Cases of suicide among adolescents are on the rise and medical practitioners are concerned about the issue. According to Ballard et al. (2016), these minors are unable to deal with stress as they struggle to understand the realities of life. They believe that the quickest way out of the problems they face is to take their lives. Klonsky and May (2015) argue that some of them even use it to blackmail friends and family, hoping that they will not die in the process. Medical researchers have tried to come up with various tools that can be used to address the problem. The paper focuses on suicide prevention among adolescents using suicide screening as a nursing tool to deal with the problem.
Overview of Selected Evidenced-Based Practice Project
The project focuses on one of the major cases of concern among medical practitioners in the United States. The research has a direct relationship with evidence-based practice (EBP) in the field of nursing. Through the new knowledge that will be generated this study, nurses will be in a better position to offer their patients proper care through improved decision making mechanisms. However, it is important to note the difference between the study and the research. This project is work in progress that may be improved from time to time based on the emerging knowledge. On the other hand, EBP should always be based on experience, patients’ characteristics, and preferences.
The study will make a significant contribution to professional nursing. It will offer guidance to nurses on how to handle adolescents who are suffering from stress. Master’s of Science in Nursing (MSN) program is appropriate in enhancing an understanding of this health problem. As Patterson (2016) observes, EBP promotes change by introducing new information in a given field of study. It will help improve quality of services offered in future family nursing.
Identification of the Nursing Concern to be Improved
According to a report by Klonsky and May (2015), an increasing number of adolescents are now considering suicide as the easiest way of overcoming problems they face in the society. Common incidences are scenarios where they are jilted (Torcasso & Hilt, 2017). Serious bullying has also been identified as a major cause of suicide among this group. The problem is that these youngsters are not psychologically mature to deal with the problem.
Suicide is currently the second leading cause of death among teenagers in the United States, closely after road accident. It is estimated that the annual rate is 1 in every 10,000 adolescent (Linehan et al., 2015). The report also indicate that 20% of girls and 10% of boys aged 12-16 have considered suicide as an appropriate solution to their problems. The problem not only affects the target group discussed above. Other stakeholders such as parents, nurses, doctors, and the government are directly affected by the issue. To parents and family members, they have to undergo the pain of losing a loved one.
Doctors and nurses are finding themselves under undue pressure as an increasing number of attempted suicide victims are brought to hospitals. Some of these patients recover, while others end up dying while at the hospital. The federal government spends a lot of money in educating these youths and it is a major lose when they die young before making major contributions to the country’s economy. Failure to address this problem may have serious consequences.
More youths will consider it the appropriate way of solving problems they have. As Patterson (2016) explains, the solution is to conduct suicide screening to identify those at risk before subjecting them to proper counseling. The solution should be proactive. Nurses should avoid reactionary approach to the problem because the consequences may be dire. The purpose statement for this EBP proposal is to determine the appropriateness of suicide screening as a tool of dealing with the issue where adolescents consider taking their lives when faces with different challenges.
PICO Question and Literature Search Process
When conducting this investigation, it is critical to develop a research question that will guide the process of data collection and analysis. It will ensure that the goal of the study is achieved. The following PICO question was considered appropriate for this qualitative research:
In pediatric patients in an acute health care setting (P) does the use of a suicide assessment tool (I) as compared to a standard pediatric assessment (C) reduce the risk of future suicide (O)?
The expected outcome of this study will be useful to future practice setting because it will establish whether suicide screening is a viable solution to this problem that affects many adolescents. In case it is determined to be an effective tool, it will become a major instrument that nurses in this field will use to handling adolescent patients who are suspected to be suffering from stress.
Literature review will play a critical role in this investigation. As Patterson (2016) explains, a researcher should always strive to introduce new knowledge to a given field of study instead of duplicating an already existing piece of information. By reviewing what other scholars have found out, it will be possible to understand knowledge gaps that need to be addressed in the study. Literature also provided a detailed background of the problem under investigation. It provides the initial information upon which new knowledge is developed. Secondary sources will be identified in two different approaches.
The first step will be to visit the library and select appropriate books and journals relevant to the investigation. The second step will be to conduct an online search. Important medical databases such as EBSCO, PubMed, PsycINFO, Cochrane, MedlinePlus, Google Scholar, The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), and Jstor will be crucial in identifying online journals. Key search terms such as suicide, adolescents, prevention and screening will be used.
Phrases such as suicide prevention, adolescent suicide, and stress management will also be critical when conducting online searches. The EBP proposal is relevant to different specialty organizations such as Association of PAs in Psychiatry, PAs in Critical Care, Society of Emergency Medicine PAs, and Society of PAs in Addiction Medicine (Torcasso & Hilt, 2017).
