Introduction
Managed Care in Veterans Affairs (VA)
The role of Managed Care for Veterans Affairs is great due to the improvements implemented to manage the resources in this area properly. Escalating costs in community hospitals for people who are supposed to be treated in specialized Veterans Affairs hospitals can be reduced by bringing the veterans back into the VA system and reducing costs in this way. As the main focus of this paper is to reduce patients’ length of stay with the help of measuring tools for monitoring and assessment of data and staff education, it is necessary to choose methodologies appropriate for organizational quality improvement plan in terms of the. Another focus of this paper concerns the process of reducing readmission rates and identifying milestones and benchmarks nationally in the United States. In this respect, it is necessary to investigate this area thoroughly.
Tools for collecting and monitoring data
Specific tools for collecting and assessing data and monitoring performance information include National Healthcare Quality Report (NHQR) Fact Sheet, Sampling (IHI Tool), Simple Data Collection Planning (IHI Tool), other tools are used to monitor and display data for better understanding and further implementation include Measuring Rare Events and Time-Between Measures tool and Scatter Diagram (IHI Tool) for comparing two variables presented with the help of graphic techniques. The current paper contains methodologies for performance improvement, information technology applications needed to improve the organizational quality management plan operation, and benchmarks and milestones concerning the national level of healthcare services in terms of Veterans Affairs system for performance improvement. In other words, methodologies used to improve the situation, make resource application more sufficient, and reduce the length of stay and readmission rates.
Performance Improvement Methodologies
Methodology One: Six Sigma
The Six Sigma is a performance improvement methodology used in health care organizations as well as in other fields of human activity such as manufacturing and production (Moyers, Shaw, and New, 2006, n. p.). This methodology is claimed to be rather effective for cost-efficiency improvement. As reported by Dlugacz (2006), this tool is “designed to reduce the negative economic impact of inefficient services” (p. 74). In this respect, this methodology can be effectively implemented to reduce the costs spent by patients within Veterans affairs system and hospitals of this system can manage their resources more effectively as well. Financial aspect is the key concept for this methodology as costs are frequently managed inappropriately due to incomplete data for measuring the situation.
Pros.
The main benefit of this methodology is that it is possible to take into account different variables and compare and contrast them in order to measure the reliability of equipment, period of stay, and other variables that influence the effectiveness of performance and sufficiency of cost and resource use. In this respect, the Six Sigma methodology can be applied to the concepts of the main focus such as reducing the length of patients’ stay and reducing readmission rates in terms of the Veterans Affairs system contrasted to the community hospitals system.
Cons.
The main disadvantages of this methodology include the reliability of data used for assessment. As the data used for measuring can be invalid or inappropriate, the results of the measurement can happen to be inappropriate as well. In other words, every figure entered into the data storage system should be double-checked in order to avoid mistakes that may lead to misunderstanding and irrelevant measures taken to improve the situation causing ineffective management of financial and human resources. Any minor misprint can cause huge mistakes in the overall performance improvement plan.
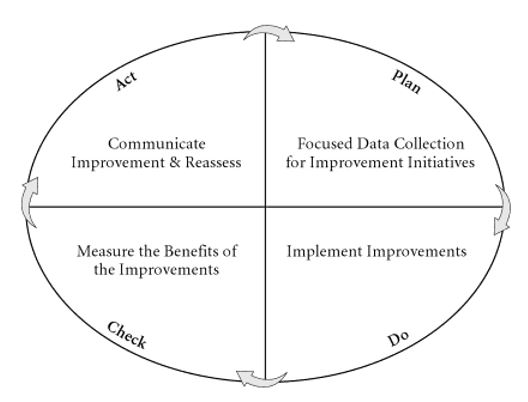
Methodology Two: The Plan Do Check Act (PDCA)
The Plan Do Check Act (PDCA) has been analyzed in the study by Dlugacz (2006) as one of the most effective in terms of health care services implementation. This methodology is the one aimed at standardization of the setting, performance, and principles of operation. Assessment and monitoring of performance contribute greatly to the improvement of performance conducted after collection and assessment of data and planning of changes to be made for improvement. The main issue concerning this methodology is its applicability to the process of reducing the length of patients’ stay at hospital as well as reducing the readmission rates with regard to the costs that have been escalating when veterans received health care services in community hospitals.
Pros.
The main benefit of using this methodology for performance improvement that every step can be thoroughly planned while the results of change implementation can be further assessed in order to make further changes accordingly. In other words, this methodology fits perfectly the characteristics of the performance measurement and improvement plan aimed at reducing the length of patients’ stay and reducing readmission rates due to the main focus of the current study. As every step can be implemented in a strict sequence, its effects can be measures properly which enables professionals that operate in this area to make further changes to accurately improve the performance.
Cons.
The disadvantages of the methodology referred to as the Plan Do Check Act (PDCA) are insignificant compared to its advantages because each stage of the performance improvement process should be planned and implemented into practice in accordance with a specific plan while even the slightest error in data will become evident while analyzing the mistake that might have possible occurred and correct everything without changing the entire plan significantly.
Methodology Three: Customer Inspired Quality
The performance improvement methodology referred to as Customer Inspired Quality “focuses on work processes that directly impact the care and service provided to hospital and medical group patients by identifying, defining, analyzing, and improving the quality and effectiveness of processes” (Moyers, Shaw, and New, 2006, n. p.). In fact, this methodology includes features of the two methodologies mentioned above though has many advantages compared to those two performance improvement methodologies. As customer’s perspective is the focus of this methodology, it can be quite applicable to the situation described in the current study that is aimed at reducing the length of patients’ stay at hospital and reducing readmission rates as parts of the Managed Care program that mainly focuses on cost-efficiency of health care services provided to veterans.
