Performance management is a cyclical process that is usually aimed at improving the performance of either a performing group or individuals or to further improve good performers. This is meant to deal with the attainment of the core business objectives. Performance management can be used to uplift the standards of a business when it is falling or an already well-performing business to increase its productivity. There are a number of principles that are used in performance management which are illustrated below using examples of the phone call.
Measurement is a major principle of performance management that enables one to establish performance measures for a total sale turnover. The relative performance of the business can be measured using this aspect so as to evaluate those areas which need implementation. Measurable behavioral goals can also be established which are meant to improve the performance of the organization.
This can be compared with current behaviors that are the actual phone calls that are logged.
The second principle is appraisal which enables the owner of the business to compare the behavioral goals with the current behavior which will clearly show the main difference between the two for example when 10 calls are being made per day, eventually it gives a shortfall of 10 phone calls per day.
The appraisal is then followed by action since the difference will help one to bring the actual behavior in line with the goal which will improve the performance for example a revised telephone can be used which will enable more calls to be made by shortening phone calls hence more calls can be made within the available time.
Then the action plan needs to be implemented. The revised script which will increase the number of telephone calls made a day needs to be introduced to telesales people since they can offer training which can support its use that increasing its affectivity.
Lastly, the implemented plan needs to be monitored by ensuring that the new plans are being followed. This can be done by reviewing various phone calls that have been made recently so that one can determine whether the new script is being used or not and check whether it is effective.
After some time, one needs to return to the appraisal stage so that the impact of the change can be accessed on both behavior and performance. This can be done by reviewing the number of calls that are made per day and the amount of sale which has been made.
Performance management is mainly used in two major contexts, that is it can be used to maximize the performance of an individual, team, or entire organization or as a way of dealing with a team is an underperforming organization, this view has been supported in work of Gillen (2007, pp 102-104). Principles of performance management are similar to the two contexts but the way they are implemented is determined by the two contexts. These two aspects help to increase the total output of the organization since underperformance can be raised and if the organization is already performing, its standards can be raised.
In maximizing performance, there is usually a collaboration between the staff and the management. Communication is mainly informal with records written which records the revised target. It is mainly a cyclical process since it is one of the constant improvements. In most cases, it involves the various process of analysis.
Improving poor performers, involves mainly confrontation and the process is usually formal since all the steps which need to be followed have to be written down. The process escalates disciplinary action when one fails to follow all the steps which can lead to termination of employment. Analysis of individual behavior and attitude needs to be done so that one can determine the underperforming individuals.
Performance management tracks performance against target and tries to come up with various ways of improving the performance but not looking at the last performance. One uses the last performance as a baseline to determine the way the organization has been fairing and what needs to be improved. The focus should be towards the future of the business by coming up with an idea of what to do in order to make things better. The aspect of performance management encompasses managing the result or the outcome that the business has already achieved.
Performance management should demonstrate the following aspects
- Have what you are aiming to which will help in setting the objective of the performance management
- Come up with an idea of what to do to achieve your objectives
- Have a way of measuring progress towards your objectives
- Be in a position of identifying various performance problems and remedy for them
Performance management underpins all the processes in various strategic change programs framework. Practice and target are quite flexible and reactive to change which are the essentials of performance management this view has been supported in the work of Armstrong & Baron (2004, pp 43-44). The contribution of activities at all levels determines the effectiveness of performance management. This runs all the way from the top management policy development to effectively run operations.
In most organizations, managers are the ones who are responsible for setting targets and managing performance against those targets that have already been set. Performance from the customer’s viewpoint is monitored by the contract manager whereas service providers provide information on supply performance.
Performance management is quite important in a business and it needs to be integrated into its life cycle since it will help an organization to mature by evolving and changing its measures in performance.
It identifies those opportunities which help in maximizing various improvements that are made in managing service delivery. It helps one to make various decisions on the routes of investment, affordability, and setting up other priorities which are involved in investment to deal with competition.
