Market segment, Target Market, Position
The major segmentation variables are –
- Geographic: Geographic segmentation indicates the division of the market into geographical units, for instance, countries, cities, suburban, urban, rural, or regions (Kotler & Keller, 2008). However, this approach is helpful when there are clear cultural differences in case of tastes, consumption, and preferences; for example, the US customers prefer light drinks but the German people like stronger drinks and Australians prefer colder more carbonated beer than the USA customers;
- Demographic: The researchers segment the market into groups in accordance with variables like age, life cycle, life stage, gender, income, generation, profession, education, ethnicity, nationality, religion, social class, etc.
- Psychographic: The VALS Segmentation System
- Behavioural: Occasions, benefits, user status, usage rate, buyer-readiness, loyalty status, and attitude are the main factors in this segment.
Target Market
Kotler and Keller (2008) suggested three issues to select a target market, such as –
- recognize and profile different groups of customers
- choose one or more market segments
- Establish and communicate the main distinctive advantages of the company’s market offering
Position
The position is significant because customers differentiated products and services from one another by means of this factor, which influences the segmented customers to purchase relevant products. However, these concepts encompass two basic issues, such as physical attributes with the functionality of the products and the way in which a brand is communicated in the market place, for example, General Motors and Toyota have different communication system with different products.
Customer Loyalty and brand loyalty
According to the view of Kotler & Keller (2008), a five percent increase of customer loyalty rate can lead to boost customer profitability by twenty-five percent to ninety percent, therefore, multinationals like BMW, Coca-cola, Easyjet, Tyco International, Australian security service provider ADT, etc take a number of measures to develop the customer relationship management program to build brand equity and customer loyalty.
Key Issues regarding Customer Loyalty
Most business organizations strive to satisfy the customer to increase loyal customer base and there are mainly five influential factors, such as –
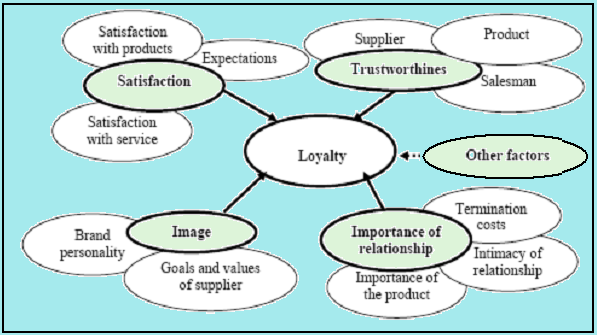
- Image: the most complex issue is the image of the brand or suppliers, which influences the firms in two ways, for instance, buyers use branded products due to the general trend them is to demonstrate their personal quality or to show them the member of the upper class. As a result, customers would like to purchase branded cars and cloths;
- Trustworthiness: Trustworthiness of the partner play a significant role to create loyalty since it is one standard to assess the value of the partner;
- Significance of the relationship: Kotler and Keller pointed out that loyalty means a desire to keep a strong relationship as it is important to reduce high risks of transaction and termination of contracts for disappointment;
- Customer Satisfaction: All multinational companies concentrated more on customer satisfaction as it is one of the most significant issues to create customer loyalty. However, BMW and Toyota try to satisfy their customers by developing new products, giving after-sales services, building a strong relationship with the customers, meeting the demand of the customers, and so on;
- Other: However, customer loyalty and brand loyalty are also interrelated with other factors such as marketing mix.
Market Research – Six Steps
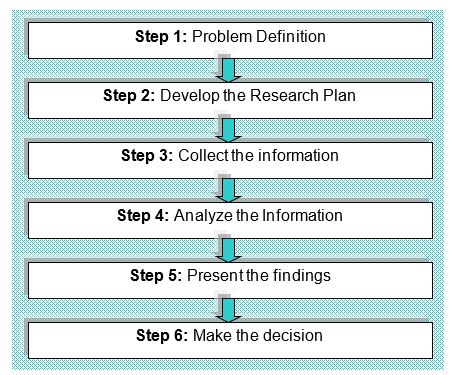
- Step 1- Definition of the problem: According to the view of Kotler and Keller (2008), it is important to define the research problem with a short overview to gather meaningful information, which will assist the researcher to take effective decision
- Step 2- Develop the Research Plan: Kotler and Keller (2008) stated that the second stage is the most significant part as the result would depend on this stage and they provided information about two data sour with many research approaches like observational research, focus group, survey research, qualitative and quantitative research. However, they prescribed three major data collecting methods such as telephone interviews, personal interviews and online interview. However, they further addressed that personal or face-to-face interview is the most versatile method though it is most expensive method but this method has option to ask extra questions to the respondents to observe more issues. On the other hand, telephone interviewing is the best system to gather data more instantaneously and it is effective method for Australian researchers because the response rate is usually higher than in the case of mailed questionnaires;
- Step 3- Collect the information: Data collection is the most expensive process particularly it is really tough to gather information from international market; therefore, many research organizations help to gather relevant information from global market such as Synovate Inc., has office in the 46 countries to conduct research on different cultural background.
- Step 4- Analyze the Information: Kotler and Keller (2008) pointed out that the researcher should tabulate the data to analyze using statistical techniques and decision models. The researchers also have the opportunity to test different hypotheses and theories to identify possible solutions;
- Step 5- Present the findings: The researchers present findings relevant to the main marketing decision facing management, for instance, Delta Airlines created a video of its primary business customers and showed it to flight attendants and airport personnel;
- Step 6- Make the decision: Top level management of the company should take decision considering the findings of the market research.
