Islamic banking implies a way of banking functioning that is characterized by consistency and does not contradict Muslim principles in relation to monetary settlement operations. The main rule of the Islamic religion is the rejection of future transactions and the prohibition of charging a loan interest by a banking institution.
Shiekh Mohammed bin Rashid (Dubai Ruler) stated that “No wonder that the adoption of the Islamic economic system constitutes a key factor for economic growth, creation of jobs and new initiatives in cooperation among local, Islamic and international institutions.” (“Islamic economic system,” 2016, para. 3).
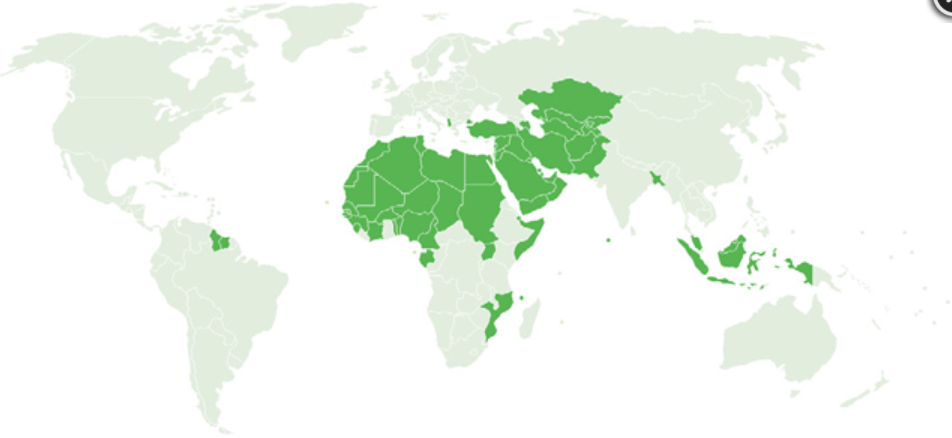
Map of the world showing the member states of the organization of the Islamic Conference (Morrissey, 2021)
Interesting and Important Fact
United Arab Emirates has a total of 4,084,613 IP addresses assigned.
Today, the United Arab Emirates is one of the richest and fastest-growing countries in the world. In 2011, the GDP amounted to 48.5 thousand dollars, and the inflation rate was 2.5%. In total, 53.8 thousand dollar millionaires live in the country, of which 778 have a fortune of more than $ 30 million. Imports to the UAE in 2019 amounted to $188 billion, and exports amounted to almost $185 billion.
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (GCC) is presented as a central regional international organization. The Council thrives on exports and financial potential free and strong position of the member countries in relations with the outside world. There are no supranational structures within the framework of the GCC. The figures pay special attention to Africa as an opportunity to create an effective Muslim market there. This is an effective way to raise investment in the country and improve its well-being.
To improve economic performance, the United Arab Emirates needs to pay more attention to the construction and tourism sectors in order not to be dependent on the fuel industry.
Islamic banks’ main concept is to work according to their commitment to the principle of Islamic Shariah.
An Islamic bank makes a profit in several ways.
- Resale of real estate in installments.
- Participation in the capital of the funded project for a certain share of the profit.
- Murabaha or purchase and sale.
- A special type of Sukuk loan.
- Securities, in the acquisition of which the bank acts more as a shareholder.
- Zakat or wealth tax.
Dynamics of Islamic Banks in the Global Economy
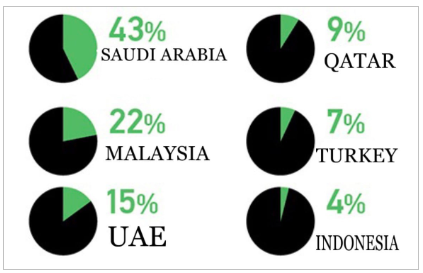
The financial system of the United Arab Emirates, especially Islamic Banking, has a large number of advantages. Firstly, it is the low cost of servicing a bank account. Secondly, this type of bank has leading growth rates. Moreover, among the strengths of the financial system are transparency and clarity in transactions and, minimal risks for the depositor, good profit from deposits.
United Arab Emirates has about a total of 4,084,613 IPs (‘United Arab Emirates IP address ranges”, n.d., para.1). Almost 55% of the UAE population are the customers of at least one of the Islamic banking products (Osmanovica & Stojanovic, 2020) Islamic banking services that bring profit are divided into:
- Mudaraba and musharaka;
- Ijara, salam, istisna, istijrar, wadia;
- Vacala.
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (GCC) is presented as a central regional international organization. The Council thrives on exports and financial potential free and strong position of the member countries in relations with the outside world. There are no supranational structures within the framework of the GCC. The figures pay special attention to Africa as an opportunity to create an effective Muslim market there. This is an effective way to raise investment in the country and improve its well-being.
Regulatory Context
Since the Islamic banking system is based on Sharia, its main legal source is the Koran and the Sunnah of the Prophet. The alternative to Islamic banking is the conventional banking system based on interest charges (Azmat et al., 2020). Industry Issue Resolution program and Science, Technology and Innovation strategies are effective ways to improve the work of Islamic Banking.
Such a solution can be a strategy of active problem recognition. It implies the introduction and improvement of systems for detecting weaknesses in the business, which are the reason for the delay in analytical development.
One of the main problems of the Islamic banking system is the absence of a legal sanction for non-repayment by a bank customer of a loan. The Islamic economic model of banking is often considered to be morally oriented. This is due to the fact that it pays great attention to the assessment of the activities of economic employees in accordance with the moral and ethical guidelines of Islam.
