange of value.
Research Evidence on Effective Employment of Human Resource Management
Policies play a significant role in developing a competent and functional organizational culture. In this case, the guidelines in a workers’ handbook stipulate the ideal approach about employees’ interaction with clients, employer, and the attainment of business objectives. Different companies utilize various policies to regulate the welfare of the laborers (Mousa and Othman, 2020). The four main approaches that profoundly feature the workers’ handbook’s paramount efficiency include technology use, harassment, fraternization policies, and leave. These components play a critical role in promoting laborers’ well-being. The interplay between human resource strategies and management initiatives contributes to an institution’s competence due to employee performance.
Strategies improving Human Resource Management and Development
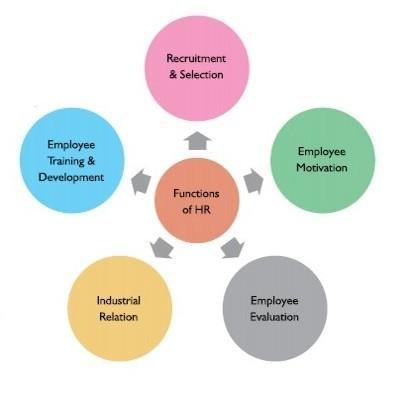
Human resource management engulfs the establishment of policies that govern the different approaches that employees should be handled in a company. It is a platform whose clarity and effective implementation determine its competitive advantage and sustainable organizational culture. Effective coordination among workers significantly contributes to the performance of laborers in attaining the firm’s goals and objectives. According to Michael (2019), there are different functions of human resource management that affect an institution’s employees. These functions include performance management, planning, recruitment, selection, human resource development, compensation benefits, employment, labor laws, and regulations (Mousa and Othman, 2020). In this case, it is essential to establish an organizational culture geared toward human resource development to equip the employees with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Theory and Practice relative to Motivation and Employee Engagement
Main Theories on Motivation and Employee Engagement
The evolving marketplace is a phenomenon that profoundly emancipates the essence of the employee needs and the expectations from the management team. According to Wigert and Harter (2017), the transition from a conventional performance management system to a modernized model enshrines satisfying the workers’ needs than the executive’s expectations. The utilization of rankings, ratings, and hierarchical-based pay structures featured prominent biasness based on the traditional performance management system. The researchers depict that the conventional approach heavily demotivates the employees because their future relies on an individual’s subjective observation and remarks (Michael, 2019). The modern workforce seeks a different form of satisfaction apart from a paycheck and a boss. The current workforce strives for a performance management system that boosts life, development, purpose, strengths, and coaching skills. Ideally, the foundational pillars of a sustainable performance management system focus on its growth and development. The advancement of the employees encapsulates the ability to gain more knowledge and skills in addition to the compensation scheme. The evolutionary process demands a contingent concept of the growth of laborers and the firm.
A sustainable performance management system features elements that promote development. Wigert and Harter (2017) stipulate that a development-oriented performance system engulfs three main phases: establishing expectations, coaching, and creating accountability. These phases engage the employers and foster the relationship-building between the managers and the laborers. The structure allows the executives to establish a rapport with the employees and continuously review their performance individually (Asian et al., 2019). Further, the essence of accountability enables the workers to provide coherent feedback from the organization’s daily encounters with suggestions for training needs to boost performance. The accountability phase ensures that the counterparts anticipate the shortcomings and take responsibility for the inefficiencies. Therefore, the performance management system asserts the core roles of the employees in an institution towards boosting the quality and competence in the global business environment.
Compensation and benefits systems are a dimension of human resource management that contributes to an establishment’s quality of services and products. Although employees attest to focusing on the performance management structure in a company, the compensation, and benefits approach is another factor that affects employees’ performance. According to Madanat and Khasawneh (2018), there is a significant relationship between employees’ performance and the compensation system. The researchers postulate that the employees became motivated and highly committed to the tasks based on compensation (Madanat and Khasawneh, 2018). Primarily, the performance outlier among the staff members encapsulates an established sustainable compensation and benefits structure in a company.
