Introduction
The International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) is a well-known company that operates in the industry of computer and information technologies (IT). Each company represented in this industry, as well as other ones, should have a developed IT infrastructure in order to successfully perform all its activities and organize working processes. In this context, it is important to focus on specific IT building blocks that are adopted at IBM to address its needs.
These five specific building blocks include hardware, software, telecommunications, networking, and data resources that are extremely vital to support the company’s operations (Brown, DeHayes, Slater, Martin, & Perkins, 2011). The purpose of this paper is to assess these IT building blocks with a focus on their visual representation in a high-level diagram and to provide the analysis of the use of these blocks in IBM’s activities.
Assessment of the IT building Blocks in IBM and a Diagram
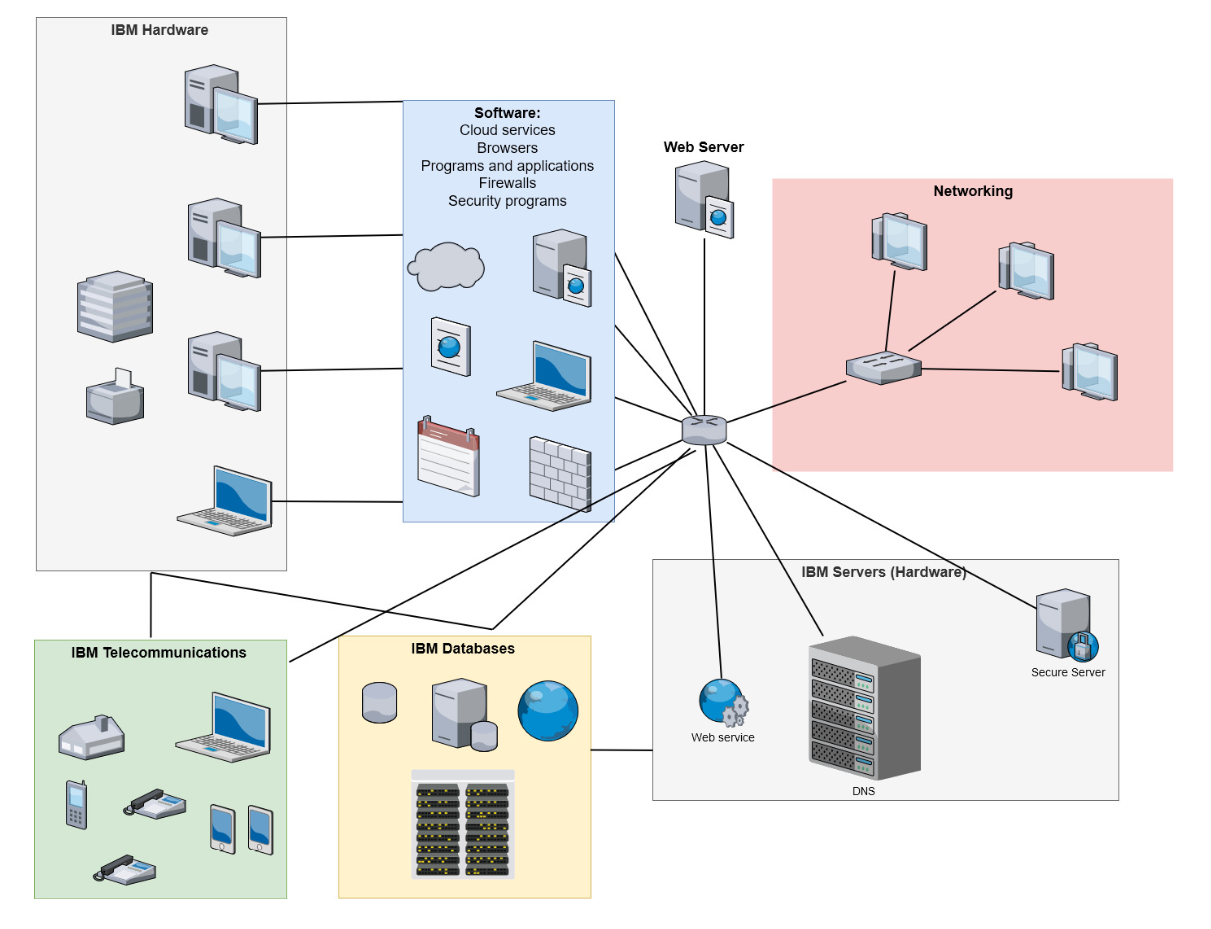
Figure 1 represents the key IT building blocks at IBM that need to be discussed in detail. The hardware block includes the company’s servers, employees’ computers, routers, printers, and other equipment that is used in employees’ daily practice. In this block, much attention is paid to the work of servers and switches that guarantee that all computers can easily share information in the office (“IT networks,” n.d.).
