Introduction
The challenges associated with human errors and vehicle safety are increasing rapidly due to populace escalation. Human transportation using vehicles is becoming challenging due to the high rate of accidents. As “Road safety facts” (2021) notes, distractions during the driving act as the main barrier to safe transportation. The only way to eliminate this problem is by implementing smart technology and self-driving cars, such as the Tesla Model S and Model X. This paper will focus on the business opportunities of smart technology and self-driving cars by discussing customer fears, wants, and needs.
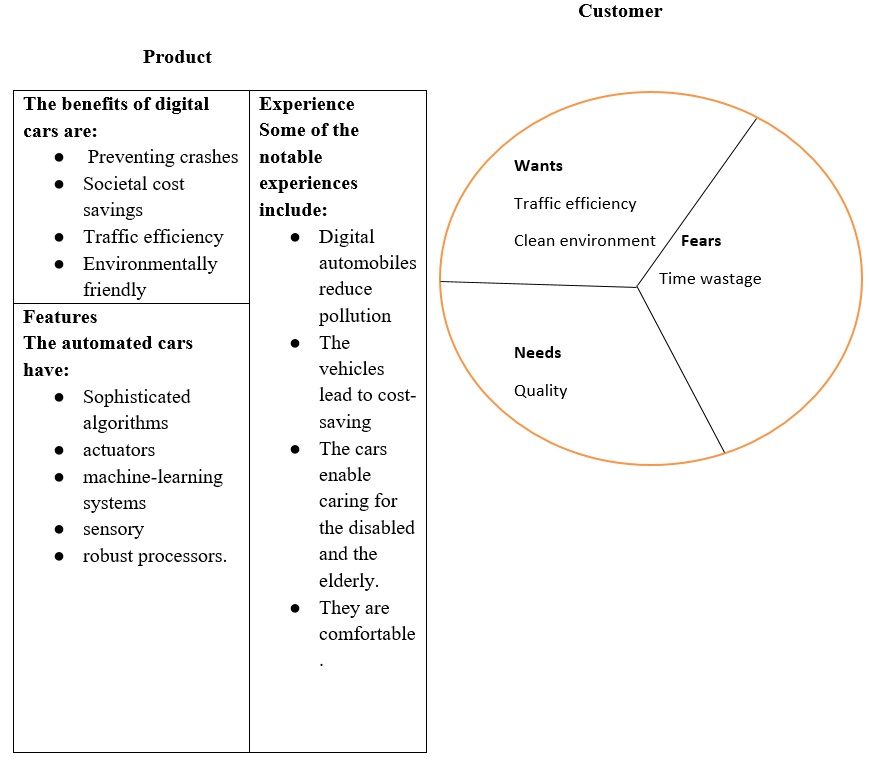
Customer Fears
The common fear associated with Tesla Model cars is whether they are worthy of the money the consumer is spending. Smart technology and self-driving vehicles will be more costly than non-automated ones due to several advantages and the several devices inserted in them. However, since Model X offers more merits, such as detecting the surroundings to reduce accidents, which is the car’s attached value, it reduces such worries. The embodiment of the technology helps minimize the client’s anxiety about time wastage (Vochozka et al., 2019). Most automated cars, including Model S, have high speed, and they can self-drive and park themselves in case of emergencies.
Customer Wants
To a greater extent, the primary customer wants traffic efficiency, and since Tesla Model has digital sensors, they can track areas with obstructions in real time. In that case, they will determine the best routes to avoid road jams while keeping an appropriate distance from other vehicles to avoid accidents (Sadeghi, 2019). The clients demand eco-friendly vehicles that do not emit more greenhouse gases, which negatively affect people’s well-being (Nielsen & Haustein, 2018). However, most automated cars, such as Tesla Model X, are environmentally friendly as they do not utilize internal combustion and are equipped with consistent accelerating and braking to reduce emissions.
Customer Needs
Smart technology and self-driving cars, including Tesla Model S, help consumers save money on transportation. According to Millonig (2019), community members will save approximately $800 billion by utilizing automated vehicles. The reduction of accident-associated expenditures and healthcare strains will result in cost-saving. The low-fuel prices and efficient transportation play a significant role in minimizing fees. Smart technology and self-driving cars offer the best transportation quality by reducing car crash risks.
Takeaways
Significantly, the identified product, the automated vehicles, including Tesla Model X cars, can solve real-world problems in the business context. The notable client fears include the high purchase of digital cars and whether they can reduce time wastage. In addition, the clients want to include automobiles that reduce traffic obstructs and are extensively eco-friendly. Due to rapid accidents on the roads, the customers need cars, resulting in cost savings by reducing the burden of healthcare expenditure strains. Most manufacturers use a human-centered design approach to have vehicles that meet clients’ demands. For example, consider a person who has a meeting in two different locations, which are located in a town. Using digital cars, which have sensors, reduces time wastage as the vehicle can monitor areas with traffic jams (Sadeghi, 2019). The business meetings can be successful and ensure that the venture clients are all satisfied.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the client’s fears, such as time wastage while transacting businesses, are reduced as the automated vehicles have high speeds and can monitor the surroundings to avoid accidents that cause delay. In addition, several customers’ wants, including a clean environment and traffic efficiency, are attained using smart technology and self-driving cars. Lastly, customer needs are met as the healthcare expenditure strains resulting from accidents are significantly reduced.
References
Belleflamme, P., & Neysen, N. (2021). A multisided value proposition canvas for online platforms. Journal of Business Ecosystems, 2(1), 1-14. Web.
Millonig, A. (2019). Connected and automated vehicles: Chances for elderly travelers. Gerontology, 65(5), 571-578. Web.
Nielsen, T. A. S., & Haustein, S. (2018). On skeptics and enthusiasts: What are the expectations towards self-driving cars? Transport Policy, 66, 49-55. Web.
Road safety facts. (2021). Association for safe international road travel. Web.
Sadeghi, A. (2019). The study of the mistakes and errors made by distracted and undistracted drivers in road safety of users. The Neuroscience Journal of Shefaye Khatam, 2(4), 83-83. Web.
Vochozka, M., Horák, J., & Krulický, T. (2019). Advantages and disadvantages of automated control systems (ACS). In International Scientific Conference “Digital Transformation of the Economy: Challenges, Trends, New Opportunities” (pp. 416-421). Springer, Cham.