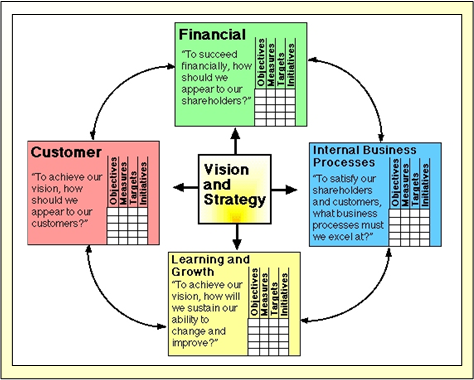
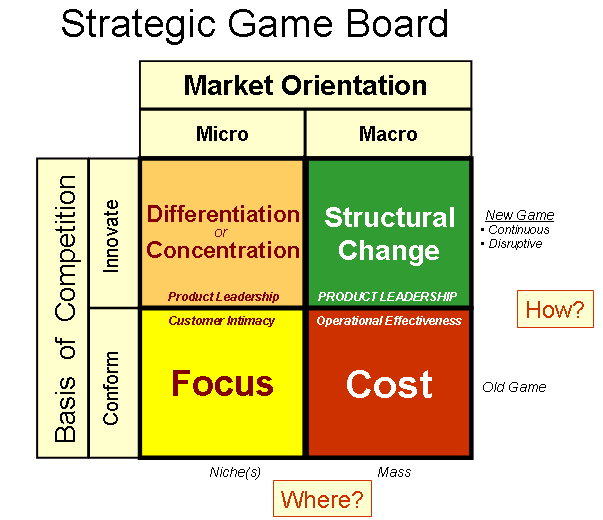
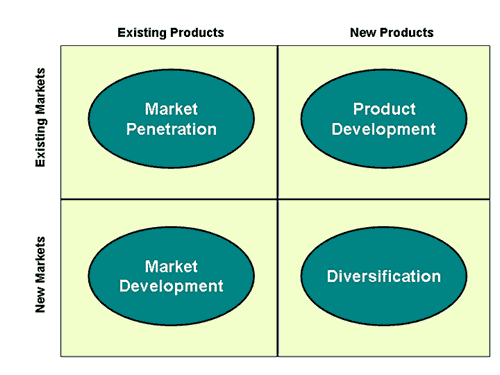
Introduction
Airline industry is one of the profitable industries today and in future. Ryanair is a UK-based company followed the structure of successful Sourthwest Airlines located in the USA. An industry with this kind of rapid change presents several challenges for companies like Ryanair, namely production costs, and monopolies. Production and technology are the primary driving factors of this industry (Drejer, 2002).
At the beginning of the new century, Ryanair looks for ways to deliver customer satisfaction at a lower cost, smaller size, and higher speed. Ryanair is profitable corporation but it will require changes in competitive strategy to remain in an industry and, under some circumstances, it can occasion the decision to exit a business or an industry. The company mission is to deliver high quality services to diverse customers. Its strategy is to expend the business through acquisitions and merges with other low cost carriers in Europe. The company proposes low cost services for business and individual customers.