To manage the results, the organization needs to focus on the level of outputs of all processes and activities that it undertakes at all levels. The outputs can positively contribute to the achievement of the desired outcome by an organization. When the output reaches the desired target, then the organization is following the right trend, and therefore its level of performance is good. A good manager needs to be more focused at to aim higher all the time. When the already set objectives are achieved, one needs to think of the next objective which can increase the level of productivity further.
The effectiveness of performance management is determined by the confrontation of all the activities at all levels of management i.e. from the top management policy development to effectively run operations. The levels which need to be followed are as follows:
l Priorities of an organization: This is the highest level whereby performance management is rooted in the organization’s business strategies. By identifying various organization priorities, one can be able to know which implementations need to be put in place to increase its level of performance.
l Strategic level: The management takes concern of its perspectives both internal and external. An organization can be able to plan for all its procedures both internal and external this view has been supported in the work of Gillen (2007, pp 102-104). The outcome is also measured either in terms of work done or staff and users satisfaction.
l Programme level: Performance management is mainly focused on producing desirable results as a result of a change of program. The already existing program can be changed completely or modified to suit the organizations which are meant to increase the output. These changes should be applied to all levels of performance management. Demonstration of what has been accomplished is done at this level.
l Tactical level: At this level, the management is concerned with output and service delivery by use of conventional service level approaches and other related measures such as volumes and quality. The output is evaluated to determine whether the percentage management plans that were used were effective and the weak areas which need to be revisited.
Despite the fact that various performance measures and indicators are quite different in various levels of performance management, they need to have a direction that will enable one to confirm whether the business or organization is on the right track which will enable it to reach its goals this view has been supported in work of Armstrong & Baron (2004, pp. 43-44).
It should also be quantitative in that it shows how much has been achieved and how much need to be done. Worthwhile is another aspect that is needed since it adds more value to the business. The outcome of performance management is realized by looking at the input that has been applied in an organization which should be compared with the output. In case the input is smaller than the output, then there must be a great failure in the performance management of that organization. Likewise, when the output is greater than the input, there is a great likely hood that the organization’s performance management tactics are applying very well. One should evaluate what is the worthiness of the organization, if it is not realizing any profit or it is stagnant with no improvement, then something should be done to increase its worthiness. These problems are mainly encountered when an organization is not using performance management or the procedure that is used to implement performance management is not effective.
When evaluating performance management one should demonstrate the value for money that has been achieved which is meant to cover three measures of performance.
The economy as a measure of performance is meant to minimize the cost of those resources that are used for any activity in regard to producing the right quality.
In measuring the value for money, the total inputs to the organization should be minimized but the desired product needs to be attained.
Efficiency shows the relationship between the output and input.
Effectiveness shows the extent to which the set objectives have been achieved and reveals the relationship between the actual and intended impact.
In performance management, metrics and measures have to be evaluated so that one can know whether he or she is doing the right thing or not, whether the right measures are being taken, whether these measures are being used in the right way, and whether one is able to determine the quality of a particular performance metric with use of smart test I.e. Specific, Measured, Attainable, Relevant, Timely. To improve performance, the current performance needs to be known which will provide the basis for generating feedback.
One needs to know what is measured since one can end up measuring the wrong thing simply because it is easy to measure which will result in the entire downfall of performance management.
There are many factors that determine the measures and procedures which are used in performance management. The main factor is the type of business processes that are being measured from input to the final product. There are a number of steps that help the organization to improve its performance management so that better outcomes can be realized.
First, one needs to identify the level of an organization’s maturity in performance management. Access what the organization has already achieved so that one can determine what implementations need to be put in place this view has been supported in the work of Armstrong & Baron (2004, pp. 43-44). This is enhanced by looking at the way the organization is performing at all levels and in all the aspects of management. Then access the way the organization is fairing and it will also help in identifying organization maturity, its strength, and weaknesses. Then one should be able to establish what he or she has done and determine the level at which the business has reached, this is done by looking at performance management at strategic program, tactical and operational levels. These areas help the manager to determine which area needs a lot of attention and proper performance appraisal.