The software block of the company includes web browsers, programs, used programming languages (JavaScript, PHP, and others) and applications that are used in different departments and units of IBM (Den Hartigh, Ortt, Van de Kaa, & Stolwijk, 2016). Thus, software is important for operations of the Research and Development department, the Marketing department, and the Accounting department among others. Specialists in these units use different resources and tools in order to perform their everyday duties. All this software allows the realization of tasks when using computers and the network.
The third block to discuss is networking that is realized at IBM with a focus on uniting all hardware in the office according to the principle of the star topology and the hybrid topology depending on the needs of the department. Thus, all users can easily share data while working on the same and different tasks (Gao, Liu, & Ma, 2019). The fourth building block to discuss is telecommunications.
In IBM, telecommunications are represented by the connected phones, and access to the wireless phone connection is also provided. The final building block to pay attention to is data resources. IBM uses databases for storing their data that are located on external servers in order to guarantee data security and protection. Data centers and database servers work to store all the information during the set period of time.
Analysis of Using the Building Blocks
When analyzing how the major building blocks are used in IBM, it is necessary to explain the role of each block for business activities and evaluate its relevance for the company. The quality of hardware guarantees the storage of data and the operational capacity in the company. At IBM, current IT operations require the highest capacity of servers and computers to process the volumes of data used by employees for developing new products and supporting clients daily (Den Hartigh et al., 2016). The quality of software is important to ensure the speed of performed operations and outcomes. It is important for IBM to use the latest software technologies to provide high-quality services to clients, but the company experienced some difficulties when shifting its operations to cloud servers.
Networking guarantees the exchange of data between the users of hardware, and for IBM, it is critical to provide both cable-based and wireless connection. The selected network topologies (star and hybrid) allow for a high speed of communication and expansion of the network. Telecommunications are important to ensure the sharing of corporate data, and IBM uses the latest technologies to support this system (Brown et al., 2011). Finally, much attention is paid to supporting databases as the main data resources in the company. The combination of both internal and external database servers is effective to guarantee that all information will be efficiently stored and then retrieved when necessary.
In spite of the fact that the currently used IT building blocks are effective to address the company’s needs, IBM requires shifting to more advanced technologies. Thus, the company’s Research and Development department needs more innovative computers and other equipment, as well as advanced software, to support their inventions (Gao et al., 2019). Furthermore, IBM can also reconsider its approach to using cloud services for storing and sharing data in order to address the current trends in the industry.
Conclusion
The analysis of IT building blocks used at IBM indicates that the company effectively applies all the components in order to guarantee that its services and operations are efficient. The currently followed approach can be regarded as effective to increase employees’ productivity. However, it is also possible to state that some improvements can be required in order to ensure that IBM uses the latest technologies that are innovative and efficient enough to support its operations.
References
Brown, C. V., DeHayes, D. W., Slater, J., Martin, W. E., & Perkins, W. C. (2011). Managing information technology (7th ed.). New York, NY: Pearson.
Den Hartigh, E., Ortt, J. R., Van de Kaa, G., & Stolwijk, C. C. (2016). Platform control during battles for market dominance: The case of Apple versus IBM in the early personal computer industry. Technovation, 48, 4-12.
Gao, Y., Liu, X., & Ma, X. (2019). How do firms meet the challenge of technological change by redesigning innovation ecosystem? A case study of IBM. International Journal of Technology Management, 80(3-4), 241-265.
IT networks. (n.d.). Web.