Introduction
Today, virtually everyone is acquainted with the word “smartphone.” It is certainly a technical and social phenomenon that touches the everyday lives of millions of people by providing rapid access to information and tremendous computer capability in a pocket-sized device. Thus, a smartphone is integral to global culture’s everyday existence. This is attributable to the fact that it constitutes a device for corporate communications, maintaining contact with family members and friends, exchanging information, and sometimes earning income by providing the content. Smartphones were initially developed ingeniously, but their designs were cumbersome and unappealing. However, after Apple introduced the iPhone in 2007, the sector experienced substantial transformation, and the company has taken the lead in establishing worldwide standards for the smartphone industry.
The topic was selected because of the writer’s passion for it. The researcher tracks smartphone industry headlines, reads online publications regarding the topic, and monitors the rivalry between various smartphone companies. In recent times, the issue of competitive advantage determinants seems to be understudied. Notably, even though the smartphone sector, like any other comparable industry, has significant shortfalls in public information, market players may conduct substantial research, with the results generally retained inside the firms’ data and not shared with the public. The lack of such data to the public underscores the importance of studying the smartphone economic market in detail to determine the key players, market and revenue share, and competitive advantage, and provide direction on the strategies that the manufacturers may adopt. Therefore, the answer is determined by the study results that offer answers to the following supplementary question: What are the smartphone industry’s size, composition, revenue, and patterns?
Literature Review
The smartphone sector is worth exploring since it has a big sales turnover and substantial opportunity for growth. According to O’Dea (2022), in 2021, smartphone vendors sold around 1.43 billion smartphones worldwide. In the U. S., smartphone sales were on track to reach over 73 billion dollars in 2021, which is four times the number a decade ago (O’Dea, 2022). Researchers commonly view smartphones as the successors of feature phones, whose capabilities are generally limited to simple text messaging and phone call capabilities (Carolus et al., 2019; Lamberg et al., 2021). Despite not being termed a smartphone during its era, Simon by IBM, originally marketed in 1994, is today considered the first smartphone worldwide (Hynes, 2021). Nevertheless, it was not until Apple released the iPhone in 2007 that cellphones became widely popular. Gradually, the sector has evolved tremendously and undergone considerable transformation. Samsung, Apple, Xiaomi, Huawei, Oppo, Motorola, Vivo, and Nokia are among the most noteworthy firms in the smartphone business, with the first two manufacturers competing fiercely for consumers’ consideration.
The worldwide smartphone market is relatively nascent but continues to expand every day. The predicted 6.23 billion smartphones in circulation as of 2021 are projected to increase to 7.7 billion in the next five years (O’Dea, 2022). Although exhibiting some indications of stalling, the market has a huge opportunity because of the fairly low market subscriber base in several regions, particularly Asia and Africa. Notably, smartphone penetration in India and China, which have the world’s highest populations, is below 70% (O’Dea, 2020.). Similarly, mobile phone exports to the African continent in the third quarter of 2019 totaled 55.8 million devices, most of which were not smartphones (Mitchell, 2020). Moreover, feature phones, known as basic cellphones, made up 59.4 percent of the aggregate, while smartphones made up 40.6 percent of the rest (Mitchell, 2020). In perspective, the continent has many young individuals who will reach adulthood in the next decade and need consistent connection and access to a variety of applications facilitated by internet connectivity.
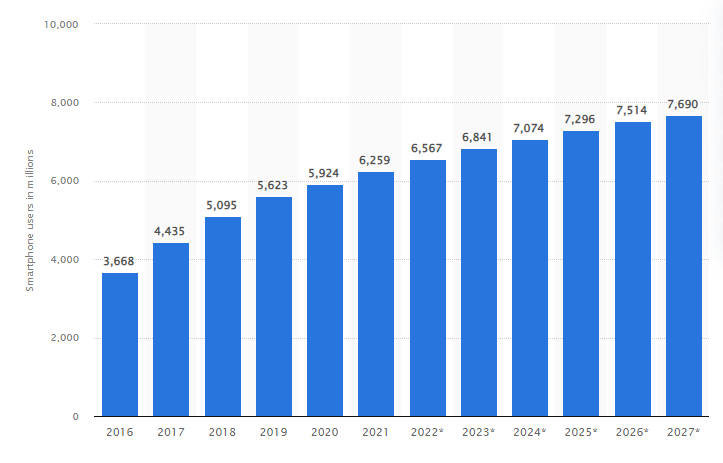
Note. The current adoption of smartphones exceeds six billion, and it is expected to increase by several million over the next decades. The United States, China, and India have the largest concentration of smartphone subscribers. Notwithstanding stagnant unit sales in the past two years, the worldwide smartphone market’s income has been on an upward trajectory, due to an increased average cost of smartphones.
