This is a research paper on market power which is a part of managerial economy. It starts with defining the topic and area of research, later getting into the path for recognition of different aspects and scopes of the topic. The major ideologies linked with market power are stated and analyzed to absorb the possibilities and opportunities in sustaining the market power achieved. The analytical methods and techniques are examined to achieve proper knowledge on the managerial possibilities of those in market power and related accomplishments. The investigation made a smooth voyage through the topic without hindrance to actuality of the subject; flow is seen in this paper administering the entire accomplishments of the research.
Introduction & Background
A research is to be carried out in the field of managerial economics. “Managerial economics is the science of directing scarce resources to manage cost effectively” (Png & Cheng, 2001, p.1). Effective utilization of available resources in order to administer better pricing strategies in business comes under managerial economies. Area of managerial economics is actually a union of three sectors namely competitive markets, market power, and imperfect markets. The topic selected for research is market power owing to the density and significance of proper knowledge area in contemporary business market. “Market Power” (Png & Cheng, 2001, p.1) can be defined as “the ability of a buyer or seller to influence market conditions” (Png & Cheng, 2001, p.4). A trader having market power always enjoys self-determination to identify purveyors, costs and control demand in the market. Acquirement and maintenance of market power are entirely different strategies. Only effective management skills can help out to sustain the acquired power. The strategies executed should consider entire aspects of sales and productivity considering the competitors.
Objectives
The objectives of research are accomplished in this section helping out in proper identification and study of various aspects of market power.
Sources of Market Power
Market power has a peculiar status in global trade which consists of many connotations giving shape to it. The sources of market power can be identified as “competitive advantage, technology, branding, attract and retain customers, cloud computing” etc. (Sources of market power, 2010, p.1). Customer conduct has changed from former stick to trademark situation to a novel and efficient requirement in the products they prefer. Technology has created innovations in entire business sector helping out in reducing delay and increasing productivity and efficiency. Branding can bring about special priorities in business and develop consistent market power. Keeping the usual consumers accompanying expansion of customers with newer targets should be observed in sustaining market power. Usage of network supported software for the management and execution of business strategies are identified as cloud computing which has become a novel trend in the field.
Measuring of Market Power
The measuring of market power is often accomplished by using various concentration ratios. Usage of measurements helps out in expanding business scope and variability owing to identification of actual position in the market. The significance of measuring market power is high because “the degree of bias in the measurement of market power is directly related to the number of markets in which the dominant firm operates” (Weisman, 2005, p.2). Measuring will also point out other traits like demand, quality of market etc.
Elasticity of Demand
Elasticity of demand is a factor often analyzed linked to market power which helps in determining consumer attachment to products according to the variations in cost. Economists around the globe use this to dig out the alertness of consumers on the increase and decrease of price of goods and services. “Price elasticity of demand is the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in a good’s price” (Elasticity of demand, n.d., p.1). The variation in cost of commodities will obviously affect the demand and sales of the products and elasticity of demand actually determines this to accuracy which points out the market power as such.
Monopoly
Monopoly is a much favorable situation in business sector which provides much liberty owing to absence of opponents. “Monopoly is the market condition in which we have only one provider of a particular service” (What does market monopoly means? 2010, para.1). Profit acquirement will be the only event happening for the firm then, leading to tremendous flourish in business sector. The well known real life example for such a successful story is that of Bill Gates, the head of Microsoft. The success of Microsoft can be counted due to its monopoly in application software around the globe helping out to determine its position which is unique and non-replaceable. Monopoly can come into existence due to various possibilities. This can be due to proper identification of resources by one where others fail or skill for that particular accomplishment is reserved for one somehow. Another reason for possibility of monopoly is the exceptional efficacy of certain products and also due to newer invention retained to the inventor alone. But, monopoly can at times be named when there are numerous players with a single leader due to outstanding performance leaving all others far behind.
Oligopoly
Oligopoly market is the usual scenario of global business. Such markets have a number of parallel producers and traders. Resulting market create a competitive nature and as a result quality as well as appearance tend to be similar so that there remains least chance for avoidance. Consumers enjoy a freedom to choose for a single product or service they need, thus generating brawny struggle among different brands. There are four theories identified in the name of oligopoly and pricing which are stated below:
- “Oligopoly firms collaborate to charge the monopoly price and get monopoly profits
- Oligopoly firms compete on price so that price and profits will be the same as a competitive industry
- Oligopoly price and profits will be between the monopoly and competitive ends of the scale
- Oligopoly prices and profits are “indeterminate” because of the difficulties in modeling interdependent price and output decisions” (Oligopoly, n.d., para.6). The theories stated above determine the strategy of pricing in oligopoly markets which keeps away the possible redundancies.
