Abstract
The research report is based on judging whether or not the Marketing Mix is a valid option used in companies for marketing purposes or not. The detailed study takes reference from multiple sources which include credible authors’ research papers and one to one interview. The marketing mix model has been elaborated to 7P’s now compared to its older version of the 4Ps.
There are multiple variations in the research report that can be found at different sources. But 7P’s are the most readily accepted new outline of the marketing mix model. We can clearly see with reference to real life examples that how frequently marketers use the marketing mix to plan. It has become a significant tool in the marketing industry today.
Introduction
Background of the Problem
How can we define marketing? The meaning that a lot of marketers study as they begin out in the business is:
“Placing the right product in the correct place, at an appropriate price, at the correct time.”
One only needs to make a product that an exacting group of populace wants, put it on retailing at some place that that populace visits frequently, and value it at a level which competes the worth they sense they get out of it; and do all that at an occasion or time they desire to pay money for that product.
There are many facts in this thought. Though, a lot of hard labour needs to go into judging out what clientele want, and recognizing where they do their shopping. Then you are required to shape out to create the thing at a cost that is worth to them.
But if you obtain just one constituent incorrect, it can result in a mess. You might be left endorsing a car with astonishing fuel-economy in a state where petroleum is very scarce or highly priced; or bringing out a course book after the beginning of the new school year, or advertising a thing at a price that’s too high to afford – or too near to the ground – to attract the potential customers you are targeting.
When one is viewing all the way through your tactics for a manufactured goods or service, the marketing mix is what one needs to be good at as it assists you avoids these types of errors (Mind Tools, n.d).
Research Objective
The objective of the research is to deeply analyze the validity of the marketing mix model – also known as the 4P’s model. This research will aim to examine the strengths and weaknesses of the marketing mix model and assess why the attention of most marketing experts as well as text books is focused specifically on Product, Price, Place and Promotion. The report will also strive to analyse the criticisms of various marketing experts and authors of what is considered to be the one of the fundamental pillars of the marketing subject.
Significance of the Research
A thorough research into the established theory will serve to re-examine the rationale of the marketing experts from a modern perspective. It will enable a better understanding of the theory for marketing students and help understand its strengths and weaknesses. The research will also allow a comprehensive look at the 4Ps of the marketing mix as they apply to the international environment. This will serve to enlighten international students as well as teachers of marketing and convey an in-depth analysis of the theory as it applies to their situation.
The research will also critically analyze the thoughts of famous marketing authors on the marketing mix framework and observe the application of the model by major international firms to formulate effective marketing strategies.
There are various authors who criticised the model which is deeply rooted in the marketing practice. Later, the research paper will be discussing how the model was revised by different authors to make it more adjustable in the era of relationship management by adding different other elements to the model.
Statement of the Problem
The nature of the problem in this research report will be based on viewpoints of different writers and the masses. It is evident that different people relate different importance to the validity of the marketing mix. We need to determine;
“Whether or not the marketing mix model is valid for marketing purposes?”
Literature Review
Introduction
This chapter will be discussing the history of the marketing mix model. A critical analysis of the idea of marketing mix will take place and its origination will also be discussed. Also, the revision of the model by different western authors in the last few decades will also be taken into consideration. In the last few years number of marketing authors also raised their voice against the validity of the marketing mix model; however, in the chapter 1 major critics of the model will be analyzed in detail. And lastly will be discussing how authors added different Ps, Cs and Ds to make the model more suitable for the business environment.
History of the Marketing Mix Model
Marketing Mix History
Marketing mix is one of the significant topics in marketing. The thought of this expression is created back in 1948 by James Culliton, he said marketing judgment should be the consequence of somewhat like formula. It is similar to the eating places which present the same recipe but the clients always go for better or the delicious ones. The idea of recipe was further sophisticated by Neil Borden and made up as the term ‘Marketing Mix’. In 1960′s E.Jerome McCarthy detailed in more particulars by categorizing the term into 4Ps idea which are product, price, place and promotion.
The marketing mix model well known as the 4P’s considered to be the most acceptable and famous generic model among marketing practitioners and marketing educators. The 4Ps model is categorized under the headings of Product, Place, Price and Promotion by McCarthy in 1960 and since then this concept has been a part of a vast majority of marketing courses and programs. This model is assumed to be a fundamental step towards effective marketing strategies. The 4Ps that is the product, pricing, placement and promotion are all embraced/included within the marketing mix model.
The origin of the model is similar to the other theories and concepts that exist in the field of marketing and it roots out from the business and management authors and educators in the USA during the period of Second World War. The economist Neil Borden introduced the idea of marketing during his presidential speak to AMA (American Marketing Association) in 1953.
In 2009, Neil Borden, quoted that the phrase was recommended to him from a section in research bulletin, authored by his associate, Professor James Clinton (1948) on the subject matter of marketing cost. This subject matter related to manufacturers’ marketing cost, in which he narrated and termed business executives as a “decision maker”, an “artiste”- a “blend of ingredient”,” who follows a pattern laid by others, who sometimes develops his own patterns as he move along, sometimes instantly adapt to the elements available, and sometimes tests and creates elements never tried before. His idea of calling marketing executive a blend of ingredients was very attracting for him, one who is regularly consumed in tailoring innovatively a mixture of marketing procedures and policies in its attempts to create profits for enterprise”.
What is Marketing Mix?
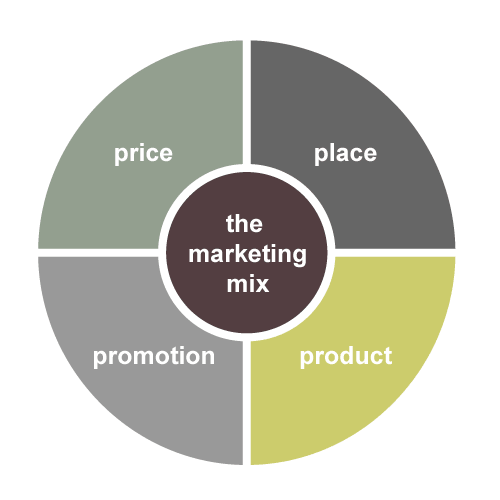
Marketing mix is the term used for the outcome which appeared out as the effect of amalgamation of 4P’s to rouse the demand of firm products and services. Marketing mix can be as well be explained as planned, calculated and controllable marketing instrument containing product, price, place and promotion use by the corporation to produce reaction from target market.
Marketing Mix Variables
Product
Products are merchandise and services offered at a price by a corporation to the target market. Marketing mix is used in a diversity of ways by corporations to motivate potential customers and customers to buy and make use of their products. The diversity of alternatives that companies can use came out from only four variables product, price, place and promotion. Some firms like product to be the focal point so they will use up more on product wrapping, quality, design, brand name and service, to offer high brand products and services to target market. Such as Mercedes Benz is a luxurious car, but has its own place market populace who feel pompous to buy and drive the car just for the reason that of the product is totally differentiated from their opponents and has many features.
Price
Price is a quantity which client pays to buy the goods and services. Price can also be a focus for customer towards certain products and services such as Southwest Airlines offer low price services to their customers by offering normal service. It means they want to segment the target market on cost differentiation not on product differentiation. The price variables encompass the following factors such as; list price, discounts, payment periods and credit terms.
Place
Place allows the firm to spread their products for the clientele. It is the physical location of the product and its availability. Physical survival is not the only criterion of place but virtual companies and businesses like Amazon and EBay are also the fraction of third P i.e. place. Wal-Mart with the huge number of retail outlets around the world moves them to the number one company in the world.
Channels
It continues living today, with the internet, additional channels than in what went before but on the whole, you have to think about three most important channels:
- Selling to the clientele: Whether you put up for sale by hand (as retailer), whether you make use of a sales team, you are, in these instances, in direct contact with the ultimate client. There are no disinterested party between you and them. Regrettably, with the exception of the retailer trade, this state of affairs is far to be the common case.
- Selling to the vendors: You produce the fun boards and you sell them to the Arizona retailers. This practice could be a bit complex.
- Selling to the wholesalers: For example, there are perhaps four or five sport articles wholesalers in Arizona. You sell your fun boards to these big men. On turn the wholesalers sell the fun boards to the retailers which finally sell to their clientele.
In the case of Pacific Boat which produces its boats in Philippines for clientele situated in the USA or in Europe, there is no substitute ways to sell the product. It will be obliged to put on the market through some big import export business. Pacific boat has not any contact with its ultimate clientele but of course it will be obliged to be acquainted with precisely their profile. If the item for consumption does not fit to the profile of the ultimate client, the customers will not pay money for it.
As you can see, the alternative of your distribution channel a great deal depends on your item for consumption and place in the industrious procedure.
Promotion
Promotion comprises of a set of methods used for communicating with the clients. The other 3Ps (product, price and place) communication is conveyed via the 4th P (promotion). The target market feels content to know concerning the new product and services offered to them. Price factor in marketing mix includes the subsequent factors; channels, coverage, assortments, locations, inventory, transportation and logistics (Sooper Tutorials, 2009).
Marketing mix perspectives
There are two perspectives of marketing mix one is from buyer point of view and other is from customer point of view.
Retailer marketing mix
The corporation see themselves as the vendor of the product the above conversation about the 4P’s tells the payback of the vendor not the client.
Buyer marketing mix
Buyer looks at the offering not with respect to the 4P’s, but buyer is probing for a way out within the product if the needs and wants are met then first P(product) match the customer first C (customer solution). Buyer for all time desires to get a good retail price for the manufactured goods to boost his profit margin, but it’s not the obsession most of the customers are really bothered about. What they are looking for is cost of the product which they have to pay by obtaining, using, preserving, stocking up and disposing the product. The second P (price) should take care of second C (customer cost) will lead the product towards the success, since the client will experience ease in buying the product at good market price.