Environmental Analysis
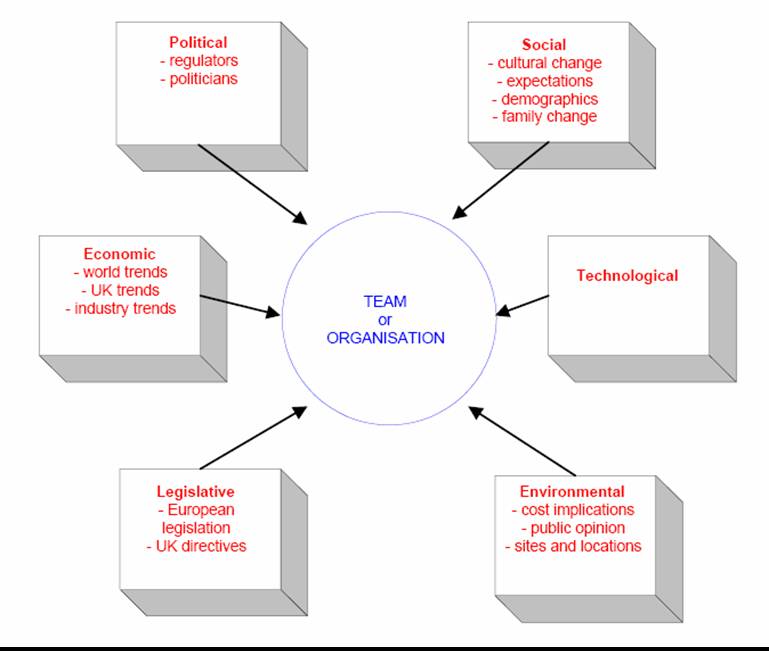
PESTEL
In the UK, political and legal environment is favorable for airline carriers because of stable political situation and protective legal measures. Ryanair operates in high dynamic environment which requires continuous optimization of a product mix and new ways of doing business. Price competition, backed by improved efficiency, is the main feature of Airline industry today. Many UK based companies fight for survival in markets faced global competitor ion.
Within rapidly changing environment, this kind of development ensures that long-term survivors are those firms who are more competitive and are better able to satisfy consumer needs and adapt to the new competitive environment. Ryanair obtains a strong brand image in the Airline industry proposing high quality products. Nevertheless, the weakness is lack of strategic vision, high labor and economic declines (Drejer 2002, see appendix 1).
Economic situation in Ireland has an impact on Ryanair as it reduces purchasing power of such carriers as EasyJet and Aer Arann. Ryanair has to develop new marketing strategy. The implementation will require additional spending, but they are essential for the company, because without these facilities it will not be able to compete on the market and increase its sales rate. Demographic and cultural situation in the country do not have a great impact on the company and its performance. This, increased number of car buyers and investments in real estate market create opportunities for Ryanair to expand its business (Buckley and Ghauri 1999).
In terms of technology and environment, Ryanair relies chiefly on an efficient market system and product improvement. The traditional market for Airline is not in maturity one, and today it offers a limited opportunity for high profits, so it sets about developing products, that are both distinctive and could be sold at a premium price. A specialized product range, based on two basic lines of business, necessitated a clear identification of target market. “Ryanair continued its policy of fleet commonality to keep staff training and aircraft maintenance costs as low as possible, using Boeing 737 planes” (O’Higgins 2007, p. 699).
The original mission had made it clear that it was in the relatively unexploited sector that Ryanair saw its clearest opportunity for innovation. As the most important, these basic lines of business allows Ryanair set out to create a range of high-quality products that are distinctive in quality and technology (Dobson and Starkey 2004).
SWOT
The opportunities of Ryanair include: high potential to growth and profitability of the company; promotion to other segments; improvement of product range. The technological advances are aimed to maximize security of customers and fasten the process of informational interchange. Intranets allow industry to react faster delivering customer satisfaction. Technology replaces traditional methods of Airline business, and causes growth of on-line operations. Improvement of Internet services and Website will help to satisfy the customers’ needs. Ryanair’s low cost approach helps the company to maintain long-run supplier relationships and ensure profitability (Drejer 2002).
“One such measure was web-based check-in from March 2006, and priority hoarding, with over half of passengers availing of this, thus saving Ryanair costs on check-in staff and airport facilities, as well as time” (O’Higgins 2007, p. 700). New technology and organizational management system open new opportunities for Ryanair. Technological innovations and creativity in production can be regarded as business philosophy of Ryanair. Unique technology management employed by Ryanair is aimed to coordinate production process with all levels of the organizational structure including their interaction and performance.
The balance of authority has undoubtedly shifted to traditional management who now has more selection over how it conducts relations with their workers and process. Innovation in production technologies and computerized system of supply chain is the main opportunity for Ryanair. It needs innovative assembly lines in order to increase volumes of sales, and storage capacity. Internet is another toll which can help Ryanair to reach its potential buyers without additional spending on promotion and advertising (Dobson and Starkey 2004).
