The dynamics of investment in the country’s economy is determined by the influence of a number of factors, among which one of the main is the change in the market interest rate. The Central Bank, acting on interest rates using monetary instruments, has the ability to stimulate or restrain investment activity. The increase in investment is reflected in the volume of GDP produced, stimulating economic growth. In the face of a slowdown in the growth rate characteristic of the entire world community, increasing the dynamics of private investment is a priority. Namely, the use of the possibilities of monetary policy plays an important role in overcoming the consequences of the economic crisis. First, the use of monetary instruments, in contrast to fiscal instruments, makes it possible to obtain results through a relatively short time lag. Secondly, there is no negative effect of crowding out the private sector. However, the sensitivity of investment to the interest rate depends on the state of the economic environment, which is qualitatively determined by the characteristics of the economic mechanism. Thus, in addition to the money market situation, a number of factors affect the effectiveness of monetary regulation.
The Central Bank has an impact on the economy through the regulation of interest rates, leading to changes in the costs of using financial resources, which is reflected in the volume of investment. In addition, changes in interest rates affect consumption when it comes to non-investing households. In turn, this provokes a change in the value of GDP.
With the expansion of the money supply by the Central Bank, first of all, the volume of excess reserves of commercial banks increases. With the growth of liquid assets, commercial banks are expanding the supply of credit resources. This connection is especially important in the functioning of the bank-oriented investment mechanism in the economic system. In such circumstances, the availability of bank credit for various economic entities that do not have the ability or do not want to use the resources of financial markets, critically affects the investment activity of the business. Pursuing an expansionary monetary policy implies an increase in the monetary base, which positively affects the volume of bank deposits and lending, and also allows economic entities to make more investments.
The sensitivity of the investment volume to the interest rate can be estimated using the elasticity coefficient, which is the percentage of the change in the dependent variable to the change in the original. The coefficient values exceeding 1 by module theoretically indicate the presence of a pronounced sensitivity of changes between the studied variables. However, excessively high values suggest a strong fluctuation of the dependent variable with a slight change in the initial parameter, which means in this case their weak relationship. The values of the coefficients from 0 to 1 in absolute value represent evidence that the dependent variable has changed to a lesser extent, which illustrates its weak sensitivity to fluctuations in the initial parameter.
The data on the interest rate on loans in the USA are presented in Fig. 1 below.
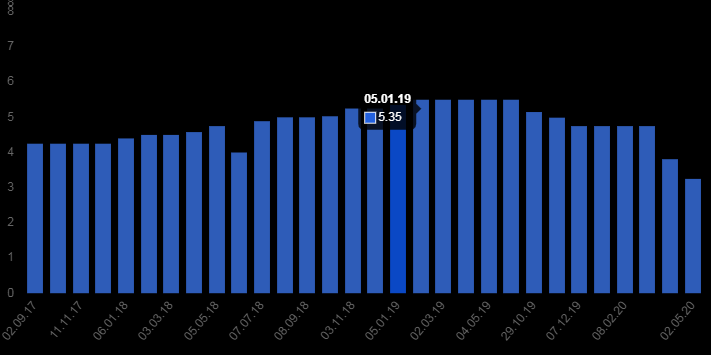
The interest rate on a loan in the United States fell to 3.25% in April 2020. The maximum rate reached 20.5%, and the minimum 2%.
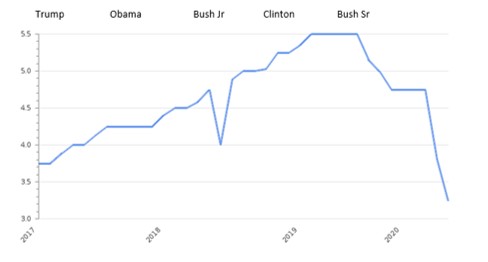
The history of the interest rate for US presidents is presented in Figure 2.
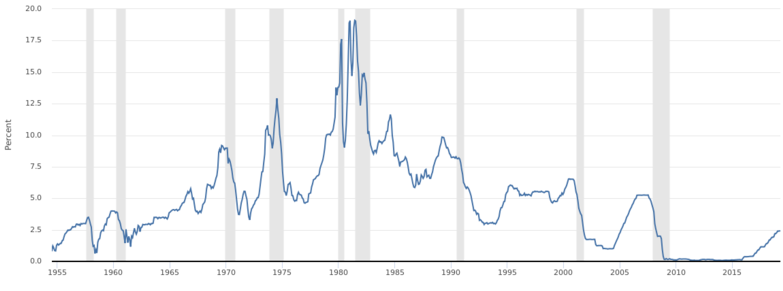
Earlier dynamics of effective rate is presented on Figure 3.
While investors expect a 9% increase in earnings per share for the S&P 500 over the next 12 months, given a more conservative view of economic growth prospects, it can be assumed that the neutral dynamics of EPS, which has been observed throughout 2019, can remain this year.
The current level of risk premium for the US stock market historically corresponds to weak growth (within 3-4%) in the near three-year horizon (on a shorter time horizon, the level of risk premium does not have a big impact on the market).
There have been examples in history when a decrease in interest rates by the Fed while maintaining a positive rate of economic growth led to the emergence of conditions for creating overheating in the markets. An increase in market volatility is expected. For the post-crisis period, corrections of the S&P 500 index of at least 7% are found almost every year. Since 1998, the Fed lowered the rate between scheduled meetings six times and each time after that again reduced it at the next meeting. Once again, when the situation in the economy came to a standstill, the country resorted to lowering the nominal interest rate, which in turn reduced the real rate, while taking into account the constant target inflation rate. Lower rates increased the value of assets, and they, in turn, stimulated consumption, which led to a decrease in the level of savings and stimulated the flow of investments.