Companies offer their product at many locations, which does not signify that their accessibility is high. In-depth analysis is necessary before choosing the location for placing the products and services (MBA-Tutorial, 2009). Companies must keep in mind the third customer C (convenience) for the buyer third P (place).
Definitions of marketing mix model
Authors such Watershoot & Bulte C, (1992), Kent (1986), Harvey et al., (1996) have also reiterated and described how the Neil Borden introduced the idea of marketing mix in various marketing journals. Therefore, Borden’s idea was that the marketer is the one who mix different ingredients (Product, Price, Place and Promotion) properly to make the business operations profitable.
This concept was embraced by many business and management’s authors over the period of time and developed further modifications of marketing mix model. (Frey, 1961) suggested that the factors involved in the marketing decision making strategy should be divided into two different parts firstly the offering must includes Product, Packaging, brand, price and service and secondly, the method or tools to offer the product should includes distribution channel, personal selling, advertising, sales promotion and publicity. One year later Lazer and Kelly further divided the marketing decision making into three parts and proposed the goods and service mix, distribution mix and communication mix which according to them are the key elements for marketers to make decisions. They proposed marketing decision variables for marketers, teachers, students and consultants to simplify the complexity involved in the marketing decision making activities.
McCarthy (1960) further reduced the marketing decision variables to 4Ps model which consists of Product, Place, Price and Promotion. He explained the 4Ps model in detail in the first ever marketing text book known as “Basic Marketing: A Managerial Approach” written by himself. According to Kent, “Both McCarthy and Kotler established themselves as high priest of the faith in his period” (Kent, 1986). It means both McCarthy and Kotler & Armstrong (2006) have played an important role in the popularity of marketing mix model. The process of adding and reducing factors does not end here, many authors such as Waterschoot and Van Den Bulte 1992, Harvey et al 1996 and Constantinides, (2002) have already suggested in their articles to add more Ps, or Cs, or Ds to make the model more effective. However, there are number of marketing writers who also argued the validity of the marketing mix model such as Kent 1986:148, Watershoot and Van Den Bulte which will be discussed later in the section of main criticisms of the Marketing Model.
The most recent marketing textbook, published in 2010 and written by Jobber (2010) Principle of Marketing explains the 4Ps as “one of the major concept in modern marketing”. 10 out of 20 Chapters in the book have been devoted to explaining the usefulness of the marketing mix model. Moreover, the fourth European edition of Kotler et al Principle of Marketing dedicated almost half of the book to explain the practical implications of the marketing mix model. Other authors such as David Jobber’s in his book the Principle and Practice of Marketing describes the model as a core concept.
It has been noticed that almost all marketing and marketing management text books describes the benefit of using Marketing Mix Model in marketing. But amazingly none of them provide explanation about how this model emerged, how it has been developed and modified over the years and notably is there any evidence to the continuation of the practical use of this theory. Therefore, after reviewing the history of marketing mix one can easily understand the reason for developing marketing Mix theory and evidence to support its continued application to marketing theory. This theory was developed as a basic tool for marketers, students and advisors to explain the complexity involve in the field of marketing.
The first marketing textbook by McCarthy, title of the book “Basic Marketing: A Managerial Approach” already revealed the fact that 4Ps were developed as a marketing management tool. The marketing mix model was invented almost five decades ago. Although over the years it has been challenged by many marketing writers, yet no writer has come close to forming a theory as acceptable in the field of marketing as the marketing mix. In 2002, Constantinides wrote a very famous paper “The marketing mix revisited: Towards the 21st century Marketing” in which he further insisted on the elimination of the limitations and said that there is need for further research (Answers.com, n.d). These remarks are discouraging and illustrate that these models have various flaws which have not been eradicated even after 50 years and challenged the value of the model (Jones, n.d).
Criticisms of the Marketing Model
Previously the history of marketing mix model was discussed. Now we direct our attention to the criticisms of the 4Ps model. According to Masterson & Pickton (2010), McCarthy’s invention of the 4Ps classification has already received a great recognition in the last decades. However, in the last few years a numbers of marketing professors and marketing practitioners raised their concerns against the validity of the marketing mix model. According to Waterschoot and Van den Bulte, “You are right to question the classical principles. All principles should be subject to the closest examination, both the logic and the factual relevance” (Watershoot & Bulte C, 1992) Philip Kotler in Waterschoot and Van den Bulte 1992 also recognized the need to develop better classification of marketing mix model.
However these marketing educators and researcher addressed the issues and criticized the marketing mix model but yet we are far behind in developing a better conceptual distinction among the large variety of marketing decision variables. Economists and social scientist have been trying to develop useful marketing theories in the past decades and but nobody could develop a general theory. Many general theories that we can hold up today in the field of marketing are either restricted to a specific situation or product category.
According to Goi (2005) the best theories are considered to be those which can be applied to predict the results of certain actions. The theories of physics and chemistry are very useful to predict the consequences of certain action or phenomenon. For instance the theories in physics can easily predict the speed with which an object falls to the ground and same is the case of chemistry we can easily predict the results of the chemical reactions of atoms and molecules. But unfortunately no one could develop such a theory in the field of marketing which has tendency to predict the results. Furthermore current marketing theories are more helpful after the fact “diagnosis”. According to Goi (2005), authors felt the need to develop predictive theories in the marketing and said that marketing educator’s are not devoting time to develop such a theory. Marketing as a course are being taught in many universities in the world and marketing practitioners are designing marketing strategies using (Product, Price, Place and Promotion) without realizing the limitations of the mix.
As we already mentioned above many authors in the field of marketing raised their concerns about the marketing mix model. At this point in time we will address the main criticism of the marketing mix model which is considered to be the most useful or significant invention in the area of marketing. Everyday marketers make decisions on the basis of 4Ps, without realizing that the decisions they are making could not be empirically tested and verified. In 1960, when McCarthy introduced the marketing mix model he was not even aware of the fact whether this model is developed in scientific terms or not.
Masterson and Pickton argued that 4Ps model has three major flaws and all three are very much linked to each other. The marketing mix model is systematically weak and it does not suggest to marketing practitioners and student how different ingredients such as (Product, Price, Place and Promotion) are being mixed and whether these variables interrelated with one another or not Masterson & Pickton (2010), Masterson and Pickton (2010) and Fitchett, (2010). Authors stated: to their comprehension the classification of elements for differentiation of the four categories termed “product”, “price”, “place” and “promotion” have never been explained… albeit casual examinations of students, textbooks and practitioners proposed a broad agreement to categorize elements of marketing mix in identical groups, the deficiency of any proper and exact specification of the elements or traits according to which these elements of the marketing mix should be explained is a key mistake”.
According to Fitchett, this criticism of marketing mix can be understood from this example: A marketer is a chief, to make the final product delicious. He needs to have a list of ingredients specifying both the quality and quantity, any of the ingredients should not be replaced with other ingredient and the amount of ingredients should be balanced in the recipe. If anything is unclear or missing or unbalanced the final product will be weak. Hence, when a marketer is not sure about what is being mixed and how the ingredients are interrelated with one another, the decisions based on marketing mix are completely worthless.
Another criticism raised by Waterschoot and Van den Bulte is that each of the four Ps is not mutually exclusive. The sale promotion, a sub category of Promotion cannot be separated from the other advertising and personal selling subcategories and same goes for the other categories of 4Ps such as Product, Price and Place. Kent 1986 also had reservations on the marketing mix model. And he argued “The listing of the “product” as one of the four Ps separate from the other three implies that price, promotion and place are not “product” decisions. However, products price is its price, products promotion is its promotion and its distribution is its place. They all are product decisions.” So both Waterschoot et al 1992 and Kent 1986 agreed that the elements of the marketing mix are not mutually exclusive.
The Marketing Mix Framework Revisited
Previously we were discussing the limitations of the marketing mix model. Now we will be analyzing how marketing mix is being revised and developed over the years. According to Goi, over the couple of years the marketing mix classification has been refined and as a result many marketing educators suggested adding one or more Ps, Cs and Ds to McCarthy’s invention. According to Zineldin & Philipson (2007) at the era of relationship marketing, the managers are being pressured to satisfy customer’s needs and wants, recognizing the importance of building long term relations with profitable customers, keeping all this in mind, right now seems to be the perfect time for marketing managers and authors to address the limitations of the marketing mix framework.
Despite the history and current status of the 4Ps model several authors have questioned the future acceptance of marketing mix model and proposed to further modify the model by adding few more Ps, Cs and Ds. According to Constantinides, it has been argued that the marketing mix only addresses the micro issues, as its ultimate focus is on seller’s perspective not customer. As a result in 1984, the Kotler suggested to add more elements to the marketing mix such as “Customers”, “Environmental variables”, “Competitive variables” and two addition Ps “Political power” and “Public opinion formation”. In 1991 Robins advised to overcome the problem of the lack of customer orientation in the marketing mix model further and recommended to add fours Cs such as “Customers”, “Competitors”, “Capabilities” and “Company”. In order to enhance the customer services aspect in 4Ps model, Doyle in 1994. advised to add two extra variables like “Service” and “Staff” to the marketing mix Moreover in the case of service marketing, relationship marketing, service marketing, retail marketing and industrial marketing additional Ps, Cs and Ds have also been added to develop an effective decision making tool.