Pros.
The main advantages of this performance improvement methodology include its techniques/guidelines such as “Discover customer’s perspective of key processes; prioritize processes; create Process Profile® graphic; identify measures; improve process; review progress; monitor customer-measures; repeat cycle” (Moyers, Shaw, and New, 2006, n. p.) and the key effects of this methodology implementation such as improved quality and reduced costs. Moreover, this methodology is more appropriate for health care organizations, especially with regard to the main focus of the current study including reducing of the length of stay and readmission rates in Veterans Affairs hospitals.
Cons.
This methodology has the only disadvantages though it does not concern the current case because it consists in applicability of this performance improvement methodology to organizations that provide services mainly. In other words, the current methodology is not used in manufacturing.
Information Technology Applications
Applications that can be used for quality improvement plan
The quality improvement plan includes such stages as monitoring of the current situation, identification of gaps, planning the techniques to eliminate the gaps, applying the plan to the situation, and monitoring the effectiveness of changes. In other words, cycle should be full in order to trace all disadvantages of the plan applied and introduce other changes that might be more effective in the current situation. For instance, “APACHE = Acute Physiology, Age, and Chronic Health Evaluation scoring method” (Ashton et al., 1995); this tool can be used as a part of the performance and quality measuring tool. This tool has also been used in the study by Knaus et al. (1993) who investigated the length of patients stay and the effectiveness of intensive care units (ICU). Moreover, Ravishankar (2008) suggests a number of other information technology applications that can be used for quality management operation. “SOX 404 that specifies IT controls to minimize financial risks; FDA 21 CFR Part 11 – electronic records, electronic signatures; FDA 21 CFR Part 820 – Quality System Regulation” can be considered IT applications appropriate for performance improvement methodologies mentioned above (Ravishankar, 2008, pp. 47-48).
The way of implementation
These applications facilitate the work of health care personnel because they facilitate the collection and monitoring of data necessary for effective operation and resource management. As the main focus of the current study is to reduce the costs spent on irrelevant procedures, length of patients; stay and readmission rates should be reduced to make the health care services more affordable for those who really need them. In other words, the applications can be implemented after monitoring the current situation and identifying the areas where gaps usually occur or may potentially occur. After that, it is necessary to apply the methodology chosen for the performance improvement plan and monitor the effectiveness of changes made.
Benchmarks and Milestones
Utilization of quality indicators
The quality indicators usually include “business needs and challenges”, “applicable compliance regulations”, current and future states as well as gaps (Ravishankar, 2008, p. 550). In other words, the main indicators of quality of a health care service organization include effective management of resources and reduced costs for patients who should stay longer at hospitals due to ineffective organization of treatment and have to pay for those stays regardless of their financial conditions. Moreover readmission rates are also high due to ineffective treatment and discharging from hospital in spite of inappropriate condition. Utilization of quality indicators should be performed in accordance with the performance improvement plan created for the current situation taking into account specific needs and demands of the health care service organization.
Potential benchmarks and milestones from quality indicators for QI plan
Potential benchmarks from quality indicators for quality improvement plan can include the ones identified with the help of Six Sigma performance improvement methodology. In other words, benchmarks can be identified with regard to the situation in Veterans Affairs organization nationally in the United States. The benchmarks can include compliance, responsibility, and costs as well as quality of health care services provided to veterans from Veterans Affairs organization that should be provided with special health care services at VA hospitals rather than in community hospitals. The milestones for performance improvement and quality indicators utilization should include the following stages of benchmarking addressed in the report by Modernization Agency (2003):
Stage One – agree best practice; stage two – assess clinical area against best practice; stage three – produce and implement action plan aimed at achieving best practice; stage four – review achievement towards best practice; stage five – disseminate improvements and or review action plan; stage six/one – agree best practice” (p. 4).
In other words, the milestones are stages of the improvement process that should be conducted in an appropriate manner with regard to the sequence of stages.
Conclusion
The process of monitoring and improving the performance quality can become easier and less cost- and time-consuming than before due to application of different performance improvement methodologies and information technology applications such as Six Sigma, Plan Do Check Act (PDCA), Customer Inspired Quality, and other methodologies that can be effectively applied to the current situation when the main focus consists in reducing the length of patients stay at hospitals and reducing readmission rates that affect the resource management as well as ineffective distribution of resources. The methodologies can be effective in different areas though Customer Inspired Quality focuses more on patients and is not applicable to manufacturing.
Reference List
Ashton, C. M., Kuykendall, D. H., Johnson, M. L., Wray, N. P., and Wu, L. (1995). The association between the quality of inpatient care and early readmission. Annals of Internal Medicine, 122 (6), 415-421.
Dlugacz,.D. (2006). Measuring health care: Using quality data for operational, financial and clinical improvement. San Francisco, CA: Jossey Bass.
Knaus, W. A., Wagner, D. P., Zimmerman, J. E., and Draper, E. A. (1993). Variations in mortality and length of stay in intensive care units. Annals of Internal Medicine, 118 (10), 753-761.
Modernization Agency. (2003). Essence of Care: Patient-focused benchmarks for clinical governance. Web.
Moyers, H., Shaw, J. G., and New, W. (2006). Methodology comparisons: Six Sigma, Lean, Theory of Constraints and Customer-Inspired® Quality. Web.
Ravishankar, N. (2008). IT applications for healthcare: leverage processes for high quality. SetLabs Briefings (Sept.), 47-58.
ReproLine. (2003). Quality improvement and performance improvement: Different means to the same end? Methodology. Web.