Theoretical Framework
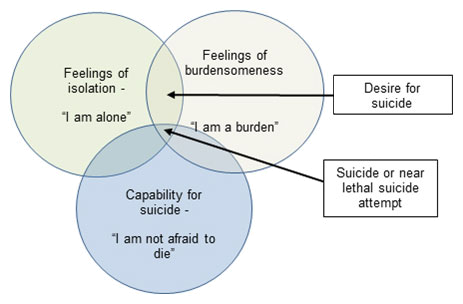
In this study, it will be necessary to embrace a number of theories that can help in understanding the issue under investigation. Theories related to stress and suicide will be particularly important for the research. Joiner’s Interpersonal-Psychological Theory of Suicidal Behavior is one of the most relevant theories in this investigation (Torcasso & Hilt, 2017). It has three main components (factors that may make an individual to commit suicide) as shown in figure 1 below.
The first component has the perceived burdensomeness that an individual feels. These are factors that make one feel that there is excess or undue pressure put upon him or her by the society, family members, or friends. Issues such as the pressure to meet material needs of the family or workplace expectations may put pressure on an individual. Patterson (2016) explains that the perceived burden may be real or imagine.
The most important thing is the feeling that an individual has about the responsibility and expectations that the society has towards him or her. It is dangerous when a person develops a feeling of despair when overburdened. The second factor is feeling of isolation, a sense of low belonging, or social alienation (Torcasso & Hilt, 2017). The individual feels that the society cares for them no more and that they are left to find solutions on their own. The third component is when a person develops no fear towards suicide. Such an individual are capable of suicide because they believe it is the only way out (Patterson, 2016). According to Klonsky and May (2015), an individual with all the three feelings can easily commit suicide. They consider their lives meaningless and that the only way out of their problem is death.
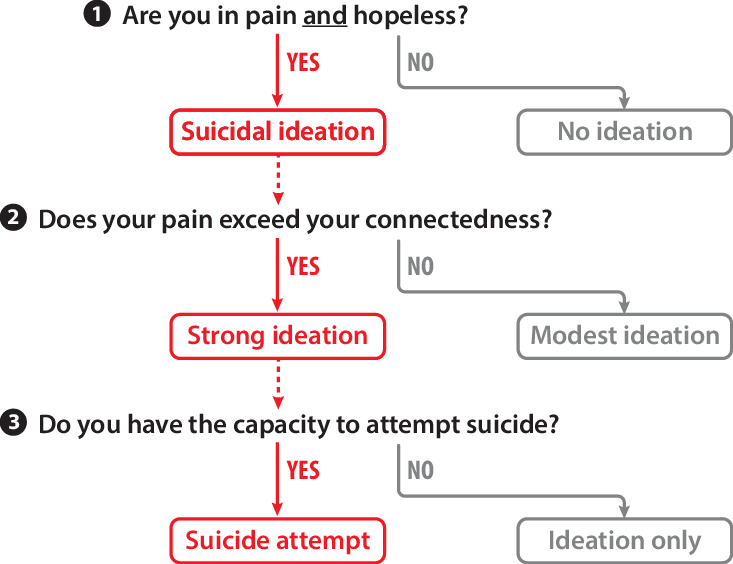
The above theory is also supported by the three-step theory that is based on ideation to action framework. As shown in figure 1 below, it outlines steps that can be taken during suicide screening of patients. The path outlined in red shows an individual on the path towards suicide. Such an individual would need urgent counseling to stop them from taking their lives.
Conclusion
Adolescence is a very sensitive stage of development. Such individuals are struggling with personal identity and sometimes they tend to be irrational. They lack the capacity to deal with stress. Recent studies show that a significant number often consider suicide as the best way of dealing with stress, social burden, and a feeling of rejection.
References
Ballard, E.D., Cwik, M., Van-Eck, K., Goldstein, M., Alfes, C., Wilson, M.E., … Virden, J.M. (2016). Identification of at-risk youth by suicide screening in a pediatric emergency department. Journal of Prevention Science, 18(1), 74-182.
Klonsky, E.D., & May, A.M. (2015). The three-step theory (3ST): A new theory of suicide rooted in the “ideation-to-action” framework. International Journal of Cognitive Therapy, 8(2), 114-129.
Linehan, M.M., Korslund, K.E., Harned, M.S., Gallop, R.J., Lungu, A., Neacsiu, A.D., … McDavid, J. (2015). Dialectical behavior therapy for high suicide risk in individuals with borderline personality disorder: A randomized clinical trial and component analysis. JAMA Psychiatry, 72(5), 475-482.
Patterson, S. (2016). Suicide risk screening tools and the youth population. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing, 29(1), 118-126.
Torcasso, G., & Hilt, L.M. (2017). Suicide prevention among high school students: Evaluation of a nonrandomized trial of a multi-stage suicide screening program. Child Youth Care Forum, 46(1), 35-49.
Zalsman, G., Hawton, K., Wasserman, D., Van-Heeringen, K., Arensman, E., Sarchiapone, M., … Carli, V. (2016). Suicide prevention strategies revisited: 10-year systematic review. The Lancet Psychiatry, 3(7), 646-659.