The iPhone had a significant impact on the sector in a number of ways. According to (Kellerman, 2014), in the early 2000s, the internet became an integral component of daily life, as voice communication declined with time. Although photography was essential and a part of ordinary life, it was associated with hippies. The overall volume of digital images captured in 2017 was 1.2 trillion, up from 400 billion six years earlier. Jabangwe et al. (2018), reiterate that the introduction of the Apple App Store and the incorporation of apps and games into the smartphone altered the mechanism by which software was built and deployed. Badran and Al-Haddad (2018), assert that thanks to the iPhone, modern smartphones offer a wide variety of applications that improve user experience. That aside, many researchers acknowledge that smartphones create revenue for developers, who build applications such as games published on respective Application stores (Kapoor & Agarwal, 2017). More importantly, the iPhone fostered the birth of the Android Operating System, which consequently led to the emergence of various manufacturers adopting the OS (Lamberg et al., 2021). As will be examined, this new operating system bolstered the income of Apple’s main rival, Samsung. Furthermore, the new operating system influenced the decline of long-term industry players Nokia and blackberry.
While the iPhone has played a critical role in the growth of the smartphone industry, its impact is dwindling. Huawei, a Chinese company, was gaining ground on Samsung and Apple in the worldwide smartphone market until the US ban which barred many telecommunication and technology companies from trading with the firm (Hosain, 2019). The company was on the verge of overtaking Apple as the second-largest smartphone vendor in the industry. In the mobile phone industry, competition is severe. Without initially designing an effective market strategy, it will be challenging for a new brand to enter this market. For the product to be well appreciated by customers and to have a significant market presence, the business strategy must change over time. This involves recognizing and promoting the unique selling qualities of the product. Market share is the proportion of a market’s total revenue or sales that a firm account represent. Samsung, Apple, and Huawei are among the Smartphone manufacturers that have dominated the market share during the previous decade.
Huawei is a worldwide leader in infrastructure and intelligent devices for information and communications technologies (ICT). With the Huawei P and Mate model lines, Huawei began establishing itself in the smartphone market share sector in 2009 (Dmitrijevs, 2020). In 2013, Huawei launched the HONOR subsidiary brand to deliver low-cost handsets with great functionality, making Huawei the second largest smartphone manufacturer, behind only Samsung and ahead of Apple (Dmitrijevs, 2020). In addition, Huawei surpassed Samsung as the world’s largest smartphone seller in the second quarter of 2020, increasing its position, when it collaborated with Leica to develop its camera to be more competitive in the photography industry (Cartwright, 2020). This collaboration made Huawei to be considered one of the best smartphone camera manufacturers, especially with the debut of the Huawei P30 in 2019 (Alkhawajah, 2019). However, Huawei’s expansion and competitive advantage in the market led to problems.
Huawei became a crucial endeavor and participant in technology and smartphone services in the fall of 2018. This competition made Huawei a crucial participant in the 5G deployment in the United States (USA), which led to the White House putting Huawei on a list of firms suspected of supplying information to Beijing in May 2019 (Hosain, 2019). This ban had severe consequences for Huawei, such as their smartphones could no longer use components from all US manufacturers, and their older cellphones could no longer get Android upgrades (Hosain, 2019). As a result, it affected its global market share as a leading producer of smartphones.
Samsung is another industrial titan that controls the global smartphone market. Android is Samsung’s operating system as of 2019, with their interface, ONE UI, and they download apps from the Google Play Store. According to consumer preference compared to Android and other operating systems, Android is the most popular (Ruiz et al., 2020). Since its launch of the android smartphone, Samsung amassed a lot of market share, and it increased when Samsung introduced the first Samsung Galaxy Note in 2011; It was one of the market’s first phablets (Haizar et al., 2020). These phablets increased customer loyalty and preference since Samsung phones often have superior CPUs compared to Apple (Haizar et al., 2020). This performance indicated that individuals could do more demanding jobs without slowing down or overheating. Moreover, Samsung phones often have more RAM than iPhones, which gives considerable performance and multitasking benefits (Ruiz et al., 2020). This factor has increased Samsung’s market share internationally due to customer satisfaction and strong demand resulting from its product’s preference and excellent quality.
Analysis
Compared to previous brands, the launch of the first iPhone’s 3.5-inch screen made it easier to watch movies, access the internet, and read news and articles. This launch made Apple’s goods well-known worldwide, and due to the unique atmosphere of the company, it was easy for anybody to use an iPhone and other Apple products (Yun et al., 2019). Another aspect that increased the market share and product popularity was the synchronicity between the Apple devices. For instance, since the MacBook, iWatch, iPad, iMac, and AirPods all used the same operating system, IOS, it was easy to facilitate communication across the devices (Varenkamp, 2019). As a result, iPhone was regarded as a successful, market-leading brand due to its brand image and consumer happiness.