According to Goi, (2009), Watershoot et al 1992, further divided the mix into three categories such as “Mass Communication Mix”, “Personal Communication Mix” and “Publicity Mix”, to improve the promotional aspect of marketing mix decision. Mass communication includes: Advertising, Exhibitions and Sponsoring, Personal Communication consists of: Personal efforts to create the awareness and knowledge about product or services and last but not least the Publicity focuses on Press Bulletins, Conferences and trips for media officials. Harvey et al (1996) also suggested adding additional 5Ps. According to Hyman in Goi to make a model valuable, it must have 8Ds. However, the question is that even after adding more elements to the marketing mix model, can it manage to get rid of its major limitations. The answer seems to be “No” because until or unless we design a theory which is not restricted to a specific product category, predictive, empirically verified and tested and mutually exclusive the problem still persists. Hence the real question seems to be the actual need of the model and if it does not manage to deal with all of these problems then why don’t we abandon it completely.
According to Masterson et al although the marketing mix model has been criticized in the last few decades but for a marketer it is impossible to imagine marketing without 4Ps (Business Knowledge Source, n.d). The 4Ps model is deeply rooted in the field of marketing and it is unlikely to think what marketing would be without 4Ps. It has been argued that marketing mix model “has become an abstract idea” which helps marketers to explain complexity involved in the area of marketing (Rafiq & Ahmed, 1995). Moreover, the marketing mix model will keep helping marketers to provide a comprehensive explanation of marketing. Due to all this the marketing mix model will always considered to be the core principle of marketing idea and will be taught in the universities and is also being practiced by marketers. One could also argue that no matter whether the 4Ps is a good or bad theory but until or unless it helps the marketers in their everyday marketing practices, we cannot leave it as an outdated concept. The marketing mix model is also considered to be constructive theory as it also helps non marketers to understand the marketing jargon (Constantinides, 2006).
After analyzing the current literature on marketing mix one could argue that the marketing mix model will stay alive until or unless someone comes up with a new idea or theory which can replace the marketing mix. Presumably it seems to be very difficult, as no one could develop such a theory even after fifty years of the invention of Mix. In the management department of various universities, the marketing mix is being taught to students as a useful manager’s tool. Moreover our future marketers will assume the 4Ps model as a valid theory.
Marketing Mix Modeling
Commerce magazines and websites are filled with information concerning the worth of marketing mix modelling as a method to assist corporations make the most of returns on their marketing investments (ROMI). In spite of the coinage of this subject matter in the medium, the facts and gears of marketing mix representations are at least 30 to 40 years old. The issue is of increasing attention partially for the reason that of the business world’s attention in growing top line returns. The last couple of decades have witnessed unparalleled cost cutting and staff cutbacks in the middle of the Fortune 500 in the U.S. The chances for further cost cuts are deteriorating in figure and extent, so the force for long-term monetary performance from civic markets can only be met by rehabilitated importance on few products and revenue expansion.
A second motive for the on the increase interest in marketing mix modelling is the propagation of new medium (i.e., new habits to pay out the advertising financial plan), together with the Internet, online centre of population, search engines, occasion marketing, sports marketing, viral marketing, cell phones, and text messaging, etc. No one knows how to precisely gauge the possible worth of these many recent habits to use up one’s advertising dollars. To raise income and profits, corporate decision-making need to comprehend the sorts of advertising savings that are most probable to create feasible, long-term proceeds expansion.
That is, what mixture of marketing and advertising savings will make the maximum sales expansion and/or get the most out of proceeds? Eureka! Marketing mix modelling may make available some answers to this demanding trouble.
What precisely is marketing mix modelling?
The expression is far and wide old and practical unsystematically to a broad series of marketing models used to weigh up different mechanism of marketing tactics, such as advertising, promotion, packaging; media heaviness levels, sales force statistics, etc. These models can be of a lot of types, but numerous regressions are the life blood for the most part marketing mix modelling. Regression is foundation on a variety of inputs (or self-determining variables) and how these speak about to a result (or dependent variable) such as sales or proceeds or both. When the model is constructed and acknowledged, the input elements (advertising, promotion, etc.) can be manoeuvred to establish the total result on an organizations sales or returns. If the head of an organization recognizes that his sales will move in an upward direction that is U$10 million for each $1 million he puts on an ad campaign, he can quickly measure if other advertising ventures make monetary sense. But in a holistic view, a thorough knowledge of the elements that triggers sales and returns in an upward direction, it is mandatory to come up with a result oriented strategy for the company. This establishes that the not only the marketing mix model provides a path for making different marketing choices and transactions, but it also helps in establishing a refined base of knowledge pool to steer strategic planning.
From a theoretical viewpoint, there are two major strategies to follow in marketing mix modelling. The two strategies are longitudinal and cross-sectional. In longitudinal analysis, the business appears at trade and proceeds in excess of a figure of time era (months, quarters, years), evaluated to the advertising input in every of those time stages. In the cross-sectional approach, the company’s diverse sales regions every obtains diverse marketing inputs at the similar time, or these inputs are methodically varied from corner to corner in the sales territories, and are evaluated to the sales and proceeds product. Both means are noise, and together have their position. Over and over again some mixture of the two means is the for the most part well-organized.
In spite of means, marketing mix modelling can be flourishing only if precise and extremely exact data are obtainable upon which the modelling can be based. The maximum blockade to victorious modelling is a lack of pertinent, exact, precise information. So the primary pace in any modelling attempt is setting up the information warehouse that will hold up the modelling. The after that step is bringing together and organization all of the past data and towards the inside it into the data storehouse, and then organization and towards the inside new information on a progressing foundation. Spotless, precise, highly exact data is completely necessary to winning modelling. The data should be exact to individual brands and manufactured goods lines, not the corporation as an entire. Attempting to replica at the business (or collective) height hardly ever works since what’s leaving on in one fraction of the corporation is cancelling out or confusing what is going on somewhere else in the corporation (Thoma, 2006).
The extended marketing mix (7Ps)
The marketing mix as discussed earlier consists of four main elements:
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion.
Getting the blend of these essentials right allows the administration to get together its marketing objectives and to gratify the needs of clientele.
It is standard practice to add few more Ps to the original/standard 4Ps, which makes it 7Ps mix.
The additional Ps have been included simply because today the focus is more towards the customers and companies have more customer oriented advertising, and simply due to the fact that the control of the economic actions in this particular state is in grab of the service sector. These 3 extra Ps are chiefly applicable to this new comprehensive service mix.
The three additional Ps are:
- Physical layout – in an era when UK was facing industrialization domination the design of manufacturing entity such as an industrial units was not of any important to the end-user, simply because they for no rationale to go within the confines of any plant.
On the other hand, today consumers routinely approach to get familiarity with goods in retail units – and they expect an elevated point of exterior and understanding of current outlets – e.g. music shops, garments outlets etc. Not only the direction should come easy to them but no difficulty should arise to reach the outlet, but they also frequently remain patient for a superior standard or appearance (Bhasin, 2011).
The importance of superior exterior mapping is vital in a variety of service providers, including:
- Students leaving to school or universities have much more anticipations about the quality of their lodgings and educational atmosphere now. As an effect schools and universities give more concentration on coming up with eye-catching educational atmosphere, lodging for students, shops, cafeterias and other facilities.
- Air traveller’s wants more striking and expect attractive and inspiring settings, such as unique lounges, with something for their kids etc.
- Hair salons are required to give relaxing sitting areas, with readable materials, access to tea for clients etc.
- Physical layouts are not only important to shops, outlets but also for online stores or websites.
- Provision of customer service –for service industry customer service is central and is considered as its heart. Clients are expected to be devoted to companies that provide them nicely – from the way of handling telephonic questions or assistance, more personally meeting the client’s face to face interaction. Albeit the ‘has a nice day’ method is a bit old, it is definitely superior than couldn’t care less method. Call centre employees and clients interacting staff are the face line of any company and therefore require being extensively equipped with good customer relation’s training and methods.
- Processes – linked with clients services are a-lot of functions engaged in creating marketing valuable in an company e.g. methods for treatment of clients criticisms or complains, processes for recognize clients necessitates and prerequisites, processes for tackling instructions etc The 7 Ps – price, product, place, promotion, physical presence, provision of service, and processes includes the current marketing mix that is scrupulously correct in service industry, but is also applicable to any shape of trade where the needs clients is prioritised (The Times 100, n.d).
To summarize service marketing or the 7P’s looks like this:
The Individuality of a service that is:
- Lack of possession
- Intangibility
- Inseparability
- Perish ability
- Heterogeneity.
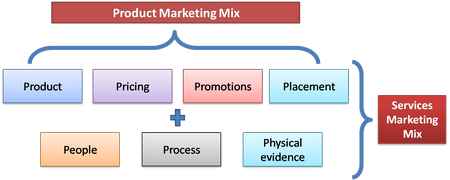
The Service marketing mix engages investigating the 7’p of marketing connecting, Product, Price, Place, Promotion, Physical Evidence, Process and People.
To convinced degree organization services are more convoluted then administration products, products can be standardized, to regulate a examination is far more easier said than done as there are more input issues i.e. populace, physical evidence, procedure to administer then with a product (Learn Marketing, n.d).
So why 7 Ps?
Conventionally, the marketing mix was urbanized for the fast moving consumer goods division, and there were 4 Ps: Product, Price, Promotion, and Place (or distribution). As service divisions have turn out to be more conscious of marketing, this marketing mix has been urbanized to also take account of: People, Process and Physical Evidence. Even if you believe you only sell an item for consumption, so the unique 4 Ps will meet your requirements, it can be helpful to believe how much of an overhaul element there is to your trade. Without a doubt, the goods-service range makes obvious that very a small number of merchandise are only merchandise and very hardly any only service.

For the most part, sell whichever products with a neighbouring service building block (for example, a customer thinks about help-line for a software vendor) or services with a substantial building block (the ability of a hair stylist is a service but tangible goods are mandatory to deliver it). So it possibly will be shrewd, even for product producers, to think about all 7 Ps in their marketing mix (Clarity, 2005).