Weaknesses involve economic problems affected European and Asian countries. Constraints of global economic environment include legal barriers and European law. Many European countries restrict access to those goods which do not meet their standards. This means that goods and materials can be barred access on the grounds that they break national rules on health, safety and environmental protection. Ryanair designed and developed all the products in order to meet international standards and local requirements. Operating on a pan-European basis involves Ryanair addressing the issue of cultural difference and consequently developing a balance between standardization and adaptation (Drejer 2002).
Since the beginning of the 1990s, airline industry decline was the main threat affected many companies. In spite of this threat, Ryanair sustains strong market position and leadership. Also, the threats involve decrease in sales of Airline industry. The changes in the environment are changed the demand, but they do not have a significant influence on customers’ purchasing power. The threat is population shift which has a great impact on sales. Increase in interest rates and non-compete clause are another problems for Ryanair during the last years (see appendix 2,3,4).
Current Problem Diagnosis
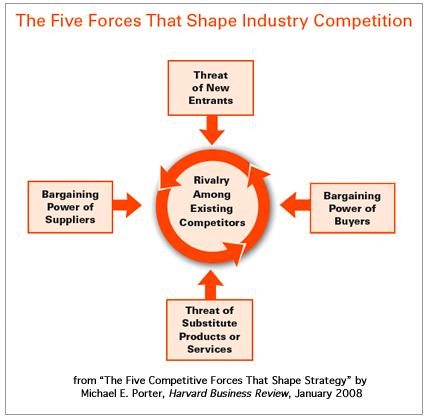
Increased competition on the international arena threatens profitability of such giants as Ryanair. The main problem was that imported Airline accounted for 20 percent of the UK airline consumption which limited price level and competition in the home market. The first group of competitors includes local companies; the second group involves international companies and international competition, and the third one is global competition.
In this case, Ryanair develops multidimensional strategy to cover three competitive segments: local (national), international and global. This strategy involves brand positioning, market segmentation, strategic alliances and value pricing strategy. New competitors may find it difficult to gain access to delivering service, which will make it difficult to provide their service to customers or obtain the inputs required or find markets for their outputs. On the other hand, these ‘mega-Airline markers’ represent the main threat for Ryanair in the UK (Thompson and Martin 2005).
Employees, who have perhaps worked within the traditional system for a number of years, must now learn a new methodology using technology with which they may not be too familiar. Resistance to change often occurs within businesses that are seeking to introduce an Internet component. If it successfully navigates this balance, it will find that it can not only maintain its current position but also expand into new territories and possibilities for profitability/growth
Strategy Formulation
The mission of Ryanair is to reach wider target audience and expend internationally. Vision is that product quality is used as a strategic weapon and the aim of Ryanair is to maintain high quality standards at costs lower than competitors. Marketing strategies are the broad approaches Ryanair intends to adopt in the longer term to achieve its marketing objectives in accordance with its marketing policies. Strategies are developed for the following: The market segments in which Ryanair will concentrate and the marketing position it proposes to adopt in each segment (i.e., the extent to which it positions itself close to a competitor but establishes differentiation through product features and price distinction, or the extent to which it attacks markers established by gap evaluation) (Drejer 2002).
The blend of controllable marketing variables required producing the response wanted in the target market. The mix includes new products, prices, promotion, advertising, field sales and distribution (Thompson and Martin 20050.
Following Mckinsey 7 s model, strong corporate culture is one of the main strengths which help the company to compete. The culture and structure of Ryanair develop over time and in response to a complex set of factors. Usually large organizations like Ryanair have more formalized structures and cultures. Increased size is likely to result in separate departments and possibly split site operations. Another important feature of Ryanair is the non-price competition which takes form of branding, advertising, promotion, and additional services to customers and product innovation. Speaking about the nature of competition it is possible to say that Ryanair has a competition advantage.
Price competition involves businesses trying to undercut each other’s prices; this will be dependent upon their capability to reduce their costs of production. Brand equity represents the added value that accrues to a product as a result of Ryanair’s prior investments in the marketing. Brand equity is thought of as an asset representing the value created by the relationship between the brand and customers over time (Mintzberg et al 2004; see appendix 1).