Implementation of Theoretical Models
There is a difference between conventional and modern performance management systems. The research study by Wigert and Harter (2017) indicates the significant difference between traditional and current structures under the mainframe of the costs and negative impact on employee relations. The researchers focus on quantifying the time lost due to the inefficiency of conventional performance management systems. A company with at least 10,000 employees loses the total amount of $2.4 million annually (Wigert and Harter, 2017). An excellent example is Gallup, which reported at least $960 billion annually of lost revenue and productivity due to dysfunctional traditional performance management systems. A performance management system’s primary role entails establishing a mechanism that consistently monitors the workers’ production quotient (Richards et al., 2019). As a result, the executive realizes the shortcomings in the laborer’s performance on a long-term basis, such as training needs and sustainable working schedules. The inefficiency of the conventional performance management systems lies in the evolutionary impact on the business environment.
Employee Engagement
Human resource management is a multidimensional phenomenon whose role in an organization engulfs boosting social capital value and competence. The sustainable growth of an organization involves the optimal utilization of the different facets of managing workers’ welfare and the performance index. Poor implementation of the elements leads to the high cost of production, low quality of products and services, and high turnover rate of employees in a corporate (Crespi, 2018). It is primarily the role of the department’s strategies to enhance a firm’s competitive advantage for sustainable growth and development. These roles include establishing the guidelines of employee interactions in a company. Another role is monitoring and assessing the laborers’ performance and laying down necessary training procedures. Finally, it is human resource management’s function to gear the financial planning process in an institution to influence counterparts’ motivation to deliver ultimately.
Role of Effective Leadership and Development
Contemporary Thinking on Qualities of a Leader
Leadership is a framework that prominently influences the nature of relationship-building among counterparts in a particular setting. Research indicates that one factor that improves teamwork coordination efficiency is optimal communication (Boyer, 2018). The sufficient flow of information among individuals intensifies understanding among employees towards achieving the primary goal, that is, customer satisfaction. In this case, managerial institutions’ responsibility is to plan and implement dynamics that enhance leadership and followership as a formative spectrum of exchanging professional values. Transactional and transformational principality foster effective interchange on morals, ethics, and strategic bureaucratic domains. Organizational leadership is a multidimensional phenomenon that encapsulates prominent correspondence among the stakeholders to advance the functional service delivery system.
Role of Leadership and Characteristics of its Effectiveness
Leadership in an organization is an essential factor since it elevates the quality of performance among employees. According to research, it is the responsibility of the managerial team to incorporate measures that enhance coordination among the workers while intensifying the exchange of distinct values (Dobusch, 2021). The research further indicates that inclusive organizational leadership involves the advertence of discrimination and assessing socio-cultural intellect apart from collaboration. In this case, the distinctive traits that enhance the optimal development of functional corporate culture engulf the team-oriented leader. It is an approach that renders the establishment of a platform that workers share their experiences for better performance outlier (Jeffries, 2018). The different leadership styles positively impact an organization’s competence in the global market. There is an interdependence relationship between strategic leadership and the inclusivity of the employees. As a formative perspective to elevate competitive advantages and acquire a contentious market position, strategic leadership focuses on the intersection of all values (Jeffries, 2018). Employees’ distinctive values encompass accountability, teamwork, and emotional intelligence through organizational leadership.
Suitable Leadership Development
The role of a leader is team-oriented, while a manager focuses on the accomplishment of tasks. The disparity between the two renders the profound distinction in their duties and responsibilities in a firm. On the one hand, a manager mainly develops frameworks and targets for the relevant department to accomplish growth and development. On the other hand, a leader establishes the ideal variables to enhance the synergism among workers to enhance the coordination (Andersen and Jakobsen, 2017). Primarily, both entities provide platforms to foster positive change within an organization (Morsiani et al., 2017). A captain’s duties ensure compliance to the regulatory mainframe, setting up policies, and spearheading the transformation. The additional roles of an administrator include the scheduling of teams, assignment of duties to staff, and career opportunities for the workers. Although both positions dynamically contribute to professionalism, their coordination cultivates a significant outcome by boosting the interrelations among colleagues.