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are those specialists who have a special interest in the company’s activities and can have an impact on the business. They are an integral part of the functioning of the Islamic Bank. They provide the capital needed to run a business and, in return, receive a return on investment. “Stakeholders’ contributions consisted of Investors, Depositors, Management, and shari’ah supervisory board” (Vegirawati et al., 2018, p. 60). The shareholders of an Islamic financial institution appoint a board of directors for corporate governance.
Nowadays, the Islamic banking cluster is at the maturing stage (Nurdin & Yusuf, 2020). At this stage of development, many necessary changes in the strategy of Islamic banks can be transferred less traumatic. The focus to improve its work should be on filling gaps not only in its work but also in the work of more traditional banking systems. The strategy includes putting a significant level of investment into product research and design. Through this strategy, the organization has an increased chance of survival from the tough competition worldwide. The fact that Islamic Banking is gaining more and more popularity is that in UAE, it gained almost 11% of new customers compared to 6% accumulated by unconventional banking (“Demand for Islamic banking,” 2019).
For the cluster to flourish, it is necessary to attract more professionals to increase the heterogeneity of knowledge about the bank’s field of activity.
In terms of aspects such as education, technology, certification, services, and production, traditional and Islamic banking systems have a lot in common. If an Islamic bank focuses on modernization and innovation, an English bank, for example, adheres to traditions. The main difference is that financial procedures are performed differently in the Islamic model. Both systems are engaged in attracting financial resources from individuals and institutions and direct them to commercial firms in need of external financing. In Islamic banks and deposits, all loans are interest-free, unlike traditional England ones. The Islamic banking system also does not have the opportunity to ensure its investments and incurs losses on projects in which they were invested.
Main Problems Limiting the Development
Main problems limiting the development:
- competitive disadvantages,
- the undeveloped infrastructure of the financial services market, an imperfect system of legal banking supervision and regulation (Alam et al., 2020).
Solutions International Islamic Liquidity Management Corporation strengthen its competitiveness in the market create a balanced system.
Recommendations
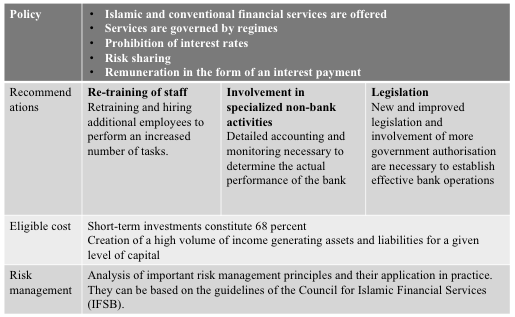
Mission
Thus, it is important to note that the Islamic Bank is a fairly young organization, but it has already been able to achieve significant results. Since I consider this phenomenon very promising, it needs to be encouraged and developed. Islamic banking serves the real economy, and its main purpose is to perform the function of making payments and working with a considerable amount of money (Suhartanto et al., 2020). From my point of view, the strength of this banking system is voluntary donation. The main mission is the development of the Islamic banking system and the consolidation of Muslim postulates both within its framework and behind its pillars.
References
Alam, M. K., Mustafa, H., Uddin, M. S., Islam, M. J., Mohua, M. J., & Hassan, M. F. (2020). Problems of shariah governance framework and different bodies: An empirical investigation of Islamic Banks in Bangladesh. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business, 7(3), 265-276.
Azmat, S., Azad, A. S., Bhatti, M. I., & Ghaffar, H. (2020). Islamic banking, costly religiosity, and competition. Journal of Financial Research, 43(2), 263-303.
Bidabad, B., & Allahyarifard, M. (2019). Assets and liabilities management in Islamic banking. International Journal of Islamic Banking and Finance Research, 3(2), 32-43.
Demand for Islamic banking to drive profitability in UAE. (2019). Gulf News.
[Dubai Islamic Bank]. (2017). Web.
Islamic economic system is the basis of economic growth: HH Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid. (n.d.).The Free Library.
Khmous, D. F., & Besim, M. (2020). Impact of Islamic banking share on financial inclusion: evidence from MENA. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 13(4), 655-673.
Khomsatun, S., Rossieta, H., Fitriany, F., & Nasution, M. E. (2021). Sharia disclosure, Sharia supervisory board and the moderating effect of regulatory framework: The impact on soundness of Islamic banking. Recent Developments in Asian Economics International Symposia in Economic Theory and Econometrics, 28, 291-321.
Kombizz. (2011). Bank Islam [Photograph]. Flickr.
Nurdin, N., & Yusuf, K. (2020). Knowledge management lifecycle in Islamic bank: The case of Syariah banks in Indonesia. International Journal of Knowledge Management Studies, 11(1), 59-80.
Osmanovica, N., Kb, P., & Stojanovic, I. (2020). Impacts of Islamic banking system on economic growth of UAE. Journal of Talent Development and Excellence, 12(3s), 1555-1566.
Sharjah Islamic Bank. (n.d).
Suhartanto, D., Gan, C., Sarah, I. S., & Setiawan, S. (2019). Loyalty towards Islamic banking: service quality, emotional or religious driven?. Journal of Islamic Marketing. 11(1), 66-80.
United Arab Emirates IP address ranges. (n.d). IP2location.
Vegirawati, T., Susetyo, D., Meutia, I., & Fuadah, L. (2018). Do contributions of Islamic banks stakeholders influence profit and loss sharing financing? : Empirical evidence in Indonesia, International Journal of Islamic Economics and Finance Studies, 60-76.
Zeitoom, N. (n.d.). Reuters [Photograph]. What’s Going on Qatar.
Morrissey, R, (2021). Effects of Islamic banking on financial market outcomes in GCC countries and Iran. Cornell International Affairs Review, 6(1).