Apple produces and promotes mobile devices, personal computers, and digital goods. Apple’s market share decreased from 14.1% in the first quarter of 2021 to 14.1% in the second quarter of 2021. (Statista, 2022b). Apple’s sales typically decreased from the fourth quarter to the first quarter of the following year, but the arrival of the iPhone 12 was enough to propel the company to a second position in the worldwide smartphone market (Statista, 2022b). Apple increased its market share after the demise of erstwhile industry leaders Nokia and RIM. Although the long-term effects of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic on sale are impossible to predict, its immediate effects were readily apparent. While substantial quarterly changes are typical for Apple’s revenue cycle, one needs to go back to 2017 to discover two consecutive quarters in which iPhone sales were less than $30 billion (Statista, 2022b). However, a robust result led by the iPhone 12 indicates that the corporation is well on its way to overcoming the early effect of the epidemic on smartphone sales.
Apple has been overtaken by Samsung in the worldwide smartphone market, as Samsung’s performance has increased. In 2021, Samsung Electronics’ net sales grew compared to the previous year (Pratap, 2022). In 2021, its consolidated net sales remained at $206.98 billion, compared to $200.6 billion in 2020. (Pratap, 2022). The company’s gross profit for 2021 increased to $99 billion from $80.7 billion the previous year (Pratap, 2022). The diluted earnings per share (EPS) grew to $5.05 from $3.36 in the prior year (Pratap, 2022). Samsung smartphones have a lower marginal cost than Apple smartphones while being more costly to create. For instance, the Galaxy S8 costs $307 but is now offered for $499 on the company’s website (Mourdoukoutas, 2018). The continual improvement in the company’s profitability has been ascribed to the extensive range of inexpensive gadgets, a necessary condition for markets like India.
Despite its limited name awareness in the West, Xiaomi is one of the most significant technology companies worldwide. In recent years, the brand has seen tremendous and rapid growth, surpassing industry leaders and competitors in terms of sales. In addition to Microsoft, Apple, and Google, the brand competes with other companies. With a 64 percent rise in revenue, Xiaomi surpassed Samsung and Apple to become the market leader (Statista, 2022c). During the second quarter, the brand placed second globally in terms of sales. The corporation earned $13.56 billion and $1.28 billion in sales (Statista, 2022c). Since its inception in 2011, the firm has sold 800 million smartphones, and while the brand was created in 2011 and its first smartphone was released in the same year, by 2014, it ascended to gain the most market share in China (Statista, 2022a). In 2015, the brand expanded its global offering of smartphones and other devices. In the second quarter of 2021, Xiaomi overtook Apple Inc. and boosted its global market share to 17 percent, becoming the second largest vendor (Statista, 2022c). As a result, the company is now the youngest on the Fortune 500 list.
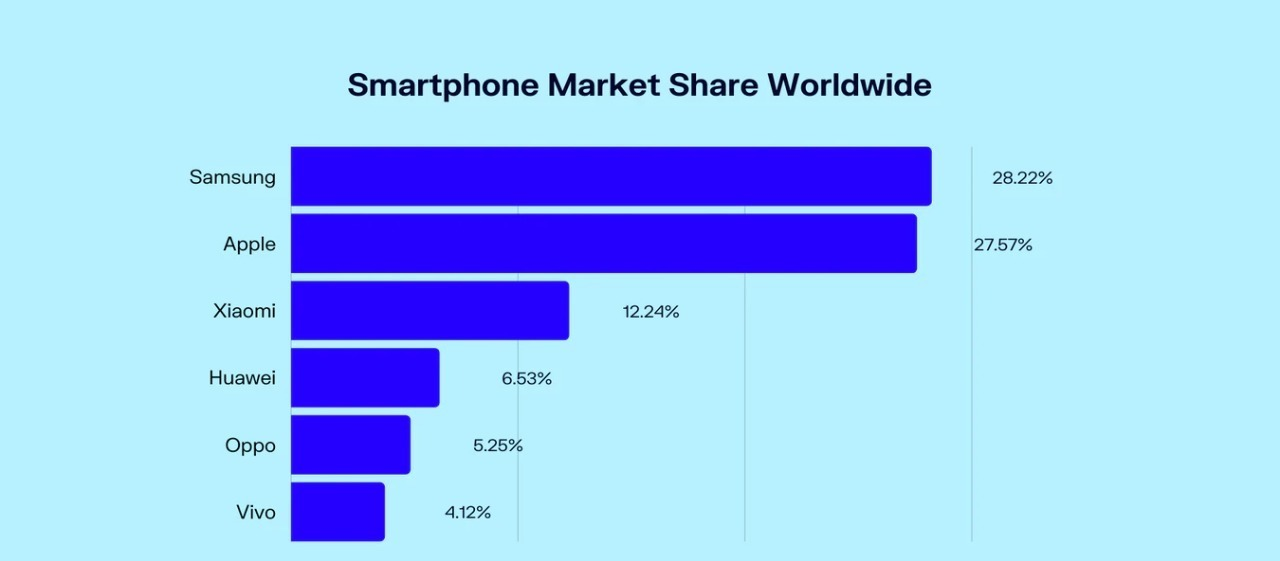
Note. With a market share of 28.22 percent as of March 2022, Samsung leads the smartphone market share competition. This data means that around 30% of all smartphone users worldwide own a Samsung handset. Apple ranks second with a score of 27.57 percent, which is just 0.65 percent behind Samsung. Xiaomi is the third-largest smartphone manufacturer, with a market share of 12.24 percent of the total volume.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, the coronavirus outbreak negatively impacts almost every business, including the smartphone market. Despite the immense potential presented by innovation, research, development, and entertainment in the smartphone market, the future of giants such as Apple remains uncertain. As the corporation updates its main product, the public’s interest continues to wane, and prices continue to rise. Samsung retains a solid position as the current leader in the smartphone industry owing to the company’s commitment to supplying a variety of high-end and budget-friendly devices so that every client can make an informed decision. Thus, smartphones are undeniably a valuable commodity for consumers, and the mobile phone industry will keep growing in the following decades.