Diversity management practices encompass integrating dynamic activities that empower personnel with the necessary skills and knowledge (Boyer, 2018). An effective diversity management practice should feature proactive measures. In this case, there are three phases in promoting diversity management practices. The first step enshrines recruiting employees and managers with skills regarding various backgrounds. The second step is the gearing of an organizational culture towards the diversity climate, and the last phase involves eradicating discriminatory behavior (Boella, 2017). Over the decades, the evolution in the business environment fostered the intensification of the level of competence. As a result, the employees emerged as the critical organization’s asset due to the influence on customer service experience. Therefore, the presence of discriminatory behavior within a company threatens its competence level in the environment (Sim, 2020). The concept of diversity management practice is an issue that demands further exploration mainly as a result of the dynamic influence on employees’ performance and contribution to the evolutionary process.
Roles and Practices of Human Resource Management
Role of Human Resource Management
Performance Management System
The performance administration system is one of the human resource management functions that measures and tracks employees’ performance. The framework is a multifaceted ideology that promotes an organization’s most valued asset, the staff. According to Mehra (2018), the performance management system empowers the workers with guidelines regarding the organizations’ engagements to boost their performance. The researcher further argues that an effective performance management system features sustainable policies to construct specific empowerment tools (Mehra, 2018). The materials engulf plans stating the health, safety and the employment law for the individuals. The clear establishment of the propositions leads to attracting good staff. As a result, the candidates get allured by an organization’s performance management system. The concept plays the role of gearing a company in employing highly skilled individuals due to the well-defined business goals. The evolution of human resource management is a concept significantly influenced by the paradigm shift in the demands of the employees in a firm.
Human Resource Planning, Recruitment, and Selection
Human resource planning is the concept of forecasting the company’s needs regarding the employees’ welfare and expectations. The human resource department’s strategy mainly influences the recruitment and selection process of the workers and candidates (Michael, 2019). Over the decades, technological advancement led to the emergence of a global village and intense competition in the business environment. As a result, companies need to optimize the groundwork process for recruitment and selection. Effective designing is a business strategy that renders a highly skilled and competent workforce in the institution. The primary role of human resource devising involves spearheading an effective and efficient recruitment and selection process. According to Mura et al. (2017), the evolution of the mainframe engulfs certain features of developmental goals from a managerial perspective. The common traits of human resource planning, recruitment, and selection encompass coaching from a leader than control from a manager.
The coaching perspective in human resource planning, recruitment, and selection enshrines dynamic factors that seek to boost employee and management relationships. Mura et al. (2017) indicate that one of the sustainable roles is innovative present and functional knowledge. The strategizing process primarily establishes the desired practical knowledge in a company based on its revolutionary and current trends. Another role is developing policies that define the relationship between a firm’s goals and objectives and the evolving market. According to the researchers, the approaches assist in articulating the institution’s core engagements towards ensuring a sustainable competitive advantage (Anwar and Abdullah, 2021). The framework also contributes to workers’ inspiration and motivation. Sustainable planning, recruitment, and selection processes orient the candidates towards attaining the job’s necessary skills and knowledge. As a result, laborers are empowered with sufficient skills and expertise to utilize competence and optimal market performance.
Sustainable human resource planning, recruitment, and selection profoundly contribute to creating value and resources in an organization. The planning phase ensures the in-depth analysis of the business environment’s emerging trends, such as the importance of a company’s social media presence for sales and marketing (Saeed et al., 2019). In this case, the planning phase focuses on the integral and necessary skills an individual must attain to foster effective recruitment and selection process (Mura et al., 2017). Therefore, human resource planning, recruitment, and selection ensure that the market dynamics integrate to develop the niche opportunity for optimal production scale.
Another significant role of human resource planning, recruitment, and selection entails identifying new market opportunities and product modification strategies. An excellent example is the advertisement of commodities through social media platforms. The online market seeks merchandise with additional features at a favorable price in most cases (Saeed et al., 2019). Therefore, the mainframe develops a proactive structure that adapts to the evolutionary trend and attains the significant share for the niche essence in the goods’ components. Fundamentally, the elements of the practice contribute towards the employment of highly skilled personnel, thus improving the workers’ asset value.
