Introduction
The world’s population has grown very fast. Early developments indicated that developed countries had the fastest-growing number of older people. However, the trend has picked up in less developed countries of the world as well. By the year 2050, it is estimated that one billion two hundred thousand people aged sixty-five years and above will live in less developed countries, while twenty-two percent of them will live in developed countries (Uhulenberg 577). This demographic change will affect the social, health, and economic progress of all countries. This article will look at the aging profile of Pakistanis (Uhulenberg 577). Fertility reduction in Pakistan has resulted in a reduction in the number of children per woman. Successive births are reduced; hence the increase of old people’s population. Changes in life expectancy have also resulted in changes in aging patterns. With proper medication, people can live longer thus increasing the number of old people.
Dependency Ratio
Pakistan is a developing country and four percent of its people are aged over 65 years; forty-one percent are below fifteen years of age; fifty-five percent of the people are between fifteen years and sixty-four years of age. The country has a youthful age structure population, where the working population has to support many old people (Uhulenberg, p. 577). This is in contrast to developed countries that have a very low dependency rate. The dependency burden being about eighty-two percent is very high for Pakistan and it creates a hidden momentum of growth in population due to the many youths of childbearing age.
Dependency Ratio = [(4+41)/55]*100 = (45/55)*100
81.8
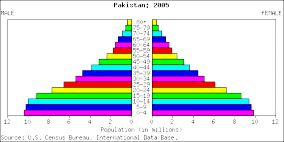
Population Pyramid of Pakistan
The population pyramid of Pakistan shows how the population has grown. The country had its population more than doubled to140 million from 60 million between 1970 and 2000. Those aged between fifteen and forty-nine rose from fourteen million to sixty-eight million. The increase in population has been attributed to the improvement in health care provision. Children were given the right vaccines; pregnant women attended the antenatal clinic; and children were born in health clinics (Uhulenberg, p. 577).
High fertility has resulted in an increased population in Pakistan. The socio-economic conditions in Pakistan are different from other countries and this has prevented fertility decline. The majority of the population resides in the rural areas and thus has no access to proper education and health facilities, resulting in a high population because women are not aware of the family planning methods.


Conclusion
The population is growing very quickly in Pakistan and this has created a high dependency rate. Improvement in health facilities and education reduces the fertility rate of the population because women reduce the number of children they bear to dedicate more time for their careers, increasing the aging population. It is projected that the population of those above sixty-five years of age will be higher in 2020 than in 2005 and highest in 2050. This is because with improved health facilities people can use family planning measures to reduce the number of children per woman. Education will also help most women to work and not be housewives; hence reducing the number of children they get.
Works cited
Uhlenberg, Peter. International Handbook of Population Aging. Chicago. Illustrated Publisher Springer, 2009.