Cost
The competitive environment in business of oligopoly or advanced monopoly market observes that “the charges levied by suppliers depend on cost and demand factors” (Salies & Price, 2004, p.1) which actually determines an important part of the market power. Scale and scope of commerce energized with mounted up practice always affect the outfitted cost. Other strategies including pricing are largely dependent on the cost completely or partially.
Pricing
Pricing is another important aspect in market power. Often, this is dependent on cost and demand strategies of market power and is regulated with the observances of the competitors’ activities and concerns on business. The nature of demand and pricing in market power are essentially interdependent and influence values of both.
Strategic Thinking
Strategic thinking is another important aspect concerned with market power. The strategic thinking is defined as a perspective that “formulates effective strategies consistent with the business and competitive strategy of the organization in a global economy” (Strategic thinking, n.d., para.1). It involves identification of strategy concerns and strategic scheduling with an extended period standpoint and settles on purposes and creates precedence. Strategic thinking helps in predicting the latent intimidation or chances offered in the contemporary market scenario.
Literature Review
This section deals with various theories, tools and techniques employed in the field of market power to seek maximum and sustained control over trade.
Price Elasticity Demand
Price elasticity demand is essential for almost every areas of market power. The demand is something that influences the market as well as marketer in business. “An important aspect of a product’s demand curve is how much the quantity demanded changes when the price changes. The economic measure of this response is the price elasticity of demand” (Economics: Price elasticity demand, 2007, para.1). The quotient obtained in the division of balanced variation in demand by balanced variation in price is the numeric value of price elasticity demand. The factors determining price elasticity demand are “availability of substitutes, degree of necessity or luxury, proportion of income required by the item, time period considered, permanent or temporary price change and price points” (Economics: Price elasticity demand, 2007, para.11). Price elasticity demand can be applied to a varied range of market power issues helping out to achieve an effective and influential position in business.
Concentration Ratio
Concentration ratios are the name given for “a family of measures of the proportion of total output in an industry that is produced by a given number of the largest firms in the industry” (Concentration ratios, 2010, para.1). These are techniques used for measuring in market power analysis. The usual ratios depend on four and eight enterprises for analysis giving sufficient substance for investigation. “The four-firm concentration ratio is the proportion of total output produced by the four largest firms in the industry and the eight-firm concentration ratio is proportion of total output produced by the eight largest firms in the industry” (Concentration ratios, 2010, para.1). Concentration ratios are generally used to point to the grade oligopoly of an enterprise and the degree of market rule of the major figures in the trade. The calculations are accomplished in comparison with the chief competitor firms in the business. HHI (Herfindahl-Hirschman Index) is a name linked with concentration ratio measurements.
Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI)
Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) is an important tool used in market power or managerial economies. HHI amalgamates the total and comparative application indicators facilitating the measurements in market power. This value increases with an increase in total concentration as well as supremacy hike by certain competitors. Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) “measures the sum of individual market shares, each squared, for each firm in the industry.”
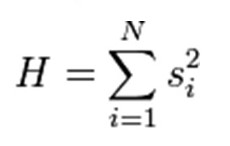
where:
- s = market share of firm I expressed as a percentage
- n = number of firms in the industry (Hooks, 2003, p.72).
The increased value of HHI indicates a highly dense market in total as well as comparative logic.
Contribution Margin and Contribution Margin Ratio
Contribution margin and contribution margin ratio are used in managerial economies to determine the sales and cost coverage in market power. “Contribution margin is the amount generated by sales to cover fixed costs” (Alberta & Calgary, n.d., para.5), whose formula is identified as “Contribution Margin = sales – variable costs” (Alberta & Calgary, n.d., para.2). It is a constructive measure in accomplishing assorted estimations often employed as an appraisal of effective power. “The contribution margin ratio indicates the percent of sales available to cover fixed costs and profits” (Alberta & Calgary, n.d., para.6), which is determined as “Contribution Margin Ratio = (sales – variable costs)/sales” (Alberta & Calgary, n.d., para.3). These help in determining the counterbalance of permanent expenses to keep record of the necessary strategies of cost and pricing related to market power.
Economies of Scale
Economies of scale are employed in managerial economies to estimate the expense benefits possible with the growth scaling of production in any enterprise. These are the aspects helping out to decrease the per product rate for any concern. Economies of scale are defined as the “reduction in cost per unit resulting from increased production, realized through operational efficiencies” (Economy of sale: definition, n.d., para.1). Economies of scale unveils the fact that increased volume of production will lead to a reduction in expense leading to a better pricing and sales strategy. The major reason for economies of scale is due to the permanent cost incurred without referring to the volume produced. Another fact is related to the mean cost which is always uneven, where initial design and planning costs are constant for any number of products.
