Hyatt Hotels Corporation, also known as Hyatt Hotels and Resorts, is an American-based multinational hospitality organization. Founded in 1957 in Chicago, IL, it is a well-recognized hospitality property chain with 1175 worldwide locations and over 127,000 employees across 68 countries on all continents. The company operates a wide range of properties, including hotels, resorts, residences, and vacation properties, segmented by type and level of luxury. The organization typically targets business class and higher-end segments as well as top luxury offerings (Hyatt, n.d.). Hyatt is a highly successful enterprise in hospitality known for consistent improvement of quality, adding of new services, and modernization of its innovative properties.
Macro-Environment Analysis (PESTEL)
Five Forces Analysis
- Threats of New Entrants – Weak force – The hospitality industry is tremendously difficult to navigate, commonly requires years operating at a loss, and is highly volatile to external influences making it not a strong business investment. To compete with top chains, it will require billions in capital to acquire infrastructure and land (Hoare, 2015). New entrants to industry are unlikely, major firms buy out smaller players who see any success in their segment.
- Threats of Substitute Products – Moderate force – To combat growing hospitality prices, substitute arrangements have been arising, such as staying at motels and hostels (levels where Hyatt and other luxury chains rarely operate). AirBnb was a rapidly emerging business with a sharing economy of living space. However, the Covid-19 pandemic has largely led to a significant drop in prices in upper-scale hotels while these other alternatives have experienced some reputation loss. Even so, there is usually no viable alternatives for business-level and above for overnight stays.
- Power of Suppliers – Weak force – Hospitality and hotels are not a commercial product that relies on specific components to produce, they are largely a service and an experience. While hotels require a lot of products, items, and outsourced services to function properly, they are all relatively generic, ranging from towels and soaps to food and working cable television with Wi-Fi. While large chains such as Hyatt build brand partnerships and reliable supply chains for every one of its locations, by all means, there is rarely any unique supply product that cannot easily be found somewhere else. Suppliers typically seek out large contracts with hotel chains as it guarantees a stable expense account, so the hospitality companies have the leverage (Kaplan, 2018). Since Hyatt operates around the globe, there may be regions where supplier force is higher due to lack of alternative suppliers, there is a need for high-quality products that only select suppliers carry (common in luxury chains), or the switching cost is high due to contractual obligations.
- Power of Buyers – Strong force – Hospitality relies strongly on consumers choosing to stay at its properties and remain loyal customers through the years, selecting the property chain in their travels around the world for business and leisure. Therefore, buyers have a strong force as their decision ultimately decides the profitability of the business. In most circumstances and global locations, buyers have the choice between several local and international hotel choices, so customer acquisition and further maintaining loyalty are absolutely crucial for hotels. Consumers in this industry have low switching costs, as prices are relatively similar across the specific segment for that client, and there are no long-term contractual obligations. The consumer wants the best offering of services and products for the lowest price when it comes to hospitality, forcing hotels to often bargains or incentives to remain competitive and maintain consumer loyalty (Britt, 2021).
- Competition in the Industry – Strong force – There are only a few select brands operating at this business and luxury level of hospitality properties. However, with virtually no differentiation among their products (each brand has its regular as well ultra-star luxury locations with largely the same amenities for each segment), the brands are forced to compete for consumers on the smallest differences such as service, quality, and potentially some unique amenity that others have not yet adopted (Campagnoli, 2020). Fixed costs are high within the industry, so companies adopt various strategies ranging from undercutting prices to building a strong reputation to diversify themselves in any way possible.
Internal Analysis
A range of internal factors can influence a corporation of the size of Hyatt Corp. Management is one critical element, as leadership and approach to management, both at corporate and local levels, can determine how the company progresses and operates. The company operates a hierarchical management structure with segmentation by both geographical region and type of product. The company follows modern corporate governance recommendations with a board of directors as well as committees on audit, talent and compensation, finance, and nomination, and corporate governance committee (Hyatt, 2021).