A Summarization of the Marketing Mix
The below mentioned elaborates the marketing mix decisions, along with the list of some of the characteristics of the 4P’s (Quick MBA, 2010).
- Product
- Purposeful
- Exterior
- Quality
- Covering
- Brand image
- Guarantee
- After sale Service/Support
- Price
- Price list
- Concessions
- Allowances
- Investment
- Lease
- Place
- Channel Partners
- Channel inspiration
- Market reach and area covered
- Locations
- Transportation and other logistics
- Standards of service
- Promotion
- Advertising campaigns (ATL & BTL)
- Personal Selling
- PR
- Message
- Electronic media / digital media
- Funds
Research Methodology
Research aims and Objectives
This research’s aim and objective is to observe and check the formation and on-going importance of the 4P’s Marketing mix model and it should be regarded as a relevant theory after validating the model through analysis.
Methodological Approach
In order to understand the validity of the marketing mix model different sources will be reached out to have a deep insight of the views of different scholars and practicing marketers.
Secondary data
Data can be collected in different ways and all it depends on the nature of the research. Therefore, with the purpose of identifying the research objectives effectively data were gathered from both secondary and primary sources. Moreover, before collecting primary data; the researcher first should focus on conducting and analyzing appropriate secondary data to successfully address the research problem.
The source of secondary data includes academic literature and computerized database. I will be gathering secondary data as it is an easily accessible, inexpensive, credible and trustworthy source. Hence, for the literature review I will be focused on academic literature which includes journal articles, teaching literature and textbooks. I will be referring to journal articles because “Journal articles provide concise information regarding theories, methodology, application and interpretation relevant to your thesis”. All the journals were selected from the third session of the Marketing Theory module outline. This course is being taught by Dr James Fitchett at the University of Leicester. Moreover, I also obtained the hard copy of the outcome of the debate conducted by the University of the Leicester on 02 April, 2011.
Time scheduled for study and writing dissertation
The dissertation is an important part of any module. Prior to writing a research report I conducted comprehensive literature review as discussed above. The time was properly scheduled and worked on daily basis as I had only eight weeks to complete the task. Because, at the last moment I had to change my research topic and started working on this research topic:
- 1 – 4 (Weeks): Thoroughly research matter for the literature review from various forums already discussed.
- 5-6 (Weeks): Organize the gathered data and choose relevant material.
- 7-8 (Weeks) (Last week): The dissertation will be brought into its final shape. With proof reading and corrections the dissertation will then be complete.
Limitations and ethical consideration
The major limitations of the research are not up to date recent literature is readily available to discuss the validity of the marketing mix model. In order to justify the research objective the few recent articles were available which are been used in the research. There were some pervious research conducted in the last few decades discussing the validity of the marketing mix model and due to time constraint I missed some of the other important areas.
The real life implication of the marketing mix model
Introduction
This chapter will be analyzing the use of the marketing mix model (4P’s) in the real world. There are number of Small and medium enterprises are using the application of 4P’s model to justify the marketing strategies they adopt. In addition, the role of famous multinational in designing marketing plans and using the famous of 4P’s as a part of the strategy will be analyzed and discussed with the example of how British Petroleum, Coco Cola and Nivea to provide the evidence of the application of the model.
Making Use of the 4Ps Marketing Mix Model
The marketing mix model can be used to assist you make a decision how to take a new proposal to marketplace. It can in addition be used to investigate your on hand marketing line of attack or the tactics currently employed. Whether you are taking into consideration a fresh or on hand proposal, go after the steps below to help you describe and improve your marketing mix.
- Begin by recognizing the item for consumption or service that you would like to investigate.
- Now go from beginning to end and answer the 4Ps questions – as defined in point above.
- Try inquiring “why” and “what if” queries too, to face up to your offer. For case in point, ask why your target viewers call for a meticulous characteristic. What if you go down your price by 5%? What if you offer additional colors? Why sell all the way through wholesalers rather than unswerving channels? What if you get better PR to a certain extent than rely on TV advertising?
- Just the once you have a well-defined marketing mix, attempt “testing” the in general offer from the clientele point of view, by inquiring client focused questions:
- Does it get together their requirements? (product)
- Will they face it where they go to market? (place)
- Will they think about its price as flattering? (price)
- And will the marketing interactions arrive at them? (promotion)
- Go on inquiring with lots of questions and creating modifications to your mix in anticipation of you being totally content that you have optimized your marketing mix, known the information and particulars and statistics you have on hand.
- Evaluate you marketing mix on a regular basis, as some essentials will call for variation as the manufactured goods or service, and its market, produce, mature and become accustomed in an ever-changing ready for action surroundings.
Key Tips:
The marketing mix can be of assistance to you to describe the marketing fundamentals for productively positioning your market proposal. One of the most excellent known models is the Four Ps, now extended as the 7P’s which helps you describe you’re marketing alternatives in expressions of product, place, price and promotion. Use the mock-up when you are setting up a new business enterprise, or weighing up an on hand offer, to optimize the impact with your target market (MindTools, n.d).
Evidence of using the Product, Price, Place and Promotion prior to the invention of the 4P’s model
The brief history of the marketing mix and main criticisms revealed the early development of the 4Ps model and how it is being modified with the passage of time. However, many marketing educators raised their voice against the validity of marketing mix idea. Now, we will go about the conferring pragmatic connotations of the mix. Van Waterschoot and Van den Bulte (1992) and Gronroos (1994) in E. Constantinides indicated that the marketing mix was developed as a management tool for marketing practitioners, students and marketing writers. Therefore, one thing is very clear; this theory was designed for future marketers to explain the marketing as a subject in a simplistic manner. According to Leeflang (1979), Leeflang and Koerts (1970) in Van Waterschoot et al, “If one views the classification of the marketing mix to be a device to help structure marketing decision making and management, the objectives the marketer is perusing while using it seem to be appropriate as classification dimension”. The marketing mix is considered to be a decision making tool for marketers because irrespective of any product category, service or industry it helps practicing professional to design and implement any particular marketing strategy. Moreover, firms have a number of options to form marketing strategies on the basis of the 4Ps model. According to Jobber each of the marketing mix variables varies depending on the type of industry and firms’ objectives and goals.
A set of options are available for the firm to make marketing decisions relating to the first P of marketing mix “product”. McCarthy pointed out that the firm usually chooses to focus on the development of right product which satisfies the customer’s needs and wants. According to Jobber to enhance the demand of any particular product and overall profit margins for the firm, an organization strongly needs to focus on the product quality with matchless features. “Place” the second P notes the apprehensions linking to the distribution of the product, the question of how distribution of the product is done, the methods which is followed for its disbursement, its channel for disbursements, and the method adopted by corporations for negotiations with their channel partners.
The third P “Pricing” concerns aspects for marketers are what should be the price of the product to meet the competition in the market and how decisions will be made to offer a discount on the particular product to customers. The last P “Promotion” provides the different ways to promote different products in the market place. In order to promote the product, marketers always have different options such as “Price variations, personal selling, mass selling, and sales promotion”. Hence, it has been assumed that an organization can mix these factors to make a perfect business plan which will indeed help them to establish long term relations with their customers or business partners. The results of the empirical study which was conducted among business executives of 550 Dutch firms disclosed that around 70 percent of the marketers use marketing mix as an important management tool in their marketing plans.
The first text book of basic marketing revealed the evidence of using the marketing mix in practice. In 1960, McCarthy further explained in his book how American Motors Company, Land O’ lakes Creameries, Magnavox Television Sets and American Optical Company achieved outstanding success after using the marketing mix model. According to McCarthy in Goi automobile manufacturing companies were facing difficulties to run their business operations in the late 1950s. However, the American Motor Company managed to survive in the competitive market and company financially performed unexceptionally well during the period of 1958 to 1959. However, the secret behind all of their success was that company used marketing mix factors namely product, place, price and promotional. And finally they achieved high profits after implementing the mix strategy.
Kent et al stated that the success story of another firm known as the American Optical which was facing direct competition from low scale companies. All of its competitors were moving rapidly to develop and deliver new products for the fashion conscious customer. In addition, as a result firm’s president called a meeting to overcome the problem and brought marketing gurus to provide solution to the problem of how customer can be retained and sales can be increased. These experts advised the company to focus on their product and promotion activities. The American Optical hired style and color advisor to improve the product quality. The company was spending large amount of capital to keep 13,000 items of inventory in their 325 branches and that was not an issue for them. Pricing was not again a major concern for American Optical. But company managed to implement new promotional strategy, instead of targeting professionals; they decided to approach consumers through magazines.
So far we have been discussing the companies who succeeded using 4Ps as their marketing strategy. However, there is a company called Analose- A Bristol-Myers who failed to benefit from the marketing mix. Therefore number of evidence found supporting the marketing mix is being used by different firms and few of them achieved their objectives effectively. But there could be other factors involved in their success which has been ignored by various authors. One could argue that they succeeded due to socio economic factors which helped the companies to gain competitive edge over their competitors. It will be foolish to believe that companies achieved their goals only on the basis of the 4Ps model. Numerous important learning’s have been performed “on the precise functions and offers of the Mix to the accomplishments of profit-making corporations is very restricted, numerous learning’s established that the 4Ps Mix is certainly the dependable theoretical path of decision-makers dealing with tactical/operational marketing matters.
Evidence of using Marketing Mix Model by Multinationals
A few multinationals supported in house NPD department because their research and development (R&D) and new product development (NPD) activities are based abroad. Marketers use the marketing mix model in the United Kingdom while taking business decisions.