Human Resources Development
Human resource development entails the integration of an institutions’ strategies with the evolving corporate culture. Organizational customs refer to the employees’ critical processes as the baseline of interaction, coordination, and relationship building. In this case, human resource development’s central role encompasses positively influencing the buildout of a sustainable business operational trend. Michael (2019) indicates that human resource development aligns the workers’ interests with the firm’s goals and the evolving market demands. The researcher focuses on the significance of the alignment based on the essential and influential enterprise goals. One of the business initiatives that justifies human resource augmentation is its intention for product burgeoning, diversification, mergers, and acquisitions (Rigby and Ryan, 2018). In this case, it is essential to establish a cooperative tradition geared by human resource development to equip the laborers with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Another business factor that ascertains organizational human resource development is the strategic innovations to establish a competitive advantage. The core value of a company refers to the magnitude of product differentiation. In the research study by Michael (2019), it is crucial to integrate human resource development strategies since they constitute the organization’s highest valued asset. In this case, the effective implementation of a commodity’s diversification approaches downsizing of production costs heavily rely on the workers’ participation. Therefore, it is the human resource development strategies’ responsibility to ensure sustainable product distinction and minimization of expenses in reducing production costs.
Human resource development significantly influences the implementation of certain imperatives on the established organizational culture in a different spectrum. A performance-oriented corporate custom heavily relies on integrating business strategies and operational philosophies. Different institutions uphold distinct firms’ traditions’ constructs (Rigby and Ryan, 2018). Despite the dynamism in the constructs and philosophies of the norms, human resource development promotes integral business ethics and values (Michael, 2019). The core enterprise morals include a team working environment, the devolution of operations, and the ideal project management strategies. Primarily, sustainable practice features an approach that promotes individuals’ personal development to enhance cost leadership. The concept contributes to cost leadership by promoting self-management and learning. In this case, human resource development’s role is to establish policies that foster personal growth in the organization, hence boosting social capital value in a conglomerate.
The contingency theory highly supports the influence and role of a structured framework on the management of employees’ relations and welfare in an organization. A company’s quality of services and products depends on a functional human resource development platform. According to Mole et al. (2017), the construct stipulates that it is essential to integrate the environmental traits with a firm’s operations. The researchers further establish that human resource development gear the competence of a company due to its compatibility with the evolutionary marketplace. Ideally, it is the mainframe’s role to ensure the efficient coordination of activities in an organization to boost the quality of commodities and services.
Compensation and Benefits
An organization’s compensation and benefits policy positively influence employee performance and the retention rate. According to Michael (2019), compensation plays a significant role as a human resource management facet in promoting innovation. The practice contributes to the institution’s level of creativity through the reward system for the achievement. In most cases, employees seek an appreciation for an extra achievement for the company, such as rewarding monetary or gifts and rankings. Therefore, the compensation and benefit system positively influence the employees’ participation and motivation to utilize innovation as the emblem of an organization’s operations.
The compensation system also contributes to fostering the value for money in an organization through the spectrum of cost leadership. A coherent structure asserts the apparent level of expenditure in a company within a particular period. Researchers indicate that cost leadership is a significant competitive advantage (Madanat and Khasawneh, 2018). Further, the compensation mainframe positively affects the essence of the approach since it lays down the level of expenditure against the income generated. Sustainable remuneration ensures that the workers are satisfied, enhancing the institution’s resources’ optimal utilization to achieve the main objective (Werner, 2021). A flawed reimbursement perspective renders dissatisfied counterparts whose focus mainly involves completing tasks without the significance of quality and competence.
Compensation and benefit is a profound competitive advantage to an organization due to its contribution to the performance management system. An efficient structure engulfs a competitive reward system that motivates the employees. Mole et al. (2017) establish that the compensation and benefit system is a competitive advantage that appreciates the contingency ideology. In the re-engineering of the performance management system by Wigert and Harter (2017), the researchers realize that the compensation system determines employees’ selection process. According to the researchers, highly skilled professionals get attracted by the performance management system and compensation level (Mole et al., 2017). A corporate with an insufficient mainframe attracts low-skill individuals whose focus lies in satisfying psychological needs rather than growth and development. In this case, the compensation and benefits system profoundly contribute to the strategic recruitment and selection of highly skilled laborers with the key objective for local and international advancement in operations.
