Introduction
Nowadays, the organization and the building process of smart cities, in which all the scientific achievements would be implemented, is the topic of multiple discussions. These ideas are widely transmitted in movies, cartoons, and books. Scientists tend to make daring predictions about the lifestyle in the future when an individual will be surrounded by modern technologies, which are designed to relieve the hardships of the daily routine. Although this issue is predominantly full of predictions, hopes, and imaginations, examples of smart cities exist in present-day developments. One of them is Shanghai, which has become “the new developing target of modern city” (Lin et al.). This way, the purpose of this paper is to review Shanghai from the perspective of implementation of technological development and prove that it presents one of the prominent examples of smart cities.
The Concept of the Smart City
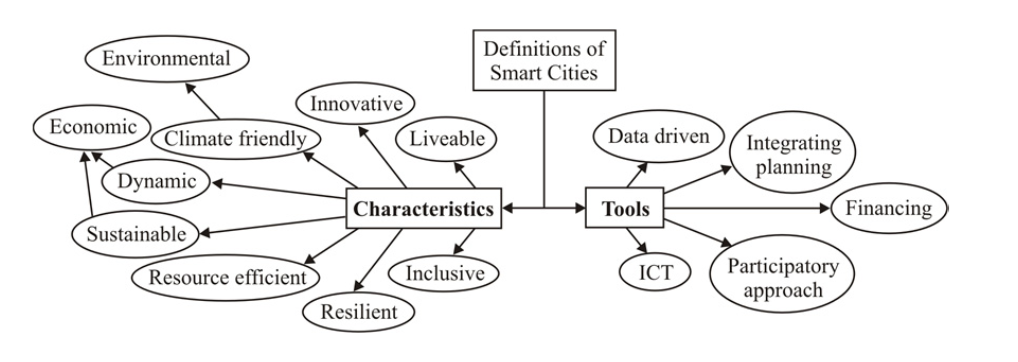
First of all, it is essential to describe the total concept of the smart city in order to evaluate Shanghai correctly. These days, the perception of this term has changed considerably in accordance with the needs of the modern community. Eremia, et al. have presented a comprehensive study in this regard and determined the criteria for the city of the future. They created a table depicted in Figure 1, which contains all the characteristics and tools. The authors mention: “The ISO Standard 37120/2014, titled Sustainable development of communities, defines 17 key indicators for the evaluation of performances of cities from the point of view of ensuring urban services and quality of life” (Eremia, et al. 16). Therefore, the indicators are “economy, education, energy, environment, finance, fire and emergency response, governance, health, recreation, safety, shelter, solid water, telecommunications and innovation, transportation, urban planning, wastewater, water and sanitation” (Eremia, et al. 16). All of them are demonstrated in Figure 1, and it is evident that a smart city should adhere to multiple criteria, which cover all the spheres of life.
The indicators may also involve sub-indicators, which are important for managers, politicians, businessmen, researchers, and people of other professions, who actively participate in creating a smart city. It is also worth noting that there are prior directions of city development, which match the aforementioned indicators. They are erecting smart buildings, which combine the control systems and the advantages of communication, supplying the population with high-quality services in the field of education, medical and social care (Eremia, et al. 17). Other directions imply establishing a smart electrical energy system, smart grid, intelligent management of water distribution and wastewater, parking management via sensors, integrated supply systems, and transport optimization (Eremia, et al. 17). Considering the criteria supplied by the researchers, it is possible to evaluate the city and propose essential changes.
2020 Smart City of the Year
Shanghai is the largest city in China and its financial center is well-known for its tall skyscrapers and modern technologies. SmartCitiesWorld news team highlight that “Shanghai has been named 2020 smart city of the year at the Smart City Live summit, run by Smart City Expo World Congress” (1). The local authorities have stuck to a smart city plan, created in accordance with the specifications of Shanghai, which was intended to be released during 2016-2020. Its focus implies “the development of a range of activities and resources including the deployment of an “intensive” digital Infrastructure, e-government services, a City Brain, and the integration of information technology and industry” (SmartCitiesWorld news team 3). The title of the plan is Smart Shanghai – People-Oriented Smart City.