All the responding companies strongly emphasized on product related features such as quality, performance, reliability, safety and convenience. In addition, majority of the business institutions are also focusing on research and development to enhance market share and reduce the existing competition. Methods adopted for pricing by organizations are diverse; the most commonly practiced method is the target profit method. However, target profit method is adopted by management “to earn fixed level of profits”. The global pricing method is not being used by many companies. It is sometimes difficult for companies to adapt global standardized pricing method because of poor economic conditions; existing competition and consumer expectations are high.
Mostly companies employed different distribution channels such as dealers or distributors and own sale force. All the companies who responded to the interview are also providing various incentives to increase the motivational level of channel members. Majority of the organizations offer discounts, prizes, gifts and sponsorship for trips to dealers and own sale force. Companies placed little emphasis on the promotional activities because “management belief in promotion to be less significant in differentiating company products and services”. Majority of the companies use below the level (BTL) marketing activities such as seminars, social events and road shows to promote their products into the market. Usually FMCGs companies use above the level (ATL) marketing activities such as personal selling, advertise on print and electronic media to attract a large customer base. However, there is enough evidence available to support the fact that marketing mix model is used by the marketing managers of leading companies of the country. It is also thought that FMCGs are leading the way in developing and practicing marketing ideas and tools in the United Kingdom. As a result, other companies have also followed the lead of FMCGs in designing an effective marketing plan and activities for their business.
How does BP’s marketing strategy use the famous marketing mix model?
British Oil industry has recently introduced the unique characteristics of how they can adopt the idea of 4P’s (Product, Price, Place and Promotion) of marketing to make the business more profitable.
Product
Organization functioning in UK, have been putting forward different commodities, such as fuel. For companies to offer buyers any point of difference is next to impossible. However, to gain a competitive edge the British Petroleum offering products (Petrol and Diesel) which are better for environment. BP is the only firm which is offering Superior fuels to its customers that are kinder to the environment.
Price
With products being familiar in petroleum industry, it is hard to distinguish with common products in the oil industry; it is difficult to differentiate the product and price among competitors. If one competitor lowers his price due to stiff competition, BP has to suffer loss in its volumes sold. Moreover, in order to bring down 1% of price, retailers are required to achieve a staggering 25% rise in volumes to achieve break even on site.
Place
BP’s strength lies in its network of services stations, which is one of its core part of its marketing strategy, as they posses some of the best geographic sites in UK which enables them to offer services to the customers. But current studies suggest that fuel retailer’s locations are the focal point for any customer to go to them. BP makes sure that it has the right presence and quality, for customers in terms of locations backed by heavy investments.
Promotion
The recent research has been conduced that customer responds well to the marketing activities. BP main differentiation drives from its loyalty programmes, as they used to increase sales volumes and give stiff competition to its competitors.
The use of marketing mix in the Product launch
Product oriented approach provides a frame work that the market can be build up by bringing in right set of range of products and its introduction within the market or another way is to find an opening in the market and manufacture a product to fulfil its demand (market-oriented approach). A market opening when found, Beiersdorf introduced NIVEA VISAGE Young utilizing on a balanced blend of 4Ps. It is essential that the company offers the right balance of the 4Ps in order to for its offering to achieve desired target. Beiersdorf had to come off with a mix which was appropriate for its products and targeted audience, as well as its own targets. In 2007 they re-introduced the NIVEA VISAGE Young variety additionally optimised its position in the marketplace, implication they manufacture method for its aid, new appearance, new covering and a new name. This case study points out of how imperative it is to come up with a right mix which forms the basis for introducing and re-introducing of a brand on to market.
The introductory step in making a balance and right mix is to comprehend your market. NIVEA used market research to aim at important market segments which recognized a cluster of customers have same characteristics such as age/gender/attitude/lifestyle. The insights and key factors grasped from the research assists in the advance of new products. NIVEA conducts its research in numerous ways (Globe360, n.d).
These include:
- Focus groups for insights coming straight from the end users
- Collection of information from customers by utilizing numerous research techniques
- Testing products with customers in markets which differ
Beiersdorf market research points that youth or people in their young age wanted precise face care for their own age group which presented them a beautification gain, in place of skin problems remedies. NIVEA VISAGE Young is a skin care variety meant at girls who did not like merchandise which presented medication but as an alternative sought after an answer for a normal healthier skin.
Rival products offered products which were trouble directed and medicated solution. This provided NIVEA an edge. NIVEA VISAGE Young provides them a viaduct in the middle of the teenage section and adult group. The company managed to reshape its offering to make it end user friendly and more useful. Beiersdorf tested his product on a group from its target market before bringing in its range to be re-introduced. This experiment formed the basis of changes in their product. Improvements included:
- varying the formula of its offering for example removal of alcohol utilized natural sea salts and minerals in others.
- offering two brand new products.
- A complete modified design pack with pallet colour and flowery pattern which attracted to younger women.
- Altering product metaphors and brining in bigger pack sizes.
Each of these amendments assisted to reinforce the product range, to efficiently cater the needs of the market. Some of these modifications and alterations mirror NIVEA’s eagerness and position on the environment. Its commercial accountability advance aims to:
- reduce covering and ravage – by means of better-quality packet sizes
- Use of additional usual products – with minerals and sea salts in the modus operandi
- intensify openings for recycling – by means of recyclable plastic in its containers.
Price
A number of things accounted for the final price of a product, for example, the cost that is incurred in producing or the objective of profit to be maximized or sales. A product’s price should reflect value for money and draw end users. There are quite a few costing schemes that commerce can use:
- Cost based pricing – it can be assured merely as covering of outlay or revenue essentials. Its main focus is on profit maximization and does not account for customers.
- Penetration price – starts with fairly low rates to make certain that there is a higher percentage of purchases and that the market share is quickly gained. This strategy persuades consumers to build up a habit of purchasing.
- Price skimming – starts off with a fairly high price for a very different product inciting customers who wants to be the first buyers to give a premium price. This strategy assists in getting maximum profit prior to a competitor’s product coming out in the market.
On re-launch the price for NIVEA VISAGE Young was a little high as compared to earlier. This demonstrated its current formulations, covering and comprehensive manufactured goods variety. However, they also had to consider that its target market were teenage girls and mothers purchasing product for their young ones. This indicates that the obtainable cost had to proffer worth of cash or it would reach out of clutch for it’s under attack market.
As NIVEA VISAGE Young is one of the chief skin care varieties meeting the smartening up wants of this marketplace section, it is efficiently the cost chief. This explains that it places the price height that challengers will go after or be condescending. NIVEA requires to frequently reconsidering prices every time a challenger enters the market at the ‘market growth’ point of the product life cycle to make sure that its costing remains economical yet aggressive.
The pricing scheme for NIVEA is not the similar as that of the vendors. It sells merchandise to vendors at one price. On the other hand, vendors have the liberty to make use of other plans for sales support. These take report of the spirited environment of the high street. They may use:
- Low cost leader: the vendor sells for less than its outlay to create a centre of attention for large quantity of sales, for instance by supermarkets
- discounting – next to other unusual offers, such as ‘Buy one, get one free’ (BOGOF) or ‘two for one’.
Place
Place refers to: How the manufactured goods arrive at the direct of transaction. This means a trade must consider concerning what delivery strategies it will use where a product is put up for sale. It also takes in other habits in which commerce makes merchandise straight accessible to their objective marketplace, for instance, through direct mail or the Internet.
NIVEA VISAGE Young plans to make use of as many related supply paths as likely to make certain the widest reach of its goods to its target market. The major path for the produce is retail channels where customers look forward to come across skin care ranges. In the order of 65% of NIVEA VISAGE youthful deals are all the way through large far above the ground street shops such as Boots and Superdrug. Superdrug is for the most part important for the ‘young-end’ marketplace.
The last 35% of sales mostly comes from huge grocery chains that store splendour beauty products, such as ASDA, Tesco and Sainsbury’s. Market study shows that approximately 20% of this younger target market purchase products for themselves in the high street stores when shopping with acquaintances. Researches also demonstrate that the conventional of buyers is in piece of information made by mothers, purchasing for teenagers. Mothers are extra likely to give money for the manufactured goods from superstores at the similar instance as doing their grocery purchasing.
NIVEA distributes through a variety of opening that are cost effectual but that also arrive at the uppermost numeral of customers. Its allocation strategy also considers the ecological bang of ship. It uses a middle distribution point in the UK. Goods turn up from European industrialized plants by funds of deal motor vehicle for efficiency for frontwards relief to retail stores. Beiersdorf does not put up for sale straight to smaller vendor as the quantity of goods sold would not be price effectual to transport but it uses merchants for these less important financial records. It does not put up for sale straight from beginning to end on its website as the costs of producing little orders would be too elevated. Though, the vendors like Tesco, characteristic and sell the NIVEA goods in their online stores.
Promotion
Promotion is how the commerce tells clientele that goods are accessible and sell something to someone them to buy. Above-the-line endorsement is unswervingly compensated for, for instance TV or newspaper promotion.
Below-the-line is where the commerce uses other promotional means to obtain the manufactured goods message across:
- Events or trade fairs assist to start a produce to an extensive audience. Events may be business to consumer (B2C) while trade fairs are business to business (B2B).
- Direct mail can arrive at a big numeral of persons but is not easy to goal definite customers inexpensively (The Times 100, n.d).
- Public relations (PR) include the varied behaviour business can communicate with its stakeholders, all the way from side to side, for example, newspaper press releases. Other PR performance includes support of high profile proceedings like Formula 1 or the World Cup, as well as aids to or contribution in charitable trust events (Nivea, n.d).
Marketing Mix of Coco Cola
The marketing mix model of the Coco Cola includes one more P (People) to design successful marketing strategy.
Product
Approximately 300 beverages are created by this corporation together with; Sprite, Fanta, Fruitopia, Coke and Powder juices too. Covering can also be contrasting from the size of 300mL, 600mL, 1.25 litres, 2 litres and cans of 375mL. One of the famous and most excellent brands is documented by roughly 94% of the inhabitants. Coca Cola grasps the best standing in the marketplace too (BookRags, 2006).