Employment, and Labor Laws and Regulations
The labor laws and regulations provide guidelines regarding the critical relationship between the employees and the organization’s management. One of the frameworks is the essence of the minimum wage. The law stipulates that a worker is entitled to at least the capped income from the government. It is a regulatory construct that shields the counterparts from exploitation by the employer (Bratton and Gold, 2017). Another legal construct is the significance of employment contracts that shield both the artisans and employers. In this case, the legal construct guidelines for the interaction between the dynamic entities. The labor laws and regulations assert fair competition in the business environment in a different spectrum due to the dynamic regulatory mainframe. An excellent example of a regulatory framework that focuses on the significance of fairness is setting the price ceiling of products and services. Price ceilings moderate the competition in the market, allowing small and medium enterprises to enter the market regardless of limited financial resources.
Labor laws and regulations play a profound role in the employment sector due to fostering equity in payment and promotion strategies. According to the legal framework, all employees deserve equal treatment despite age, race, and gender disparities. The entity’s ideal impact involves eradicating workers’ marginalization in a corporate while promoting teamwork settings (Bratton and Gold, 2017). Further, the legal framework enhances laborers’ relations by establishing trade unions. The trade unions’ primary role involves monitoring entities among their counterparts. Essentially, the restrictions positively affect human resource management due to the laid down relationship-building policies within a firm. Employment, labor laws, and regulations contribute to the green initiative through the scope of employee engagement. Promoting justice and equity in society is a sustainable initiative that renders peaceful co-existence and growth index.
The labor laws and regulations play a role in promoting fairness in business competition by ensuring the easy accessibility of financial resources from banking institutions. According to Bratton and Gold (2017), labor rules allow associations to seek financial assistance from banking institutions to facilitate operations. The charter protects the workers from retrenchment due to foreclosure from lack of financial resources and stiff competition in the marketplace. The legal framework articulates the engagement guideline to foster health and safety in a different spectrum (Crespi, 2018). A workplace that is a health risk to the employees illegally founded and is the employer’s responsibility to facilitate safety practices in the corporate. Labor laws and regulations provide a guideline that encompasses an organization’s cultural core values.
The Need for Professional Human Resource Practitioners
Organizational leadership is a multifaceted phenomenon involving integrating a company’s values and the employees’ interests. It is a framework that attributes to the management and guiding of individuals while completing tasks. An excellent example is the development of an organizational culture that stipulates the nature of interactions among employees. Research establishes that team-building is a structural entity that incorporates norms and cultural practices within an enterprise that promotes inclusivity (Agarwal et al., 2020). One of the inclusion strategies involves the participation of workers in the development of the company’s employee policy handbook. In a different spectrum, researchers indicate that the involvement of workers in the policy-making process advances the performance and effectiveness during the implementation due to the comprehension of critical initiatives. Organizational leadership is a vital pillar towards establishing an influential corporate culture and inclusive society.
Influence of Organizational Culture and Ethics
Leadership as an ethical practice entail enhancing the effective human resource management quotient for competence purposes. According to research, a charismatic leader focuses on the aspect of improving interrelation among distinctive characters (Syakur et al., 2020). Optimal communication among employees fosters the establishment of a sustainable organizational culture that governs the operational guidelines. Different firms utilize distinct aspects in promoting the competence of a company. One of the crucial baseline foundations is the establishment of critical outliers that enhance relationship-building among the counterparts. A captain’s roles in an institution include incorporating policies that constitute perspectives on managerial initiative (Sim, 2020). It is the responsibility of a manager to ensure sustainability based on the exchange of value hence the importance of utilizing transactional and transformative domains in the leadership spectrum.
Conclusion
Consequently, the primary responsibility of the managerial team involves articulating quotients that enhance the advancement of business operations. Integrating transactional and transformative approaches in leadership renders the executive accountability mainframe efficient. The cumulative aspect triggering the development of customs indicates an interdependent overview of human behavior and the operational outline regulations. Implementing competitive strategies enhancing coordination among workers fosters the emergence of a significant advantage against other institutions in the marketplace. The core approach to adjust the spectrum on production scale encompasses the integration of executive and laborers’ needs and intentions to boost customer satisfaction standards. Notably, it is the accountability of distinct stakeholders to ensure the sufficient exchange of value among counterparts in a corporate as a formative aspect of intensifying functional organizational culture.
Reference List
Agarwal, S., Ramadani, V., Gerguri-Rashiti, S., Agrawal, V., and Dixit, J. K. (2020). Inclusivity of entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurial attitude among young community: Evidence from India. Journal of Enterprising Communities: People and Places in the Global Economy.