Evaluation of Strategic Options
Vision of cultural and social values has a direct impact on Ryanair and its market performance. This factor could be interpreted as strength but globalization process and changing international relations show that cultural and social values become opportunities rather strategies for global airline carriers. A solid understanding of cultural preferences is important for any company that markets such products internationally.
Ryanair leverages superior cultural understanding to compete effectively with large foreign firms. It is possible to say that it has an advantage drawing from tradition. Recent years many people are concern about their health and quality of water they use. Industry structure and market position of Ryanair suggests that threat of entry is low. Airline giants like Ryanair resist strongly, so it makes it difficult for new organizations to enter the Airline industry (Grant, 1998). For Airline company ability of a firm to use its resources and capabilities to develop a competitive advantage through distinctive competencies does not mean it will be able to sustain it.
Two basic characteristics determine the sustainability of a firm’s distinctive competencies: durability and imitability. Thus, it ensures that it obtains a leading position and is able to compete with direct and indirect competitors. New economic landscape, Ryanair has to choose a new strategy aiming to address new market and environmental changes. Taking into account current situation, it is possible to say that Ryanair has to develop a completely new vision of its marketing system based on global strategies.
Specification in Ryanair is determined as a result of an organization’s policy, which in turn resulted from decisions on its market policy, which in turn resulted from its consideration of the market or customer needs, requirements, and the activities of competitors. This is the process of designing quality into the service. Sales strategy is on a one-to-one basis (see appendix 5,6,7).
Strategy Implementation
In relation to competitors, Ryanair provides comparable buyer value but perform the activities more efficiently so as to attain a cost advantage, or perform the activities in a unique way which raises the value to the consumer and thus allows them to command a premium price – the concept of differentiation. The activities performed may be grouped into two categories: those associated with the core activities of on-going production, marketing and servicing are referred to as primary activities while those providing inputs, technology, human resources and infrastructure to support the manufacturing function are referred to as support activities. Quite clearly, the primary activities draw on a wide variety of support activities in their on-going management (Gardiner, 2005).
The case of Ryanair market position allows to say that marketing becomes an orientation for the total business, a way of business life. Customers and consumers are perceived as the reason for business existence and their wants and needs become the bases for designing total systems of action. A narrower conception, which is an extension of the business orientation, is concerned with the basic management activities — the entrepreneurial functions-that have to be performed to manage micro-marketing systems. Through marketing, the critical role of consumption is recognized and cultures become reoriented from Producers’ to consumers’ cultures (Drejer, 2002).
Some critics state that the weakness of Ryanair is lack of promotion campaigns aimed to attract new customers, and absence of competitive advantage. High labor and energy costs are the main threat for Ryanair. Economic recessions and industry declines affect Ryanair and its market performance. The role of Strategic Alliances is made all the more complex and thought provoking because of the competition of ideas between different academic and political standpoints.
Ryanair proves that Strategic Alliances are the best form to reach global dominance and reduce competition. So, it creates new opportunities for Ryanair on the global scale. Joint venture is another important part of Ryanair’s international strategy. From the economic side Airline industry has to spend its own resources in order to meet the requirements focusing on technological efforts, security. Ryanair has also realized rapid expansion through capital injections (Gardiner, 2005).
Performance
In order to control performance, Ryanair applies financial measures and statistical control tools. The approach is ‘inside-out’, suggesting that Ryanair is seeking competitive advantage must first examine and develop its own distinctive resources, capabilities and competences before exploiting them in their environment. In the long run, however, it may be possible for Ryanair, through its choice of strategy, to change the strength of one or more of the forces to the company’s advantage.
Taking into considerations the statistical data of Ryanair it is possible to say that it is profitable because the value exceeds the cost of performing various factions which include: financial management, technology management, organization and human resource management, supply and bound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, sales and marketing. Significant variations in national markets originate often in straightforward economic differences.
Ryanair cannot survive just waiting for the customer to come to it. Instead, it gets better at focusing on the specific market segments whose needs match our offerings. The marketing controls consists of the way in which the various component parts and techniques of the marketing effort are combined and varied in order to achieve marketing objectives. Both of these methods are applied successfully to problems of planning and control.