Price
Worth of Coca Cola brands differ from dissimilar volume and amount. Costs obtainable by the corporation are real and willingly conventional by the inhabitants too. This is all due to the augment rate of requirements.
Promotion
Promotion is one more significant matter as well as a major instrument of marketing mix of Coca Cola. This product did endorsement from the very beginning in an effectual mode in command to keep hold of clientele and to draw them. This is the most excellent way with the help of which insists can add to and that can boost the income too. The endorsement of Coca Cola comprises of television, radio, internet, billboards and pamphlets too.
Place
Coca Cola is one of the most important brands that are with no trouble obtainable worldwide. You can discover it all over the place due to the greater than before rate of command. Wherever at any occasion, you can find this make and this is all since of the schemes put into practice by Coca Cola (Marketing Mixx, 2010).
People
Young people are the major goal of this make (Slide Share, 2010). Separately from this, children and aged persons do attempt this too and be grateful for it too. In command to pull towards you more customers, Coca Cola always tried to put into practice magnetism and effectual plans with the assist of which useful results can with no trouble be generated.
The Future of the Marketing Mix Model
Introduction
The famous marketing authors, the marketing mix model is considered to be the most acceptable and famous generic model among marketing practitioners and marketing educators. Therefore, in order to examine the validity of the above statement I obtained the hard copy of the major outcome of the debate organized by the School of Management, University of Leicester on 2 April 2011, where marketing educators and marketing professionals from Asia, Europe and American attended the conference. However, this chapter is purely based on the article written by Dr Fitchett, as paper present after the conference.
The Major Findings of the Conference
The outcome of the conference revealed that the marketing mix model is considered to be the most effective and widely used principle among marketing educators and professional marketers except one associate professor of the Indian Universities. However, they considered the 4Ps is a framework to organise the marketing subject to better explain the complexity involved in the field of marketing and does not use it. As Fitchett in 2010 also pointed out that this theory was developed as a basic tool for marketers, students and advisors to explain the marketing as a subject in a simplistic manner. It is very much clear that the marketing mix model is commonly recognized and accepted by the majority of the participants.
All the participating marketing educators working in their countries are projecting the positive aspects of the marketing mix to their students. Moreover, they only focused on western marketing textbooks written by Philip Kotler and Armstrong etc to future marketers for the better understanding of the marketing ideas and concepts.
The Management of Marketing Mix Model
Earlier we discussed that the majority of the multinationals operating in the United Kingdom such as Pharmaceutical, financial institutions, FMCGs, industrial goods and cellular companies etc have been using the elements of mix model to design effective business strategies. However, in this section we will also analyze how marketing managers working in the FMCGs and Paint manufacturing firms are being benefited from the mix model.
A marketing manager working in FMCGs considers the marketing mix model to be very useful while taking any business decisions because it helps to make all major product, price, place and promotional decisions effectively. Now we will be discussing how does he use the mix? If he has to launch a new product category, he will first investigate the opportunity to market the product. In other words he examines the size of the potential market and consumers need for the specific product. If the specific product fulfils the needs and wants of the potential buyers and no concerns exist to manufacture a new product, he will take a decision about what should be the price of the product to meet the competition in the market. Once the pricing issue is resolved the decision will made about which distribution channels will be used i.e. modern retailers, high frequency stores, cash & carry’s and direct and indirect coverage etc. Finally, the best option would be selected to promote the product such as above the line/below the line mix, clutter breaking advertising, FMOT exploitation and POS (Point of sale) material etc. The FMCGs use, above the line marketing (ATL), marketing activities such as personal selling, advertising on print and electronic media to attract large customer base.
The marketing mix is considered to be a decision making tool for marketers because irrespective of any product category, service or company it helps marketing managers to design and implement any particular marketing strategy (Austin, 2010). However, marketing mix varies from industry to industry and company to company. It contrasts within the corporation division to division and product to product (E-Consultancy, 2011).
The Variety of Understanding Marketing Mix Model
All the participants in the conference describe their basic understanding of the idea of the marketing mix. All of the marketing educators said that a set of four variables are available for the firms to fulfil the needs and wants of the customers and at the same time the business goals are also achieved in the most optimal way. It means in the eyes of these three respondents the mix model is helpful for the firm to achieve its business objective after satisfying customer’s needs and wants. In 2006 E.Constantinides also reiterated in his article that in the era of relationship marketing, the managers are being pressured to satisfy customer’s needs and wants and recognizing the importance of building long term business relations with profitable customers. The other participants described the marketing mix as:
- It is a great concept to put things in perspective but teaching is at times gets very confusing but since there are other model as simple as this one so the simplicity of the model makes its most attractive”.
- “In brief marketing mix model is composed of 4 traditional elements i.e. Product, Price, Place and Promotion. But according to some new researchers in the last few years and chartered institute of marketing, marketing mix is comprise of 3 additional elements i.e. People, process and Physical Evidence.”
- “Marketing mix and I believed in the Unilever model of 6 Ps is very useful framework for decision making and helps you remain focused”.
- “ A set of tools required to promote a product or group of product”
- “My understanding is to get the ideal marketing (best combination of 4Ps) which will ensure the optimum equity for a brand lasting for generation catering to target market”.
It is pretty much clear that the majority of the participating marketers and educators believe that the marketing mix is just the combination of four elements i.e. Product, Price, Place and Promotion and decision making tool which fulfils the needs and wants of the customers.
Almost all of the participants more or less agreed on the fact that the model provides us with just a generic framework to design strategies but it does not provide us with an in-depth analysis of the problem and therefore it fails to deal with specific problem of customers. In other words we can say that it can be used as a guideline but it is not tailored to customers’ specific needs and wants. This is contradictory with what was said above in the answer that the model provides solutions to customer’s needs and wants.
All the participating marketing educators and marketers said that we design marketing strategies using strategic marketing model and theories other than 4Ps. Almost all respondents were familiar with other marketing models such as VALS framework, hierarchy of need theory, model of consumer behaviour, new product development, product life cycle, Osterwalder & Pignuers E-Marketing Ontology (for business over the internet), Porters Model of competitive advantage, Porter’s five forces model, blue ocean and red ocean strategies, Strategy map and balanced scorecards, Scenario Planning, the marketing mix model, marketing triangles along with the Kraljic model and Kotler textbook for designing marketing strategies.
But interestingly out of nine only one participant was able to explain how he designs marketing strategies while working in P&G. The marketing manager said: “the concept of multifunctional teams is helping companies not only achieve the above but go beyond the traditional mix with an expert from each area forming part of the final strategic objective. A direct reference to the mix is not kept in mind however since there is an expert from each area all the basics will naturally be adhered to. For perspective a team typically comprises of Brand, Finance, Sales, Plant, Market Data expert etc.” Up till now the marketing educators and marketers justify that the marketing mix model is the most effective model and is widely used principle. It helps marketers to satisfy customer’s desires and acts as a guiding principle to make effective marketing strategies but the reality is that none of them were able to explain how they actually design marketing strategies.
In the last few years, a number of western marketing professors and marketing practitioners challenged the validity of the marketing mix model. However, we have not seen any article written by any South Asian marketing educators raising concerns on the validity of the mix model. In addition, all the participating marketing professors and practicing marketers in this research were aware of the positive aspects of the mix but out of nine respondents only five were able to respond to the question regarding awareness of the criticisms of the 4Ps model.
Marketing manager of P&G believes that “One of the most common criticisms about creating a marketing mix is that the marketing mix approach can actually lead to unprofitable decisions because of the fact that the decisions are not based on financial objectives; basically those objectives would be increasing shareholder value which we handle through the hybrid mix approach aligned by the whole multi functional team.” Marketing manager working in ICI pointed out that the mix’s ultimate focus is on seller’s perspective, not the customer. E.Constantinides also argued that the marketing mix only addresses the micro issues, i.e. it describes the seller perspective and not the customer’s. As a result Kotler (1984), Robins (1991) and Doyle (1994) added more elements such as Customer, Capabilities, Competitors, Company, Service and Staff to overcome this problem. The other marketing educators thought that the 4-S web marketing is the main criticism of the marketing mix because this model is not implemented in the Pakistani environment and it doesn’t give the consolidated picture or framework.
However, Van Waterschoot and Van den Bulte in 1992 argued that the marketing mix has three major flaws and all three are very much linked to each other. He further explained that the 4Ps is systematically weak and it does not suggest marketing practitioners and student how to use different ingredients such as (product, price, place and promotion) and whether they are being mixed and whether these are variables interrelated to with one another or not (Butler, 2011). Kent in 1986 revealed that everyday marketers make decision on the basis of the 4Ps model, with realizing that the decisions they are making could not be empirically test and verified. Lastly, both Kent and Waterschoot agreed that the elements of the marketing mix are not mutually exclusive. Indian marketing professor and marketers are not actually aware of the major flaws of the 4Ps model. It may be because of Indian educators focus more on western marketing textbooks written by Philip Kotler and Armstrong etc and less research work is conducted in the country (Rosen, n.d). However, marketing text books project the positive aspects of the marketing mix model.
Why the Marketing Mix is an Important Tool?
The marketing managers and professors also provided different reasons of why the marketing mix is still being used as an important tool in most of the multinationals and business schools as it has many flaws. According to Fitchett, the marketing mix is deeply rooted in the field of marketing. It also explains complexity involved in the area of marketing. However, those five respondents who suitably replied to this question agreed with Fitchett analysis and their reasons are as follows:
- “It is embedded in the marketing world and will remain in use till a relevant replacement is provided”
- The marketing mix is considered to be a constructive theory as it helps students and new entrants to understand the marketing jargon and also argued that multinationals does not consider the 4Ps as a “core tool” because it’s foolish to reply on the 4Ps “as the theory of choice of guarantee marketing success”. This is contradictory with what he said above in the answer that the model provides solutions to customer’s needs and wants and at the same time companies achieved their goals.