Digital Infrastructure
The major purpose of the plan is the implementation of digital infrastructure, which is required for achieving the status of dual gigabit. Among other aims are full 5G coverage in the business district of the city, as well as gigabit fiber coverage for the majority of Shanghai. Another useful innovation is e-government, with more than 14.56 million citizens registered of the total 24 million. Winning the Enabling Technologies category with its Digital City – Technology Makes a Better City initiative by its Government Services Data Bureau is among the achievements of Shanghai as a smart city too. It highlighted the improvements in the field of livelihood services and governance capabilities. They are considered to contribute to establishing a city, which includes the implementation of modern technologies, tolerance to other nations, and application of innovations on a regular basis.
There are also other innovations, which were implemented in Shanghai, which should be mentioned. In Cities of the Future, it is claimed that “in the Xuhui District, Shanghai, Huawei, and the Urban Operation and Management Center jointly developed the “12345” intelligent sensing system by using AI technologies” (The 2020 Smart City Award Goes to Shanghai). It is designed for the purpose of analyzing the interrelationship among time, space, and people, which are widely discussed dimensions. It leads to creating “a closed-loop process intelligent awareness discovery, data analysis, and man-machine collaborative handling” (The 2020 Smart City Award Goes to Shanghai). Such innovation allows to address hot topics, predict risks in advance, and supply sufficient information for making the most appropriate decision.
Urban Area Construction
Construction of the urban area is one of the focuses of the development plan of Shanghai too. The overall aim was the erection of IoT, Data Connection, and Intelligent Connection (The 2020 Smart City Award Goes to Shanghai). The building process involves applying innovative design, which matches the world standards. This way, it is planned to establish an Urban Operation Management Center in Huangpu District, using closed-loop operation and modern management models. In present-day developments, the aforementioned area has 15 applications in the fields of public security, public management, public service, and economic operation (The 2020 Smart City Award Goes to Shanghai). In order to establish the competent management of such a megacity, unified network management supports smart city governance in this district.
Ecology
For a significant period of time, ecology has presented a pressing concern for Shanghai. This city has a great number of residents, and some modern implementations may seriously threaten the local environment. For this reason, the government concentrated on addressing this topic by releasing sufficient measures. Such concerns as global climate change and resource constraints have been taken into consideration. According to Cities of the Future, “Shanghai is committed to becoming a more adaptable and resilient eco-city and a benchmark for international megacities” (The 2020 Smart City Award Goes to Shanghai). It regards creating more green places in the city and low-carbon and sustainable establishment of pilot spaces and infrastructures. Therefore, the majority of environmental issues can be solved in the long run.
Economics
Shanghai is the economic capital of China, and the active pace of financial and trade development is one of its major advantages. Another strong point is overseas transport, as the largest world port is situated in Shanghai. Its gross domestic product dimension is the highest one of all the cities of Mainland China. Shanghai has a broad private sector, which occupies half of the economic activity of the city. Therefore, the fact that Shanghai’s market is one of the strongest ones is undeniable (Wang, et al. 91). In addition, its market is popular among private and international investors. It is also the major port for both internal and external trade, and the amount of export and import operations equals 20% of the total dimension for the entire country.
Furthermore, the city contains a free trade zone, which has a world-class infrastructure. It is also home to the service sector, which creates the fourth of the Chinese gross domestic product dimension and equals 40% of the foreign trade (Wang, et al. 84). Apart from that, the Shanghai stockbroker exchange is also situated here. Consequently, the economic development of the city is approaching the postindustrial stage. The most important industries for Shanghai are markets of financial and estate services, wholesale and retail sales, transport, housebuilding, and production.
Conclusion
These days, Shanghai appears to be an illustrative example of a smart city, which every government should be determined to follow. Its development plan resounds to all the requirements, which are presented in the concept of smart cities. It combines a rapid pace of economic growth with addressing ecological concerns. In addition, modern technologies and innovations are widely implemented in the city in order to relieve the daily routine of its residents and improve the quality of their lifestyle.
Works Cited
Eremia, Toma, et al. “The Smart City Concept in the 21st Century”, Procedia Engineering, vol. 181, 2017, pp. 12-19.
Lin, Quan, et al. “The 5I Model of Smart City: A Case of Shanghai, China,” 2015 IEEE First International Conference on Big Data Computing Service and Applications, 2015, pp. 329-332.
“The 2020 Smart City Award Goes to Shanghai”. Cities of the Future, 2020.
SmartCitiesWorld news team. “Shanghai Crowned Smart City of the Year at Smart City Live 2020”. Smart Cities World, 2020.
Wang, Jiang, et al. “Decoupling Analysis of Economic Growth from Water Use in City: A Case Study of Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou of China”. Sustainable Cities and Society, vol. 41, 2018, pp. 86-94.