Introduction
Human resource policies are codified decisions that an organization establishes to support its administrative personnel functions, employee relations, performance management, and management resource planning. This report tries to determine the effectiveness of human resource policies by focusing its study on Qatar (Budhwar & Debrah 2009; Budhwar & Mellahi 2007).
Research question
The main objective of the research is to show how Human Resource Policy (2009) in Qatar has influenced employee migration from the public sector to the private sector and the general economic impact of this (Afiouni, Ruël & Schuler 2014).
The other objectives include:
- to determine stakeholders and employees satisfaction after the implementation of the HR policy in public sectors;
- to investigate level and change in productivity in both sectors (Paauwe 2009) as influenced by HR Policy introduction;
- to investigate the impact of the HR Policy on the components of the economy in all sectors;
- to address the limitations of labor markets and their effects on employment choices in public sector;
- to determine the relationship between salary and education level in both sectors (Dougherty 2009);
- to investigate the challenges facing the HR Policy implementation and possible solutions.
Context of the study
The human resource departments play a vital role in the development of national economic stability. According to Al-Hamadi, Budhwar and Shipton (2007), human resource departments play vital roles in modern corporations. They determine how productive the organization will be in its market or if it will meet its objectives. A properly instituted human resource management contributes to a successful industry (Grama & Alexandru 2011).
An example is how Microsoft Incorporation began its operations in the U.S. market from nowhere to being the economic powerhouse. Indeed, human resource policies have a great effect on job satisfaction because they improve the productivity and development of any country (Al-Yahya 2010). It is the mandate of any researcher to contribute to his country by measuring job satisfaction concerning the new HR policy and to suggest effective professional solutions (Harry 2007).
Methodology
The research sample will be random. This gives an equal chance of selection to every organization all over the country. This includes employees, key stakeholders in private and government institutions, and Non-Governmental Organizations (Iles, Almhedie & Baruch 2012). According to Jacob (2012), a minimum sample size of 30 is appropriate. The following formula is used:
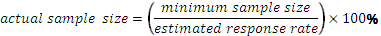
Draxler (2010) estimates an approximate response rate of 30 percent, which gives a sample size of 100 respondents. The methodology will involve the collection of secondary data from the New HR Policy Manual (2009) and from published and unpublished materials such as articles, business journals, newspapers, and periodicals, which support the research objectives results (Williams, Bhanugopan & Fish 2011; Terrell 2012).
Primary data collection will be in completion with the help of interviews and questionnaire responses from employees, key stakeholders in private, semi-private sectors and Non Governmental Organizations. The questionnaires will be either closed or open-ended.
Requirements for study
The interpretation of the quantitative and qualitative data from these surveys is to discuss and examine the hypotheses of the research. Comparison of the results with the existing body of knowledge in published literature will broaden the interpretation. Qualitative analysis will help identify key policies that would sustain the diversification of the labor market. A deductive research approach is preferred to review, gathering of information, and draw conclusions to support the findings (Levi 2012; Filliâtre, 2011).
Outline program of work
While the primary area of examination lies within strategic management of human resources and expectations of policy application, the researcher will not look into the effect on productive output but rather on the extent of achievement of the human policy. The paper aims at examining the HR policies of organizations in the quest to achieve their strategic plans (Yaseen 2013). The high investment of resources into the development of Qatar is so intensive that questioning is inevitable.
In summary, the aims of the research are:
- to investigate employee’s job satisfaction with the formulation of the HR Policy;
- to determine whether or not the productivity of employees has been changed or affected by these new HR policies;
- to determine whether the HR policy is able to stop the migration of highly skilled employees from the public sector;
- to compare between the reformed government sector and other sectors in job satisfaction according to the implemented HR policy (Paauwe 2009).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the results expected from the research will have a strong influence on the case study in Qatar, which will have great importance to scholars. The Gulf Region and Qatar are among the countries with the fastest-growing economies (Jreisat 2009). A properly written thesis will incorporate the core elements of HR policy in the New Qatar HR Policy Manual 2009. This will meet the expectations and objectives of the study (Ali 2010). According to Chen and Chuang (2013), the critical features it is bound to explain include organizational, personnel, labor and industrial management. Therefore, the most appropriate title of the thesis report would be, “The Role, Challenges and Solutions to Human Resource Policies in High Growth Economies: A case study in the State of Qatar”.
Reference List
Afiouni, F, Ruël, H & Schuler, R 2014, “HRM in the Middle East: toward a greater understanding”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 133-143.
Al-Hamadi, A, Budhwar, PS & Shipton, H 2007, “Management of human resources in Oman”, International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol.18, no.1, p.100.
Ali, 2010, “Islamic challenges to HR in modern organizations”, Personnel Review, vol. 39, no. 6, pp. 692 – 711.
Al-Yahya, K 2010, “The over-educated, under-utilized public professionals: Evidence from Oman and Saudi Arabia”, Journal of Management & Public Policy, vol. 1, no. 2, pp.28-47.
Budhwar, P & Debrah, Y 2009, “Future research on human resource management systems in Asia”, Asia Pacific Journal of Management, vol. 26, no. 2, pp.197.
Budhwar, P & Mellahi, K 2007, “Introduction: Human resource management in the Middle East”, International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol. 18, no.1, pp.2-10.
Chen, S & Chuang, C 2013, “Human resource management practices and organizational social capital: the role of industrial characteristics”, Journal of business research, vol. 66, no. 5, pp. 678 – 687.
Dougherty, C 2009, A Comparison of Public and Private Sector Earnings in Jordan, International Labor Office, Geveva.
Draxler, C 2010, “Sample size determination for Rasch Model Tests”, Psychometrika, vol. 75, no. 4, pp. 708 – 724.
Filliâtre, J 2011, “Deductive software verification”, International Journal on Software Tools for Technology Transfer, vol.13, no. 5, pp. 397 – 403.
Grama, C & Alexandru, G 2011, “promotion of human resources in modern organizations”, Land Forces Academy Review, vol.16, no. 2, p. 175.
Harry, W 2007, “Employment creation and localization: The crucial human resource issues for the GCC”, International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol.18, no.1, p.132.
Iles, P, Almhedie, A & Baruch, Y 2012, “Managing HR in the Middle East: Challenges in the public sector”, Public Personnel Management, vol. 41, no. 3, pp. 465-492.
Jacob, W 2012, “Research Methodology”, Vision, vol.16, no.1, p. 73.
Jreisat, JE 2009, “Administration, Globalization, and the Arab States”, Public Organization Review, vol. 9, no.1, pp. 37 – 50.
Levi, I 2012, “Deductive closure”, Synthese, vol. 186, no. 2, pp. 493 – 499.
Paauwe, J 2009, “HRM and Performance: Achievement, Methodological Issues and Prospects”, Journal of Management Studies, vol. 46, no.1, pp. 121– 134.
Terrell, S 2012, “Mixed-Methods Research Methodologies”, The Qualitative Report, vol. 17, no.1, p. 254.
Williams, J, Bhanugopan, R & Fish, 2011, “Localization of human resources in the state of QatarEmerging issues and research agenda”, Education, Business & Society: Contemporary Middle Eastern Issues, vol. 4, no. 3, pp.193.
Yaseen, Z 2013, “Clarifying the strategic role of the HR managers in the UAE educational institutions”, Journal of Management and Sustainability, vol. 3, no. 2, p. 110.