References
Alkhawajah, W. (2019). Huawei: An information and communications technology company. Journal of Information Technology and Economic Development, 10(1), 1-10.
Badran, O., & Al-Haddad, S. (2018). The impact of software user experience on customer satisfaction. Journal of Management Information and Decision Sciences, 21(1), 1-20.
Carolus, A., Binder, J. F., Muench, R., Schmidt, C., Schneider, F., & Buglass, S. L. (2019). Smartphones as digital companions: Characterizing the relationship between users and their phones. New Media & Society, 21(4), 914-938.
Cartwright, M. (2020). Internationalising state power through the internet: Google, Huawei and geopolitical struggle. Internet Policy Review, 9(3), 1-18. Internationalising state power through the internet: Google, Huawei and geopolitical struggle (econstor.eu)
Dmitrijevs, R. (2020). Research on Marketing Strategy of Huawei Mobile Phone in European Market. Open Journal of Business and Management, 8(3), 1138-1150.
Haizar, N. F. B. M., Kee, D. M. H., Chong, L. M., & Chong, J. H. (2020). The impact of innovation strategy on organizational success: A study of Samsung. Asia Pacific Journal of Management and Education (APJME), 3(2), 93-104.
Hosain, S. (2019). Huawei ban in the US: Projected consequences for international trade. International Journal of Commerce and Economics.
Hynes, M. (2021). The Social, Cultural and Environmental Costs of Hyper-connectivity: Sleeping Through the Revolution. Emerald Group Publishing.
Jabangwe, R., Edison, H., & Duc, A. N. (2018). Software engineering process models for mobile app development: A systematic literature review. Journal of Systems and Software, 145, 98-111.
Kapoor, R., & Agarwal, S. (2017). Sustaining superior performance in business ecosystems: Evidence from application software developers in the iOS and Android smartphone ecosystems. Organization Science, 28(3), 531-551.
Kellerman, A. (2014). The internet as second action space. Routledge.
Lamberg, J. A., Lubinaitė, S., Ojala, J., & Tikkanen, H. (2021). The curse of agility: The Nokia Corporation and the loss of market dominance in mobile phones, 2003–2013. Business History, 63(4), 574-605.
Mitchell, J. (2020). Will mobile phone penetration maintain African momentum? Fdiintelligence.com.
Mourdoukoutas, P. (2018). Samsung Beats Apple In The Global Smartphone Market As Chinese Brands Close In. Forbes.
O’Dea, S. (2020). Smartphone users worldwide 2016-2021. Statista.
O’Dea, S. (2022). Topic: Smartphones. Statista.
Pratap, A. (2022). Samsung Net Revenue. Financial Data & Stats – Statstic. Web.
Ruiz, E. H., Restrepo, C. A. P., Lopez, C. A., & Kee, D. M. H. (2020). Samsung: Customer loyalty strategy in Malaysia and Colombia. International Journal of Accounting & Finance in Asia Pasific (IJAFAP), 3(2), 57-67. Web.
Statista. (2022a). Market share of Xiaomi smartphones in APAC 2022, by country.
Statista. (2022b). Apple iPhone smartphone market share worldwide 2007–2022.
Statista. (2022c). Smartphone market share worldwide 2009–2022, by vendor.
Varenkamp, P. (2019). iPhone Acquisition Using Jailbreaking Techniques (Master’s thesis, NTNU). finalProduction_636949205280976692 (ntnu.no)
Yun, B. S., Lee, S. G., & Aoshima, Y. (2019). An analysis of the trilemma phenomenon for Apple iPhone and Samsung Galaxy. Service Business, 13(4), 779-812.