In the baseline scenario, one can expect a slowdown in US GDP growth to 1% y/y (from the expected 2.3% in 2019). Acceleration of inflation at the beginning of 2020 is unlikely to be sustainable ‑it is expected that the CPI will drop by the middle of the year, but will return to 2% again by the end of next year. In the eurozone, a slowdown in external demand and a decrease in stocks (due to weak industrial production) have had a restraining effect on GDP growth since mid-2018. As a result, in 2019 a slowdown was expected in the eurozone economy to 1.2% y/y. Outsider was Germany, the most dependent on external demand; overall, in 2020, the eurozone is expected to grow at a level of 0.8-1% y/y.
The details of the interim trade agreement, announced but not concluded, on December 13, 2019, between the United States and China under the “Phase 1” are rather vague. So, it is assumed that the United States will reduce tariffs per 100 billion dollars of Chinese imports from 15% to 7.5%. At the same time, 25% of tariffs on $250 billion of Chinese imports will remain in force. In response, China, among other things, must ensure the purchase of agricultural products from the United States at $40 billion per year.
The global spread of coronavirus forced the US Federal Reserve System (FRS) to lower the interest rate of federal funding on March 3 immediately by 0.5 percentage points to 1-1.25%. This is the first case after the 2008 crisis, when the Fed did not wait for the next meeting of its committee on open market operations. However, the rate cut in the US may not be the last this year.
The Fed had three reasons to urgently soften monetary policy. The central bank hoped to instill confidence in society, prevent deterioration in lending conditions and mitigate the negative effects of the spread of the virus on the US economy. However, in the coming weeks, the situation may worsen. Moreover, the number of sick and dead is also growing in the United States. The probability of interest rate reduction to zero is quite high.
U.S. Treasury bonds also point to this possibility. These securities are considered a safe haven in the market, where investors can go in difficult times. The yield on 10-year treasury bonds during the last stock market crash fell to a historic low, dropping below 1.3–1.4%, which served as support three times in 2012–2019. If in November 2018 it exceeded 3%, and at the beginning of 2020 it was almost 1.9%, then in the last two weeks it began to fall.
At the same time, the Fed did not warn the central banks of other G-7 countries about its plans to urgently lower interest rates on March 3 and did not urge them to do the same. Such behavior is unusual, because before, in hard times for the global economy, leading countries coordinated their actions. For example, during the global financial crisis in October 2008, the Fed, the ECB, the Bank of England and the central banks of Sweden and Switzerland lowered interest rates at the same time. They were joined by the People’s Bank of China, although it did not participate in their discussion.
This time, the Bank of Canada was the first to respond to the Fed’s decision, lowering its interest rate from 1.75 to 1.25% the next day. However, the ECB, the Bank of England and the Bank of Japan have yet to make a choice. The ECB deposit rate is already minus 0.5%, so the eurozone central bank will probably have to react in a different way. The situation in the interest-bearing futures market shows that many investors expect the Fed rate to drop to 0.25-0.5% by the end of April. Market participants expect US interest rates to remain low for the next two to three years.
Global Central Bank rates are presented on Fig.4-5.
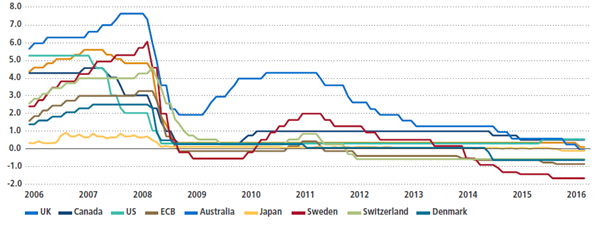
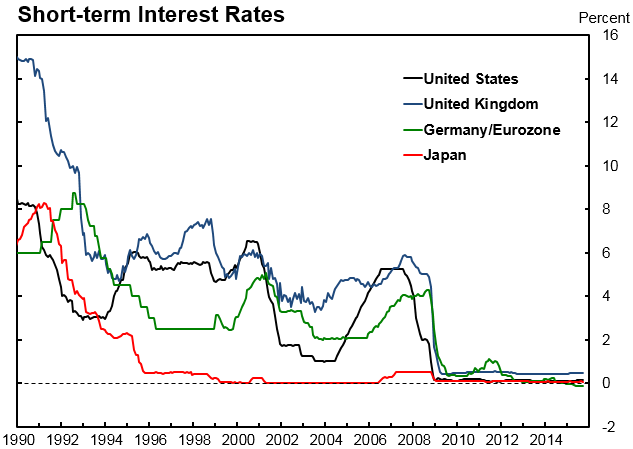
Negative interest rate policy (NIRP), as seen from an analysis of interest rate policy in 50 countries presented by Bloomberg, is now becoming part of the generally accepted macroeconomics, based of statistical data such as FDI,GDP growth, average FDI, GDP per capita, retirement age, education level, regression. Although the NIRP looks innovative, its analytical foundation is based on pre-Keynesian macroeconomic considerations. However, economists have forgotten Keynes’s warning that interest rates cannot solve the issue of demand shortages. Savings and investments may not respond to lower interest rates, therefore, no matter how low the interest rate, AD does not increase because investments do not increase and savings do not fall. In fact, there is no interest rate that could provide full extent of employment.
There is a very simple, intuitive reason why negative interest rates do not affect investments. When the firm’s return on investment reaches zero, it will prefer to use any additional financing to acquire non-produced assets whose returns are still positive. Negative interest rates will lead to a boom in mergers and acquisitions financed by debt, which will raise prices for existing assets but not increase new investments.
Bibliography
Mahmoud, A. Finance and Economics Reimagined: A Very Simple Guide to Understanding Interest Rate, Inflation Rate, Money Supply and Much More, Amazon.com Services, 2016.
Markets. Rates & Bonds. Bloomberg. Web.