New Product Development
The fact that some variables like consumer preferences, technologies, rivalry patterns, and economic indicators are always altering in the market, businesses needs to construct a constant stream of new products or services in its pipeline for future diversification. New products can be obtained by a business by two methods; firstly, by mergers and takeovers, and secondly, by new product development projects run by the firm’s own internal R&D teams.
The first method was used by global giant Cadbury – as it observed significant growth rate in the organic chocolate market, rather than attempting to develop a chocolate by itself, it went on to takeover a relatively weaker participant in the market that possessed a distinctive capability to produce high quality organic chocolates – Green and Black. Conversely, second method has used by Apple in 2007 with the launch of the iPhone – groundbreaking product that resulted in a massive success for the company.
However, it is important to note that in order to achieve such huge success in new product developments, it is not just sufficient to come up with great plans about the highly innovative products, but the most essential aspect lies behind the fact that the research and development team should have highly expertise and knowledge. Recent researches show the fact that a high number of new products fails within the first few weeks of introduction owing to the fact that the research and development teams are not so specialized.
Another key concern behind failed launches is that adequate marketing researches have not carried out during the development period. Marketing researches, both primary and secondary, are keys to the success of new products; in addition, the field surveys should have carried out both in terms of quantitative and qualitative researches for potential outcomes. The firms also need to have group discussions between the surveyors and R&D teams, because joint efforts from every part of the company are essential.
Public relations
Public relation is the most prevalent discipline of an organisation that used as powerful mass promotional tools to structure strong relation of the company with its different stakeholders through get hold of positive exposure by generating excellent corporate image. Public relationship department would act to mitigate all rumours and keep its keen effort to establish a clean and fair public image with a series of promotional activities, if there are any rumours that shock on the clean corporate image; public relationship department would drive to tone down those adverse events.
Modern corporate world is interested to handle with public relationship as an alternative to the regular advertising that irritate the customer base who are reluctant to waste their valued time by observing marketing literatures of convincing approach. Public relations handle with enormously persuasive feature stories concerned with customers emotional belongings; concentrate upon on going marketing campaigns, corporate news, legend features, and events those are more authentic with the corporate practice to generate positive public image.
Public relationship is a tools alternative to the traditional sales and marketing effort that irritate customers with sales staff’s visit and advertising drives, under this practice, customers receive the promotional events and corporate messages as a news rather than as a direct sales approach. As a marketing tool, public relations could be accustomed with the existing market trend watchfully planned public relations campaign aimed to the promotional mix elements that could handle extremely effectual and economical for the potential customers and significantly cost effective rather than traditional advertising.
Public relations always aimed to generate an assortment of favourable publicity that creates a superior corporate image handling with complimentary stories, and events coordinating with press relations, product exposures, and public affairs while the main concern is to promote products, innovative ideas, and encouraging activities to influence the public awareness to a great extent of lower cost rather than advertising..
Consumer decision-making model
Kotler and Keller (2008) stated that consumer decision-making process is different from each other; as a result, the scholars concentrated on different issues to discuss the procedure, for example, many customers respond considering economic factors while other customers only consider brand image of the company.
However, the following figure shows the model of consumer decision-making more elaborately
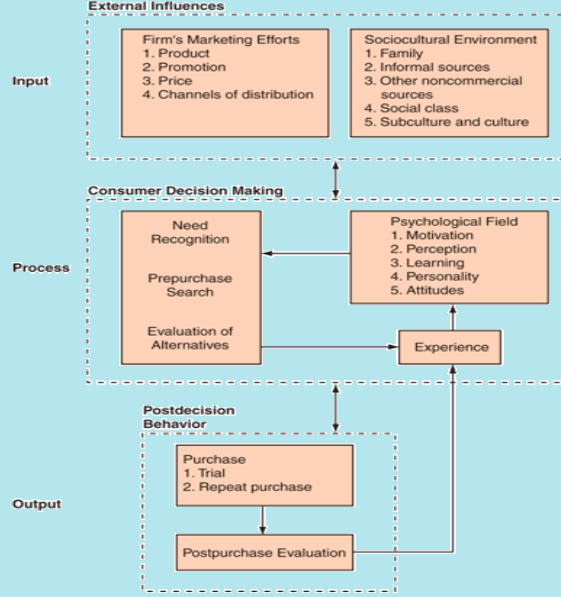
However, Kotler and Keller (2008) further stated that customers mainly consider five steps (like problem recognition, need identification and information), though some customers take decision without considering these factors. However, the customers mainly focus on the following issues

- Problem Recognition: Firstly, the customers identify their actual needs, for example, a customer may admire to purchase same brand model of the neighbour. On the other hand, the customers would like to know more information regarding the new products, as a result, the marketers should concentrate on the customers’ demand, innovation and discretionary purchases to increase customer base. At the same time, some customers may like to purchase MP3 players, HDTV and cell phone but some need more like LCD, digital cable box, digital video recorder, USB flash drive and so on;
- Information search: it is surprising that the customers often search for limited amounts of information and the main sources of information are personal, commercial, public and experiential;
- Evaluation of Alternatives: There is no specific rule that customers consider to take final decision but the customers must try to satisfy their demand along with seek certain benefits from the product solution. However, the customers select the products considering specific brands, product category, benefits, previous buying experience, attitudes, needs and many other factors. On the other hand, Kotler & Keller (2008) stated that the attributes of interest to customers vary by product, such as, a customer must consider site, hygiene, and price to select a hotel, but he would not consider same thinks to purchase tires or cloths;
Reference List
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L. (2008) Marketing management. 13th ed. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L. (2008) Marketing management. Web.