Diseconomies of Scale
Diseconomies of scale are antagonistic to economies of scale. “Diseconomies of scale occur when Average Costs start to rise with increased output” (Diseconomies of scale: Definition: Diseconomies of scale, n.d., para.1). The tendency of expense to increase with the increase in production volume termed as diseconomy is often due to various failures in management and structuring of the firm. When the enterprise is enormously large, there can be a wider gap of contact within the members leading to diseconomies. Unfriendliness and hostility within the firm can bring about discouraging effect in workers which can make diseconomies occur. There should be influential supervision within a firm that can be demolished due to expanded working population directing towards poor commanding and management resulting in diseconomies. Main action possible against diseconomies is to disintegrate the huge scenario into manageable fragments thereby decreasing hierarchical gap.
Nash Equilibrium
Many resolution theories are being proposed for different games involving varied number of players; Nash equilibrium is one among those available in managerial economies. “A Nash equilibrium is a profile of strategies such that each player’s strategy is an optimal response to the other players’ strategies” (Fudenberg & Tirole, 1991, p.11). Nash equilibrium reveals the factuality that independent variation undergone can achieve least in business, especially market power, whereas joint or dependent revolution is necessary for any strategic possibilities. “A Nash equilibrium is strict if each player has a unique best response to his rivals’ strategies” (Fudenberg & Tirole, 1991, p.11).The main advantage of strict equilibrium is regarding its stout retort to minute variations and novelties in existing business scenario giving up a better opportunity and advantage in trade.
Findings and Analysis
The investigation on market power revealed various aspects involved in it and their position in managerial economies. The actuality of their position in determining firms’ status and profit strategies are identified which is closely attached to success of the firm. The sources and measurements should be accomplished in any marketing scenario for identifying the situation and possibilities for their power deviation either increase or decrease. Elasticity of demand must be recorded effectively owing to its influence in pricing as well as strategic thinking of the firm. The monopolistic or oligopolistic markets are to be identified and dealt accordingly as there are much differences prevailing between both that need proper attention. The expense, price and strategic thinking require substantial concentration for developing and sustaining market power. The avoidance of these while performing managerial functions often will lead to unexpected and terrible outcome. Proper significance in the case of implementation of tools and techniques available in managerial economies area should be observed without much redundancy. This can help achieve the set targets and profits without bringing any negative effect on market power. The development of market power is easily possible at many times, but sustaining of the same poses real time threat due to novelties and developments in much varied areas of business. Best is to adopt innovations keeping the internal as well as external contact with close observance of competitors’ activities and performance along with developing and evaluating requisites for self and finally implementing those with least chance for redundancies.
Conclusion
The research on market power in managerial economies posed a real time exposure to various aspects and levels of the topic. The different sectors within it were identified helping out in realizing the scope and scenario of market power. The unveiling of various possibilities and probabilities of market helped to coin the factual picture of market power and its traits. The tools and techniques were identified and analyzed to obtain hope and path for sustained market power. The demand, cost, pricing etc. turned out to be clear and pure in substantial evaluation and examination on the matter of market power. The success of business can be in terms of market power which has to be consistent leaving out not even the slightest gap for opponents to enter into. The study on different aspects of market power accompanied by tools and techniques employed for the same sector helped in conquering the field to maximum potential. The achieved latency can be utilized for developing a proper strategic thinking by close observation of various aspects and making use of achieved knowledge and techniques. The importance of awareness about the existing and possible strategies of market power is revealed along with acquirement of essential techniques and tools.
References
Alberta., & Calgary. (n.d.). Contribution margin and contribution margin ratio. Bizwiz. 2010. Web.
Concentration ratios. (2010). Amos Web.
Diseconomies of scale: Definition: Diseconomies of scale. (n.d.). Economicshelp.Org. 2010. Web.
Economics: Price elasticity demand. (2007). NetMBA.Com. Web.
Economy of sale: Definition. (n.d.). Investorwords.Com. 2010. Web.
Elasticity of demand. (n.d.). pp.1-4. 2010. Web.
Fudenberg, D., & Tiorle, J. (1991). Game theory. MIT press. Web.
Hooks, A.J. (2003). Economics: Fundamentals for financial services providers, 2nd Ed. Kogan Page. Web.
Oligopoly, (n.d.). Tutor2U. 2010, Web.
Png, I.L.P., & Cheng, C.W.J. (2001). Introduction to managerial economics. pp.1-7. Web.
Salies, E., & Price, W.C. (2004). Charges, cost and market power: The deregulated UK electricity retail market. Dane prairie.Com. pp.1-24. Web.
Sources of market power. (2010). eHow. eHow Business & Finance. Web.
Strategic thinking, (n.d.). Leadership.au. 2010, Web.
Weisman, L.D. (2005). A generalized measure of market power. pp.1-10. Web.
What does market monopoly means? (2010). Buzzle.Com. Web.