Andersen, S. C., and Jakobsen, M. (2017). Policy positions of bureaucrats at the front lines: Are they susceptible to strategic communication?. Public Administration Review, 77(1), 57-66.
Anwar, G., and Abdullah, N. N. (2021). The impact of Human resource management practice on Organizational performance. International journal of Engineering, Business and Management (IJEBM), 5.
Asian, S., Pool, J. K., Nazarpour, A., and Tabaeeian, R. A. (2019). On the importance of service performance and customer satisfaction in third-party logistics selection: An application of Kano model. Benchmarking: An International Journal.
Boella, M. J. (2017). Human resource management in the hotel and catering industry. Taylor & Francis.
Boon, C., Den Hartog, D. N., and Lepak, D. P. (2019). A systematic review of human resource management systems and their measurement. Journal of management, 45(6), 2498-2537.
Boyer, S. W. (2018). Biblical leadership development: Principles for developing organizational leaders at every level. Springer.
Bratton, J., and Gold, J. (2017). Human resource management: theory and practice. Palgrave.
Crespi, G. (2018). The Public Service Loan Forgiveness Program: The Need for Better Employment Eligibility Regulations. Buff. L. Rev., 66, 819.
Dobusch, L. (2021). The inclusivity of inclusion approaches: A relational perspective on inclusion and exclusion in organizations. Gender, Work & Organization, 28(1), 379-396.
Jeffries, R. (Ed.). (2018). Diversity, equity, and inclusivity in contemporary higher education. IGI Global.
Madanat, H. G., and Khasawneh, A. S. (2018). Level of effectiveness of human resource management practices and its impact on employee’s satisfaction in the banking sector of Jordan. Journal of Organizational Culture, Communications, and Conflict, 22(1), 1-19.
Mehra, M. R. (2018). Human Resource Management and its importance for today’s organizations. Journal of HR, Organizational Behaviour & Entrepreneurship Development, 2(2), 15-20.
Michael, A. (2019). A handbook of human resource management practice. bookboon. com.
Mole, K., North, D., and Baldock, R. (2017). Which SMEs seek external support? Business characteristics, management behavior, and external influences in a contingency approach. Environment and Planning C: Politics and Space, 35(3), 476-499.
Morsiani, G., Bagnasco, A., and Sasso, L. (2017). How staff nurses perceive the impact of nurse managers’ leadership style in terms of job satisfaction: a mixed method study. Journal of Nursing Management, 25(2), 119-128.
Mousa, S. K., and Othman, M. (2020). The impact of green human resource management practices on sustainable performance in healthcare organisations: A conceptual framework. Journal of Cleaner Production, 243, 118595.
Mura, L., Ključnikov, A., Tvaronavičienė, M., and Androniceanu, A. (2017). Development trends in human resource management in small and medium enterprises in the Visegrad Group. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica, 14(7), 105-122.
Richards, G., Yeoh, W., Chong, A. Y. L., and Popovič, A. (2019). Business intelligence effectiveness and corporate performance management: an empirical analysis. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 59(2), 188-196.
Rigby, C. S., and Ryan, R. M. (2018). Self-determination theory in human resource development: New directions and practical considerations. Advances in Developing Human Resources, 20(2), 133-147.
Saeed, B. B., Afsar, B., Hafeez, S., Khan, I., Tahir, M., and Afridi, M. A. (2019). Promoting employee’s proenvironmental behavior through green human resource management practices. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 26(2), 424-438.
Sim, S. H. (2020). Workplace sexual harassment and labor inspection: Focused on labor inspectors’ experience of dealing with sexual harassment cases. Economy and Society, 128, 235–265. Web.
Stone, R. J., Cox, A., and Gavin, M. (2020). Human resource management. John Wiley & Sons.
Syakur, A., Susilo, T. A. B., Wike, W., and Ahmadi, R. (2020). Sustainability of communication, organizational culture, cooperation, trust and leadership style for lecturer commitments in higher education. Budapest International Research and Critics Institute-Journal (BIRCI-Journal), 3(2), 1325-1335.
Werner, J. M. (2021). Human resource development: talent development. Cengage Learning.
Wigert, B., and Harter, J. (2017). Re-engineering performance management. Gallup.com.