The second step involves evaluating where performance management is important for your business. Different areas within the organization need to be studied keenly so that managers should not overlook those areas that require percentage management the most. One should survey different areas of the business and find where this aspect is most applicable. Regular questions need to be asked such as, is it most applicable in setting directions? or ensuring delivery of benefits? or improving alignment?. Then one should identify the value of the business. The areas which need to be considered most depends on the value of the business. One needs to know whether these areas are already performing so that they can aim at increasing the performance or there is underperformance that needs to be improved. The two aspects are handled differently which requires a lot of attention so that the organization will focus on increasing productivity.
The third step resolves any mismatch that has taken place in steps 1 and 2. Performance management is reviewed in the four levels of performance management and a clear evaluation should take place to show whether there are any weak areas that can be sported. The weakness of an organization can be brought about by either poor management or other external factors that inter fear with the output of an organization. One should come up with a clear technique that will enable one to come up with a clear finding. To be more customer-focused, a balanced scorecard or an EFQM technique should be used this view has been supported in the work of Risher (2005, pp 18-26).
Step four involves establishing where you want to be and come up with ways of building performance management in all the processes of the business. This will enable one to come up with a target for the business, have measurement and review processes for business-oriented things such as staff, services, products, and processes. One needs to come up with a number of measures that need to be prioritized against a particular perspective and effectiveness. To accomplish this one should come up with benefits management as a norm and use various databases to collect information and analyze their trends together with performance management in business life cycle and programs.
The final step involved feeding the information that has been acquired to the performance improvement. This is a very important step since it evaluates whether the other steps were implemented effectively. It involves monitoring what has taken place and evaluating whether what was set was achieved, looking for those opportunities which need to be improved and how to improve them this view has been supported in the work of Risher (2005, pp. 18-26). One should also evaluate what is achievable, the importance of the organization, and find out what was finally achieved. This involves active assessment of one’s own target, and look for a benchmark in the outside organizations. When one realizes that the target has been met, then one can come to the conclusion that the performance management was effective.
Performance management is an aspect that focuses on the positive process of the organization and a system that can create a culture in which success is applauded. However, in some instances, poor performance exists. This can be possibly be attributed to poor leadership, improper management, or other systems of work that are defective.
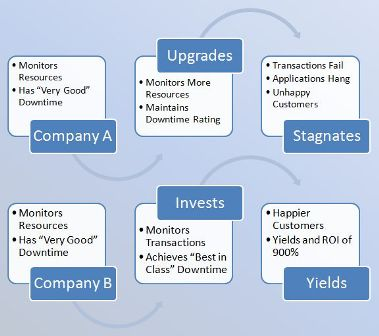
When proper performance management strategies are put in place, great achievement can be realized. A scenario of two companies was considered, a distinct difference was realized whereby the company which applied proper performance management to the one that did not apply any aspect of performance management was noted. For instant, company A has not invested in proper performance management solutions but still, it can be able to have good yields but also it reveals that it has a percentage of the lost revenue. Company B on the other hand used proper percentage management
Solutions this has hence increased the downtime ranking and this has lead to increased revenue.
Therefore, Performance management is basically a term that is mainly used to improve the performance of a team or individual based on its principles of Measurement, appraisal, action, and monitoring. This has been manifested in many different forms depending on its intentions whether to improve good performers or on whether it is meant to deal with the underperforming individual. It applies mainly to individuals, organizations, or groups. It involves a number of stages which when followed effectively can improve the management of an organization thus increasing the total output. It ensures that the organization has worked under certain goals which need to be achieved. This increases the motivation of staff since they will work towards achieving certain objectives.
References
- Armstrong M. & Baron A., 2004, Managing Performance: Performance Management in action, London
- Cunneen P., 2006, How TO improve Performance: Journal of People Management. Vol 12, pp. 42-43
- Risher H., 2005, Getting Serious about Performance Management: Journal of compensation and Review, vol 37, pp. 18-26.
- Gillen T., 2007, Performances Management and Appraisal, 2nd Ed, London, pp. 102-104