- “Lack of Substitutes”
Although almost all practicing marketers and educators use the marketing mix model, some of them still believe that the marketing mix will always considered to be the core principle of marketing ideas as there is no substitute to this model available and it also helps marketers to provide a comprehensive explanation of the area of marketing.
According to Goi, unluckily no one could develop such a theory in the field of marketing which has tendency to predict results. Moreover, the marketing theories are more hopeful after the fact diagnosis. Majority of the respondents agreed with the Goi and felt that the McCarthy’s (4Ps Model) is a descriptive theory. The results revealed that fours marketing educators and one practicing marketer considered the mix a descriptive theory. The remaining three marketing educators and one marketer thought that it has potential to be predictive theory. According to one of a marketing educator it is predictive “because all of the elements in the marketing mix are the entities that we can see and observe easily”. And the marketing manager working in multination thought “It is not a descriptive theory and is very much applied practically whether implicitly or direct but it is essential for basic marketing concepts and start”. Therefore, the majority of the participating marketing educators and one practicing marketer believe that the mix has no potential to be predictive at all.
Over the couple of years the marketing mix classification has been refined and as a result many marketing educators suggested adding more Ps, Cs and Ds to McCarthy’s invention. All the participating marketing educators and practicing marketers were asked about does marketing mix include more Ps to develop an effective marketing tool. The outcome of the conference disclosed that participants recognize the importance of adding more Ps and Cs. These seven respondents gave high importance to packing, people and personal and also suggested positioning, publicity, physical evidence, process, paradox, persuasion, passion, perspective, paradigm, communication, customer cost and customer convince should be included. But other participants felt that adding more Ps to marketing mix is not the solution until or unless we design a theory which is not restricted to any particular situation and empirically verified and tested. As a result still majority of the Asian marketing educators and practicing marketing believe that more Ps and Cs should be added to make the model more useful.
. Marketing educators, who assign students course work which involves the application of the model, also believe that the mix model is helpful for marketers in fulfilling customer’s desires, helpful while taking any business decisions, acts as a guiding principle to make effective marketing strategies and is still a widely used principle. In addition including those three marketers who thought that the 4Ps is a predictive theory concluded that it is not a useful due to number of reasons (Wikipedia, n.d).
- “ It is more of a descriptive theory as it incorporates the model at a very initial stage”
- “No not yet, unless we purpose a more robust alternative”
- “No, it should be modified due to the fact that the business environment is changing rapidly and the influences is felt even sitting miles away from where it happens”
- “Not yet. The question is not about redundancy but about the redefinition of this model”.
It can be concluded that the marketing managers working in the multinationals consider the marketing mix as a valid theory (Sounds Like Branding, 2010). However, the majority of the marketing educators are not satisfied with the McCarthy’s theory. Despite all this, marketing educators assign students course work which involves the application of the model. They feel that the mix is just a guiding principle to design successful marketing strategies (Webber, 2005).
The way to the real-time future of marketing mix
As soon as you hear the expression “marketing mix”, what do you imagine…? Pause! Think… Pause!
Does that sound well-known to you? Isn’t it well again to authenticate and comprehend the customer previous to start generating a new marketing-mix.
Watching the most recent videos on your YouTube channel, chatting to “friends” on Face book or subsequent the most up-to-date conversations on Twitter is one thing. Inferring conclusions out of these discussions on the social networking world is another. And captivating actions like weighing up ad words opposed to email opposed to social network marketing or blogs opposed to micro-blogs for your marketing mix afterwards is a third step.
Wrapping up might also be that marketers become conscious that B2B populace still read print if at all possible to online or love real face-to-face dialogues. They may hit upon that these commerce judgment makers think twice prior to them taking on in discussions. Ladders are desirable (like social media observations) previous to you start understanding your own marketing mix could pay out.
Additional marketing openings have by no means died even though social media still hypes. And there is a rationale why the “marketing mix” turn of phrase was fashioned some years ago. Not merely as it is a straightforward to comprehend expression. Further as we use it in our everyday business as marketers with not even becoming aware of anymore. It is in our DNA. It is a requirement. Will it ever be detached?
Evidently, there is not a clue. In over 50 years not a soul found one. Why is that so? Well, the human race is determined by human beings and their approach to turn out to be well-known and attentive of new belongings is a go-ahead procedure. Some populace become accustomed rapidly, others are slower.
The concoction of having dissimilar admittance points accessible, and those interrelate with each other, is the marketing mix of the prospect. Even though they may have a solo objective or focal point they are aspiring at, the marketing mix is supposed to be associated to one general line of attack: Engage the customer (Meyer-Gossner, 2010).
Analysis
It can be concluded from the various research sources mentioned in the literature review that Marketing Mix model is still a valid in today’s world and is widely practiced throughout the world, be it MNC’s, or small businesses or even new ventures the marketing mix framework still lives to be one of the most important tools of the marketing industry.
Marketing Mix implementations in UK
In order to sell a product, to make customers loyal to a brand, and keep them involved, a proper combination of the marketing mix needs to be formed. Businesses in UK give special attention towards marketing mix. They concentrate on all 4ps, and make sure that they come up with a proper blend aptly suited for their target market. We have several examples from different industries which we can discuss regarding the practices implemented/adopted by leading companies for their products in UK market.
Product
The product element and how it is used in UK can be gauged by the fact, as to how much the market is developing new products. How many sub-products/ variants they are coming up with. For instance if we talk about the cereal’s market in the UK, we can take Kellogg’s as an example. How many new products or sub-products they come up with. They have several breakfast cereals which covers their product element of the mix. Another example we can take is of Manchester United. The soccer team itself is a product, with sub-products such as t-shirts, caps etc. Another aspect that is given high importance is the design and usage of the product. If we continue with the example of Manchester United, the design of it’s T-shirts reflects its traditions, its fans and its culture. Usage covers the aspects of being a sport t-shirt, usually being sweat free etc.
Price
The price element in UK is more tied to the quality, competition and cost. Brands like Marks & Spencer charges its customer much low price as compared to brands like Zara does. Price factor majorly in UK is determined by the quality of the product. The perception of quality is the determining fact in UK market. However, it varies industry to industry. A prime example in this regard would be soft drink industry where competition is high and prices are charged, keeping in mind the prices of competition.
Promotion
Promotion is generally part of every business, and it comes in different forms. Businesses in UK promote its products in different ways. Some opt for the big budgets whereas some opt for traditional promotions techniques. In a holistic view, promotion is thought to be the most concentrated element of the marketing mix in UK. Promotional shows, brand ambassadors, sales promotions, advertising, games etc are several of the ways that are implemented in UK. A prime example would be sales in different outlets during different occasions, where offers such as buy one get one free, bundle offers, 50 per cent off etc offers can be seen. Promotional activities play a vital role in UK and are considered the most practiced and concentrated element of the marketing mix.
Placement
Placement in UK is as much practiced as other elements. If we consider the example of Chips in the UK market, we would find that brands are looking for spaces in malls, supermarkets, parks etc. Businesses in UK give it as much attention as it is given in any other part of the globe. Another example which can be taken is of gas stations. It is central to place your product, at right places. In UK, Shell has installed all its gas stations at key areas, where its customers have easy access.
An outstanding marketing mix in one era may not be as effectual in an additional period. The marketing mix transforms with time.
PCs are improved products, have a great deal lesser prices and different ways of distribution measured up to with ten years ago. Nowadays, thousands of people purchase PCs from side to side mail order. Ten years ago this would never have been the case.
The Marketing Mix has to modify to get together new market circumstances.
In the early on 1960s Product Performance – miles per gallon, steadfastness were very vital.
Sales promotions accelerate financial plans. So now the advertising encourages the sales promotions to a certain extent than the merchandise itself. It can also transform over space.
This is predominantly true in international markets where definite approaches to publicity and promotions are satisfactory in some countries but not in others; or where the allocation system is limited; or where the price construction is completely dissimilar.
The most favorable mix is partial by the company’s long term strategy on do again sales, its positioning plan, the target marketplace assortment, the firm’s possessions, levels of competition and the aptitude, or readiness, to alter the mix according to a particular market’s necessities.
Conclusion
Although descriptions and account of the Mix model or “Mix theory” feature in almost all marketing and marketing management textbooks it is very rare to find any explanation about how the model came about, how it was developed and changed over the years, and perhaps more importantly, whether there is any evidence to support its continued application to marketing theory. None of the seminal textbooks of marketing and marketing management subject the Marketing Mix framework to any type of critical scrutiny or present alternative and contested views about the model.
To sum up, the marketing managers working in the multinationals consider the marketing mix as a valid theory. However, the majority of the marketing educators are not satisfied with the McCarthy’s theory. Despite all this, marketing educators assign students course work which involves the application of the model. They feel that the mix is just a guiding principle to design successful marketing strategies.
However, there is plenty of evidence and arguments to support the view that marketing theorist and marketing professional should stop relying on the marketing mix as guiding principle in their decision making. There are some who continue to argue that the mix is valuable (for example Zineldin and Philip son 2007) but it is difficult to find adequate response to all the main criticism of the model.
But even though the Mix is flawed in conceptual terms there are many reasons why it is unlikely that it will disappear from the marketing imagination. We might even question whether the mix model should be thought of as a marketing theory at all. The mix is deeply embedded in the identity of marketing both as are of the study.
Marketing Mix Modelling… Its Success and Failures
What is the reason behind a successful or a failure of marketing mix program at different companies?
