In this era of technology, many companies are grappling with the issue of environmental conservation and sustainability. Sustainability is the ability to use resources sparingly for the sake of the future. Many of the companies emit effluents without considering the effects of such actions on the environment and the lives of the future generation. Such callous actions have led to the depletion of the ozone layer and the resultant climate change whose effects are in the whole world. This paper discusses the steps the company has taken towards sustainability and the criticism the measures have faced.
One company has stood out in this struggle: the Pepsi Company. It has managed to not only ensure sustainability. It has also significantly reduced its cost of operation and maximised on its profits due to its sustainable actions (Slack et al. 2009).
Pepsi is an international company that specialises in the production of soft drinks. The company decided to reduce its cost of production, especially on buying water for use in the enterprise, through embracing a recycling method where water utilized in the company is not let to run (Heizer & Render 2014). Instead, it is channelled to a water-recycling machine and reused in the production of drinks. This device has helped the company save $45 million dollars over a period of 10 years (Campbell & Mollica 2009). This amount was a reduction in the cost of water and energy. However, the recycling criterion uses chemicals that require further testing for their effectiveness in providing healthy water.
The company has not been selfish with this technology. Rather, it has been generous as it has shared it with farmers and NGOs in its vicinity. This step has ensured water sustainability, not only within the company but in the whole community. Initially, members of the community were using the company’s machines in recycling its water, but with time, the company has shown them how to come up with simple tools that work in a similar manner. But the community is adamant about using this technology (Christopher 2011). The health institutions and environmentalists have not approved this method as the best was to save the environment.
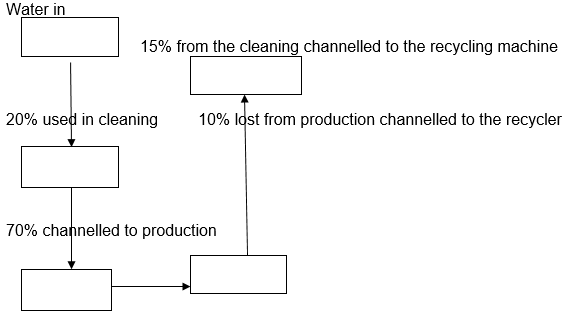
From the flow chart, 25% of the water used is saved from disappearing and is recycled and reused.
The company has managed to turn all its waste from what was previously considered to be garbage to a money-minting resource. Specifically, it uses pyrolysis in converting waste into clean energy that is useful for both the company and the surrounding community (Slack & Lewis 2010). It has reduced its expenditure on energy by $5 million per financial year and has raised its profits by $20 million in each fiscal year. All these inventions are only concerned with profit generation. The company does not have any plan that seeks to give without benefiting from the innovation.
The company has also adopted the use of renewable energy for most of its operations. It has installed solar panels that produce a total of 400 megawatts of power. It has saved them a total of $20 million that the company would have paid for electricity (Goodall 2012). They have also been able to share part of this energy with the community at affordable rates. The company has also built a huge windmill for the community around. This windmill cost the company about $5 million (Morana 2013). It pumps water from a dam to more than four hundred houses with about four thousand people.
However, many critics have termed all these efforts as profit-oriented. Notably, they think that the water recycling project is only for increasing their profits and cutting on their expenditure and not helping the community (Heizer & Render 2014). They have also accused them of having been used to carelessly disposing of their liquid waste without even considering its effects on the community.
According to the critics, it was until they discovered the amount of money they could get from water recycling that they adopted it. They also think the waste recycling project was only meant to raise funds by selling the energy produced to the community. They say this due to the lack of such an initiative in the past. Allegedly, just as it was with water, waste was deposited anywhere within the surrounding of the company. They argue that when the company realised that it could raise some money from waste recycling, it decided to work on it.
In summary, Pepsi has done everything possible to foster sustainability. It has ensured that there is environmental sustainability through proper waste management and the reduction of water wastage. But the company also seeks to benefit from all its projects. The environmentalists have also not presented a comprehensive report on the effectiveness of the projects. These practices have just helped increase the company’s profits and cut down on the costs of production. The company has embraced energy-producing methods that will continue serving it and its neighbours for many years to come. These two steps bring about economic and social sustainability. Therefore, what critics say has some truths in it.
References
Campbell, T & Mollica, D 2009, Sustainability, Farnham, Surrey, England: Ashgate.
Christopher, M 2011, Logistics and Supply Chain Management, Prentice Hall, New York.
Goodall, C 2012, Sustainability, Hodder & Stoughton, London.
Heizer, JH & Render, B 2014, Operations management: sustainability and supply chain management, Pearson Education Limited, Harlow.
Morana, J 2013, Sustainable supply chain management, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA.
Slack, N & Lewis, M 2010, Operations strategy, Prentice Hall, New York.
Slack, N, Chambers, S, Johnston, R & Betts, A 2009, Operations and process management: principles and practice for strategic impact, Prentice Hall, New York.