Culture is a significant internal factor. Hyatt attempts to follow corporate social responsibility and business ethics principles outlined in official codes and guidelines. According to official releases, Hyatt maintains an employee-centric culture to generate positive attitudes and care that can be passed down to the guests. Human resource management is another internal factor to consider, to ensure that the company maintains a healthy workforce, does not experience staff shortages that would impact the quality of service, and has a loyal development program within the company allowing for upward promotion mobility (Helvey, 2014).
Hyatt uses HRM strategically and offers both training and development programs for its employees wishing to grow within the company and building a strong culture within. Other internal factors may include resource management, location, product offerings, marketing, finances, and technological or economic change.
Financial Analysis
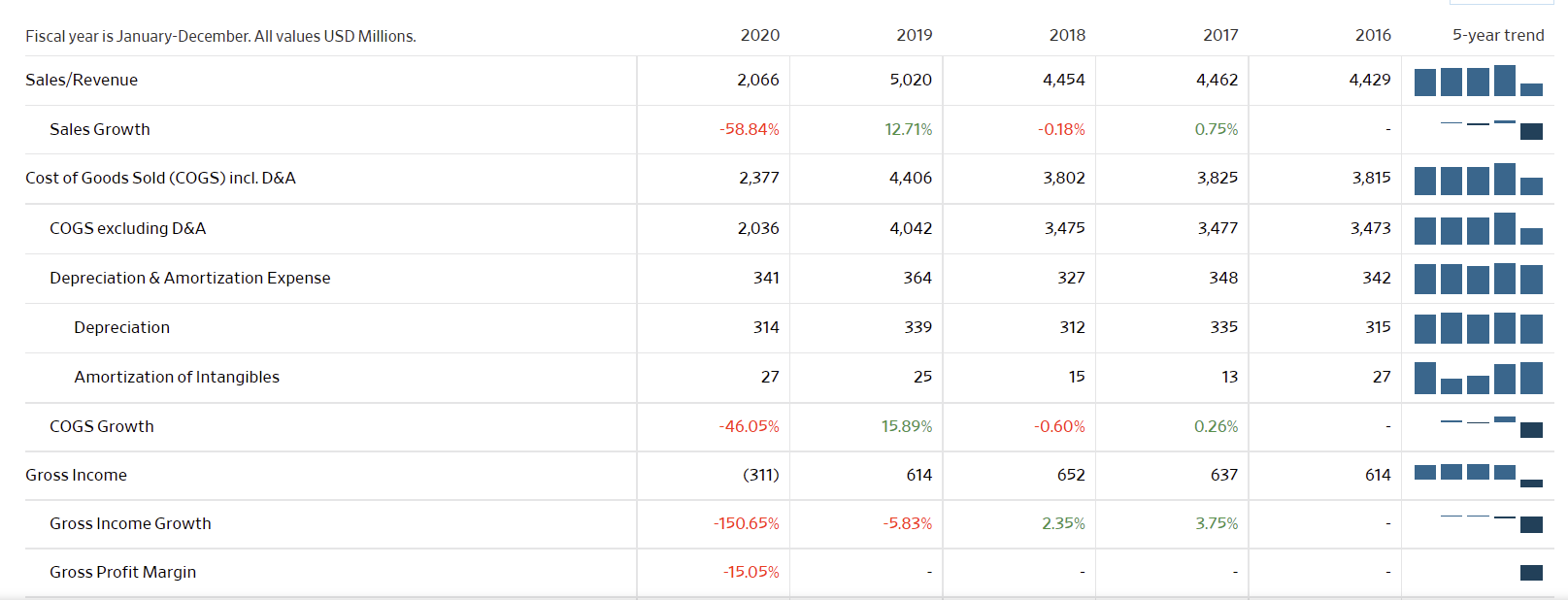
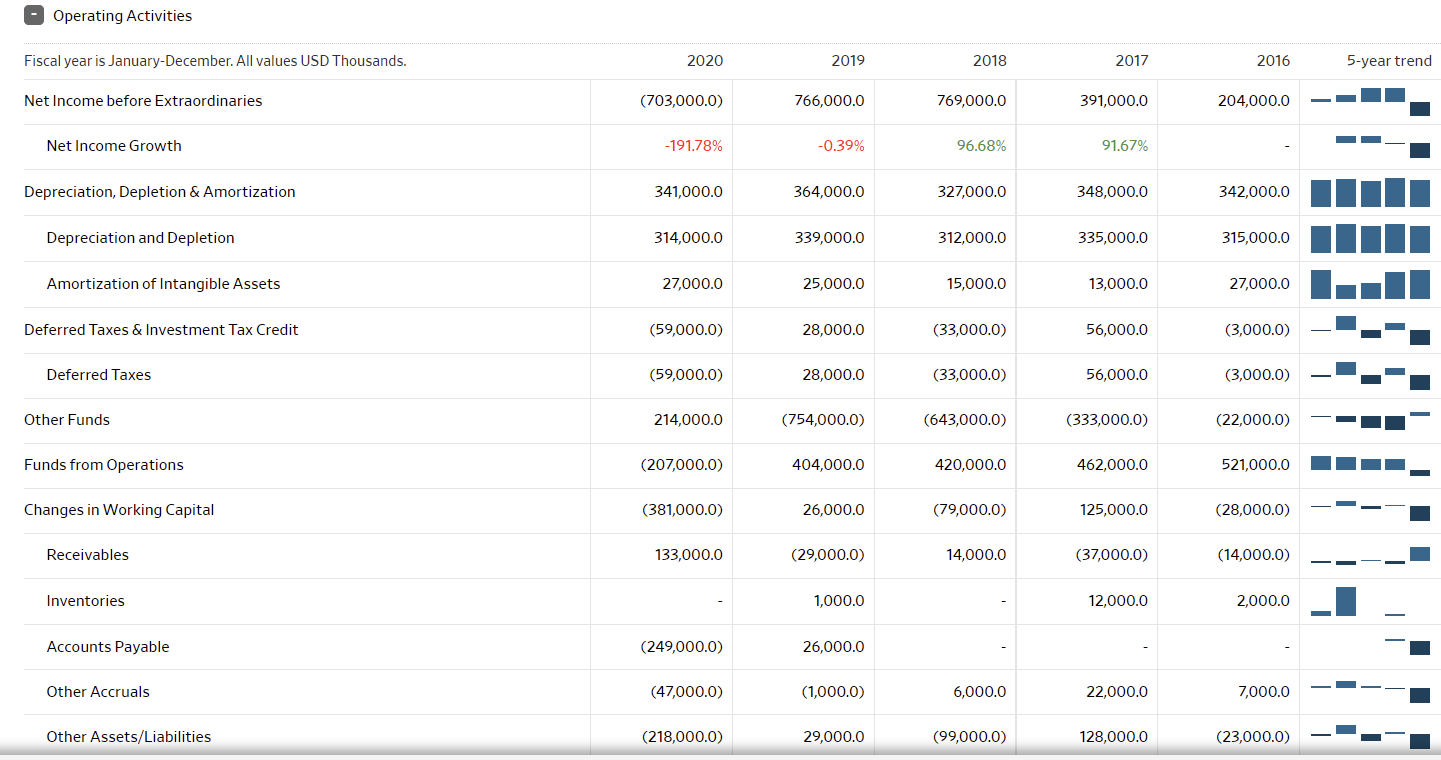
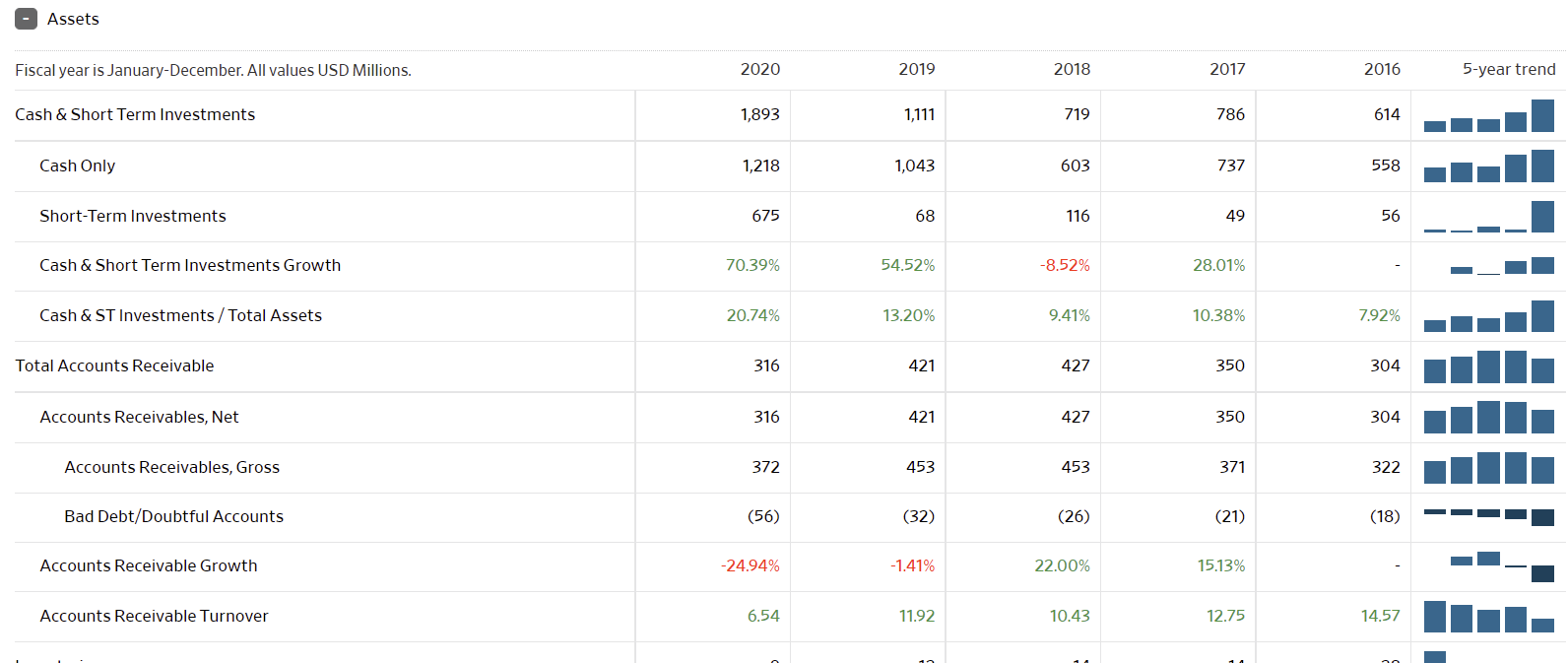
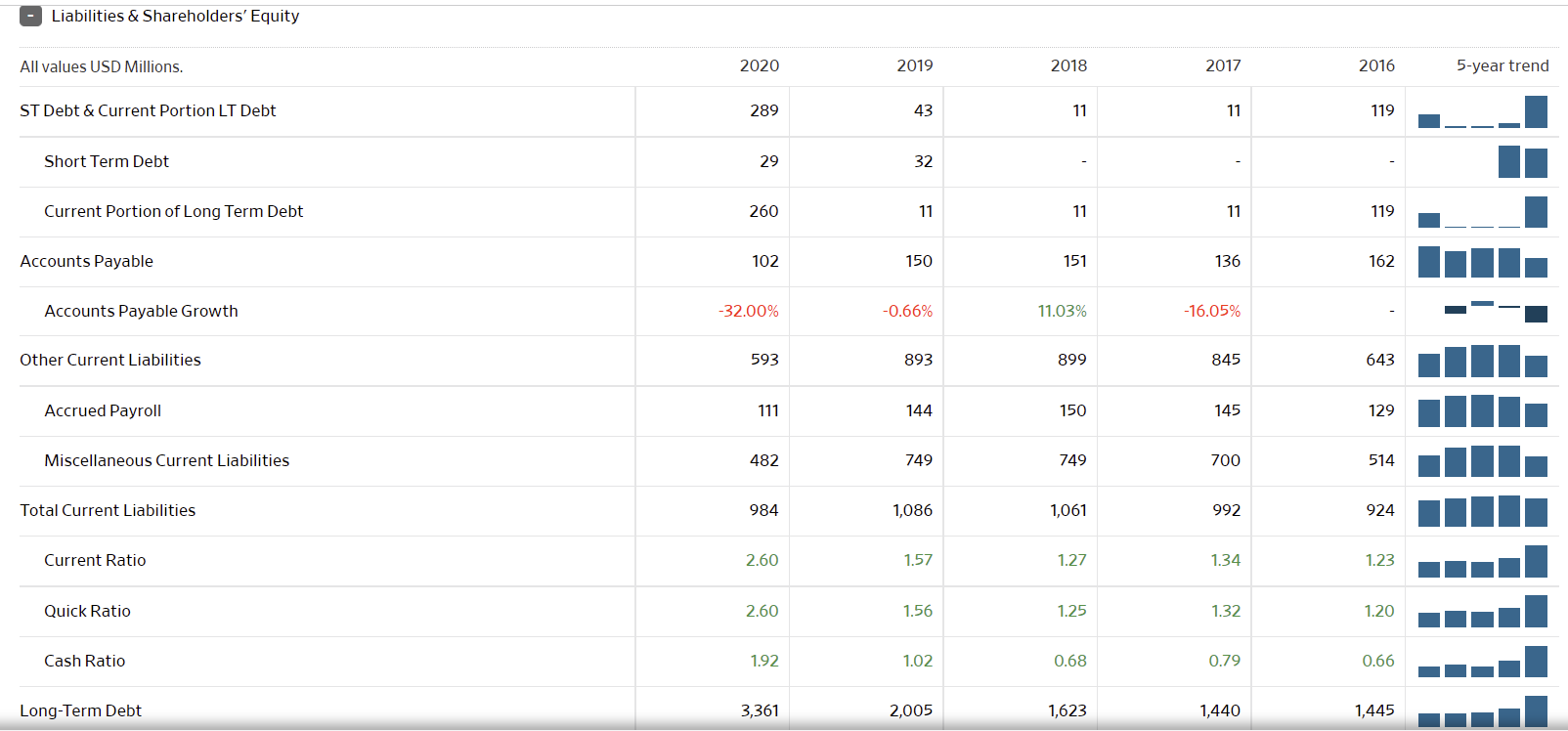
The graphs below represent the most fundamental data on Hyatt Corp. over the last three years. Notably, 2020 was one of the hardest economic years for firms that relied on travel and mass gatherings, as due to the Covid-19 pandemic, travel was restricted and lockdowns continue to persist regionally into 2021. Globally, hotel occupancy dropped by as much as 75% resulting in $125 billion losses in the industry and more than 3 million jobs lost, with an expected total loss of $910 billion in travel-related economic output in 2020 (Aharon et al., 2021). Virtually all lodging and hospitality companies saw significant net losses.