The history of marketing mix
- Then ‐ commercialized in the late 1980s in Consumer Packaged Goods (that’s where the data was)
- Now – being used globally across almost every industry to measure and optimize marketing performance, sales performance and provide insight into operations and external factors
- Industry examples:
- CPG – sales volume and profit
- Retail – transaction and revenue
- Telecommunications – acquisition, retention, churn
- Financial services – acquisition, usage, retention, growth/cross‐sell
- Travel – bookings and utilization
- Pharmaceuticals – TRx, NRx
- Automotive – leads, sales etc…
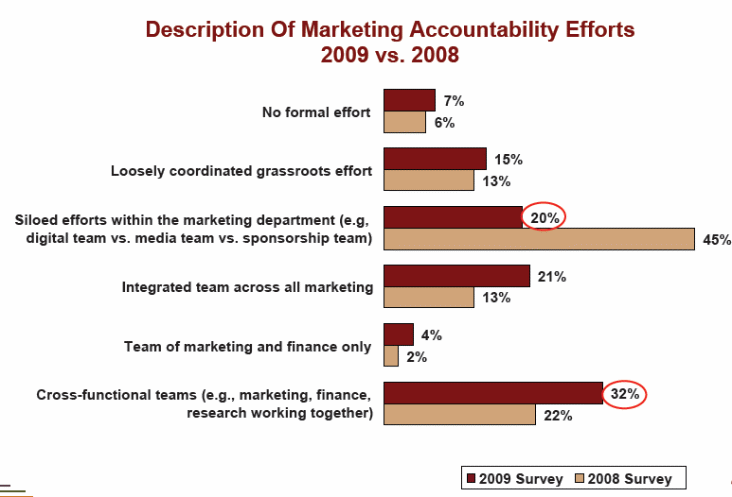
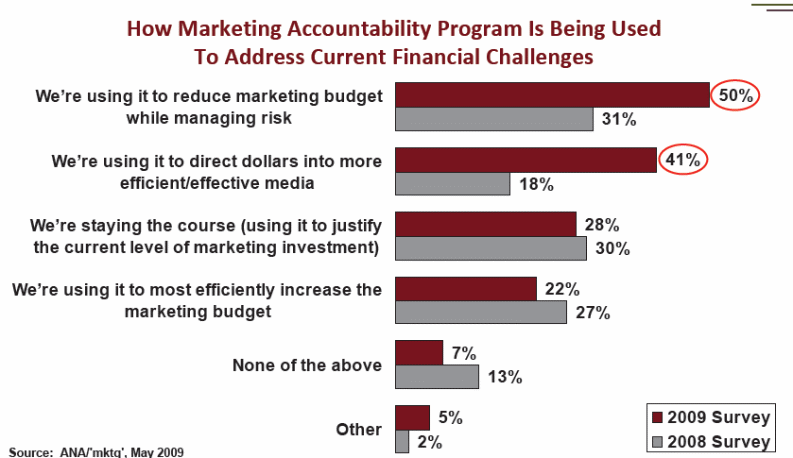
Marketing Mix Models include inputs that represent all significant business influencers.
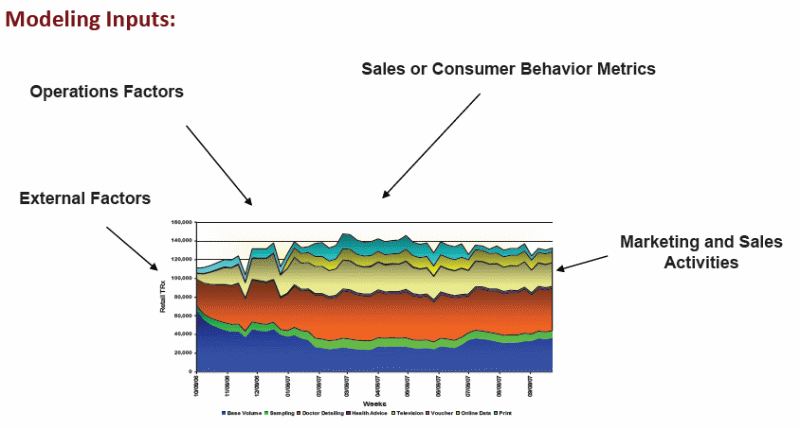
Recommendation
Why is everyone in different industries adopting the marketing mix model?
Benefits
- Apples‐to‐apples comparison of all marketing/media
- Visibility into variables beyond marketing
- Accounts for non‐marketing factors to apply “fair credit “to marketing
- Cross‐media optimization
- Portfolio optimization
- Causal forecasting
Challenges Faced by Organizations in Implementing the Marketing MIX
I have seen organizations realize up to 40% improvements in marketing ROI within twelve months. It’s not just a challenge to practice application of a successful version of marketing mix project; it’s a mandatory for the program to focus equally on the technical and other organizational bits.
- Non-availability of data…or in the making for the data to be ideal
- Keeping a balance between extrapolative vs. expressive
- Made for execution
- Representation at the accurate level
- Interpret at the correct level
- Achieving afore buy‐in and triggering usage
Keys to a successful program
- Select the correct points in the buy out funnel
- Reach inter‐department coordination –early and often
- Match analytics with the most recent company challenges
- Interpret, incorporate and triangulate to tell the complete story
- Create it onward‐looking
- Include digital and up-and-coming media
- Administer customer’s hopes and expectations
- Modernize and update analytics regularly to put the correct data in the hands of the accurate people at the correct time
- Educate, Educate, Educate…. then Educate again
- Conduct test and experiment with admiring and modern tactics (Brooks, 2010).
References
Anon., 1983. Marketing Intelligence & Planning. Journal of Marketing Practice: Applied Marketing Science, Web.
Answers.com, n.d. Marketing Mix. Web.
Austin, T., 2010. Looking Back, Looking Forward: Shaping the Future of Research in Marketing.
Bhasin, H., 2011. Service Marketing Mix.
BookRags, 2006. Coco Cola Marketing Plan.
Brooks, D., 2010. Webinar: Success and Failures in Marketing Mix Modeling. Web.
Business Knowledge Source, n.d. The Criticism of a Marketing Mix Approach to Marketing.
Butler, E., 2011. Leicester’s and Leinster’s Heineken meeting is a delicious prospect.
Clarity, 2005. The Marketing Mix. Web.
Constantinides, E., 2002. The 4S Web-Marketing Mix Model. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 1(1), pp.57-76.
Constantinides, E., 2006. The Marketing Mix Revisited: Towards the 21st Century Marketing. Journal of Marketing Management, 22, pp.407-38.
E-Consultancy, 2011. The Future of Digital Marketing 2011. Web.
Fitchett, J., 2010. Session 4 Notes, Generic theories and models in Marketing. England: University of Leicester.
Free World Academy, n.d. FW15-Marketing Mix.Web.
Frey, A.W., 1961. Advertising. 3rd ed. New York: The Ronald Press.
Globe360, n.d. Historical Milestones. Web.
Goi, C.L., 2005. Marketing Mix: A review of “P”. Journal of internet banking and commerce, 10.
Goi, C.L., 2009. “A Review of Marketing Mix: 4Ps or More?”. International Journal of Marketing Studies, 1(1), pp.2-6.
Harvey, M.G., Lush, R.F. & Cavarkapa, B., 1996. A Marketing mix for 21st Century Marketing. Journal of Marketing Management, 22, pp.407-38.
Jobber, D., 2010. Principle and Practice of Marketing. McGraw Hill.
Jones, J.C., n.d. Definition of Marketing Mix – Product, Price, Place & Promotion.
Kent, R.A., 1986. Faith in the four Ps: An alternative. Journal of Marketing Management, 2, pp.145-54.
Kotler, P. & Armstrong, G., 2006. Principle of Marketing. 11th ed. Pearson.
Learn Marketing, n.d. Service Marketing Mix / Extended Marketing Mix. Web.
Marketing Mixx, 2010. Marketing Mix of Coca Cola.
Masterson, R. & Pickton, D., 2010. Marketing: An introduction. 2nd ed. UK: Sage Publications.
MBA-Tutorial, 2009. Marketing Mix History. Web.
McCarthy, E.J., 1960. Basic Marketing. A Managerial approach.IL.
Meyer-Gossner, M., 2010. The way to the real-time future of marketing mix. Web.
Mind Tools, n.d. The Marketing Mix and 4 Ps.
Nivea, n.d. The Use of Marketing Mix in Product Launch. Web.
Quick MBA, 2010. The Marketing Mix.
Rafiq, M. & Ahmed, P.K., 1995. Using the 7Ps as a generic marketing mix: an exploratory survey of UK and European marketing academics. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 13(9), pp.4 – 15. Web.
Rosen, K., n.d. Customize Your Knowledge to Meet Your Prospects’ Needs. Web.
Slide Share, 2010. Marketing plan for coca cola company by TUF students.
Sooper Tutorials, 2009. Marketing Mix. Web.
Sounds Like Branding, 2010. The Philosophy of the Four Es – Why Brands Need to Embrace This Model in Their Marketing.
The Times 100, n.d. The extended marketing mix (7Ps). Web.
The Times 100, n.d. The use of the marketing mix in product launch. Web.
Thoma, J.W., 2006. Marketing Mix Modeling.
Watershoot, V. & Bulte C, V.d., 1992. The 4P classification of the marketing mix revisited. Journal of Marketing, 56, pp.83-93.
Webber, S., 2005. The Marketing Mix. Web.
Wikipedia, n.d. Marketing Mix.
Zineldin, M. & Philipson, S., 2007. “Kotler and Borden are not dead: myth of relationship and marketing and truth of the 4Ps. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 24(4), pp.229-41.