Both are effective tools for specifying, coordinating, and integrating activities, situations, and resources that are interwoven in order to reach project aims on time. The main advantage of these techniques is that they do not require large-scale computers except for complex situations. Managing the organization is therefore not just about managing functions, but managing linkages between those functions. More will be said about the integration of various facets of the value chain in the discussion on implementation strategies.
For Ryanair, technology related products are defined broadly to include both physical products and services. Products are perceived as means of problem solving for both buyers and sellers. The discussion relates to both consumer and industrial goods. Product-line management involves the addition of new products to the line, and the deletion or modification of current products. Product diversification (horizontal, vertical, or heterogeneous), may be the result of internal product policies or mergers.
Reasons for diversification vary from spreading risks to using by-products and increasing profits. New product policies and strategies may be offensive or defensive, convergent or divergent (Drejer, 2002). Ryanair may adopt a followership or leadership posture, and may choose a strategy of segmentation or product, differentiation. By differentiating new products they try to bend demand to meet their supply and so insure a niche in the marketplace.
Each of the new phases of the product- process (conceptualization, exploration, development, marketplace preparation, commercialization, and appraisal), is considered. Technology related product development should be seen as one of the core foundations of corporate planning. Its success or failure shapes corporate destiny. Because of this, particular attention is given to a conversation of new products, technology related products and diffusion processes, the product life cycle, and new-product failures. Channel balance, which is difficult to achieve for Ryanair, must be realized at various levels.
Conclusion
Economic forces affect Ryanair by the impact that they have on market potential and, at any point in time, market actualization. In addition, economic forces in a country may be influenced strongly by the infrastructure that exists, including the communications, energy, and transportation facilities. On a broader scale, the extent of economic development of a market influences the lines of business and methods by which business can be carried out in a country. Infrastructure is affected, as are all types of institutions within the country. Still, Ryanair obtain strong market position introducing new ways of doing business.
Communication, employed by Ryanair, is affected by internal and external environment, by the nature of the task, and by technology. Difficulties in communication can arise with production systems where workers are stationed continuously at a particular point with limited freedom of movement. Ryanair tries to penetrate deeper into current market. International expansion and global strategy is to aim at a particular target market.
One of the main functions of global and international promotional activity is of course to influence the perceptions of the consumer. Ryanair maintain policy of product standardization in order to sell them around the world under the same brand. In order to change and improve current situation, Ryanair should attract more customers and introduce new product lines including related technologies and markets.
This strategy will help Ryanair to survive and remain competitive in spite of market changes and economic crisis. Since buyers are often other-directed, they are concerned with what other group members think of them and their taste. Taste is not an acquired or inherited phenomenon. Consequently, opportunity exists for designers, manufacturers, and marketers to upgrade tastes. Learning implies repetition over time. What may be rejected in product design or color today may be viewed approvingly after a second, third, or fourth exposure.
Bibliography
Barnes, F. C., Tyler, B.B. Ryanair in 2005. Case 23. Strategic Management Textbook. Edit. M. Hitt, R.D. Ireland, R.E. Hoskisson, 7th, pp. 246-267.
Buckley, P.J. Ghauri, P.N. 1999. The global Challenge for Multinational Enterprise. Pergamon.
Dobson, P., Starkey, K. 2004, The Strategic Management: Issues and Cases. Blackwell Publishing.
Drejer, A. 2002, Strategic Management and Core Competencies: Theory and Application. Quorum Books.
Gardiner, P. 2005, Project Management: A Strategic Planning Approach. Palgrave Macmillan.
Grant, R. M. 1998, Contemporary Strategy Analysis, (3rd edn.). Oxford: Blackwell.
Mintzberg, H., Lampel, J. B., Quinn, J. B., Ghoshal, S. 2004, The Strategy Process. Pearson Education.
O’Higgins, E. 2007, Ryanair – the low fares airlines. University College Dublin.
Thompson, J. L., Martin, F. 2005. Strategic Management: Awareness, Analysis and Change. Thomson Learning.
Appendix