Looking at the Hyatt Corp. balance sheet, the company is at average financial health, it is not healthy, but it is not failing. First, the company has a relatively large cash pile, larger than all years prior. It is also seeing an increased cash net flow this year, up from 2020. The company does carry debt liabilities worth more than its current cash and revenue. At the same time, its stock value has continued to grow since 2020, making the company value at a $9.31 billion market cap, allowing it to easily raise funds to cover debts and liabilities. The company’s current, quick, and cash ratios to liabilities are exemplary, demonstrating signs of a decently healthy company. As travel begins to pick up on larger scales internationally, with many countries opening their borders, Hyatt should see its revenues increase exponentially, potentially to a greater extent than before the pandemic.
SWOT Analysis
TOWS Analysis
References
Aharon, D. Y., Jacobi, A., Cohen, E., Tzur, J., & Qadan, M. (2021). COVID-19, government measures and hospitality industry performance. PLOS ONE, 16(8), e0255819. Web.
Brit, P. (2021). What does customer experience in the hotel industry look like today? CMS Wire. Web.
Campagnoli, R. (2020). Competitive Agility: How the hospitality industry can win amidst new challenges. Entrepreneur. Web.
Helvey, K.M. (2014). Recruiting from within: How Hyatt hotels engineers talent mobility. Web.
Hoare, D.J. (2015). Hospitality industry characterized by high fixed costs. Web.
Hyatt. (n.d.). About Hyatt. Web.
Hyatt. (2021). Corporate governance highlights. Web.
Kaplan, D. (2018). Five tips for managing hotel supplier relationships. Web.
WSJ Markets. (2021). Hyatt Hotels Corp. Web.