Professional Marketing Analysis of Volkswagen’s Engineering and Technological Products
Introduction
Volkswagen is a German automobile company. It has its headquarters in Wolfsburg. The firm was found in 1937. It was founded by the German Labour Front. Since its inception, the company has emerged to be one of the leading vehicle manufacturers in the world. It is the largest automaker in Europe (Maurer, 2013). In the German language, the term ‘Volkswagen’ stands for people’s car.
Today, the company operates under the international brand of Das Auto. The phrase means ‘the car’. The organisation has three car brands in the list of the world’s ten top-selling automobiles of all time. They include Volkswagen Golf, Beetle, and Passat. The three models make the manufacturer top the list of the companies with the most brands in the list (Maurer 2013).
Volkswagen Cars Company has businesses in different fields. They include the development of outsized bore diesel engines. The engines are used for marine and stationary applications. A case in point includes those used in turnkey power plants. The group also manufactures turbomachinery and chargers. It is also involved in the assembly and distribution of chemical reactors and compressors (Mullineux, Southworth & World 2000). In addition, Volkswagen develops slide bearings, car transmissions, and couplings. In addition, the company manufactures specialised gear components. The mechanisms are used in wind turbines and evaluation systems.
In this paper, the author will discuss five different components of the Volkswagen Automobile Company in relation to its engineering and technological products. They include analysis of the company’s consumer, market, competition, and distribution aspects. The final aspect of evaluation is the marketing mix adopted by the firm in the promotion of the selected engineering and technological goods and services.
Consumer Analysis of the Company’s Engineering and Technological Products
Since its founding, Volkswagen Car Company has been involved in the development of various technological products. They include hybrid electric, hybrid, flexible fuel, and neat ethanol vehicles (Long 2014). With regards to the component of consumer analysis in relation to a technological or engineering product, the author will evaluate the company’s electric automotive.
Volkswagen began its electric car manufacturing initiatives in 2009. Within the same year, the organisation recruited Karl-Thomas. He was made the CEO of Electric Traction. The first electric car product was the two-door E-UP. The vehicle was unveiled during the 63rd Frankfurt Automobile Exhibition. The event was held in 2009. It measures 3.19 meters or 10 ft 6 in length. In addition, it has a three plus one seating design. The car also uses 60 kilowatts electric motor positioned at the front (Plunkett 2013). The primary function of the motor is to drive the front wheels.
E-UP’s production started in 2013. Upon its release into the market, the vehicle’s customer analysis reports showed a positive reception. The clients favoured the product for a number of reasons. They include the car’s capability and pace and a good battery range, which is rated to hold power for more than 100 miles in perfect conditions and 50 in freezing times. The vehicle is also fitted with a regenerative braking system, which allows drivers to add range (Schrott 2014). In addition, the battery has an eight-year 100,000 mile warranty.
Market Analysis of Volkswagen in Relation to Engineering and Technological Products
Market analysis is also referred to as a documented investigation of an industry. The component entails conducting research on the attractiveness and dynamics of the market (Stone & Desmond 2007). It is considered to be an element of industry evaluation. As a result, it is also viewed to be an aspect of global environmental assessment. The market study allows a company to identify its various attributes. The elements include strengths and limitations. Others include risks and opportunities. The evaluation is based on reports from such aspects as inventory purchase, facility and workforce expansion, promotional activities, and acquisition of capital tools. Market analysis has various facets. They include market size, growth rate, trends, industry cost system, and profitability. Other dimensions are distribution channels, key success factors, and details. The primary goal of the assessment is to determine both the current and future business dynamics (Reuvid & Sherlock 2011).
Companies around the world strive to ensure they manufacture products that match the current market trends and demands. An example of Volkswagen’s engineering product is flexible fuel vehicles. In 2003, the company produced the first vehicle in the Brazilian market. The model operated on any mix of E20-E25 gasoline (Maurer 2013). In addition, the car had the capability of using 100% hydrous ethanol fuel. The automobile was referred to as VW Gol 1.6 Total Flex. Due to the brand’s success, people rekindled their interests in ethanol-powered cars. Due to this, flex technology was well adopted in the Brazilian market. The rapid consumer acceptance resulted in the success of VW Gol 1.6 Total Flex.
By 2005, the new Volkswagen brand had sold 295,523 Total Flex automobiles and light-duty trucks. In addition, the company sold 53,074 gasoline-driven vehicles (Plunkett 2013). By 2007, there was a significant increase in total sale volume. The number of flex-fuel cars sold rose to 525,838 units. In 2008, positive growth was also reported with sales of 564,959 units. The success meant that Volkswagen produced 96% of all new automobiles and light-duty trucks on sale in 2008. The company produces a broad range of flex-fuel cars for the global market. They include Fox, Saviero, Golf, Parati, and Kombi. Others are Polo Hatch, Crossfox, Gol, and Sedan. Between 2003 (when the first flex-fuel vehicle was produced) and 2009, Volkswagen had sold over two million units (Long 2014).
Competitive Analysis
In the automobile industry, it is difficult to find a global brand that maintains clarity and consistency in its design and model. However, Volkswagen Cars Company has managed to make German engineering and reliable technological inventions its trademark. One of the group’s technological products that are developed to compete with rivals is hybrid cars.
Volkswagen and Sanyo merged to develop a unique battery system for hybrid vehicles (Long, 2014). The major aim of the group is to ensure all its products have a hybrid alternative. An example of a product with this capability is Volkswagen Touareg. Automobile companies sustain stiff competition by producing a wide range of luxury car brands. Majority of Volkswagen’s models are less expensive and complex. The reason is to gain mass-market appeal. With the new Touareg midsized SUV, the group has produced a complete luxury vehicle to compete with major rivals. The competitors include Lexus GX hybrid, BMW X5, Land Rover LRV4, and Acura MDX (Plunkett 2013).
The model is based on a platform similar to the Porsche Cayenne. Since it is meant to offer a genuine luxury experience, the car provides buyers with a wide range of impressive features. They include economic fuel consumption, comfortable and lavish interior design, functional tugging capabilities, and the option of choosing hybrid diesel power trains. The model has proved competitive in the market. Touareg’s high-quality interior rivals those of BMW and Mercedes Benz (Schrott 2014).
Analysing Distribution Channels of Volkswagen’s Engineering and Technological Products
For decades, Volkswagen Cars Company has focused on the development of complex technologies for various strategic environments. Its engineering products include electric cars, hybrid, flex-fuel, and neat ethanol vehicles (Schrott, 2014). All of these products have recorded significant success in different markets around the globe. The company’s car brands have won several awards over the years. To a large extent, these achievements have been influenced by the firm’s effective distribution channels. The engineering product that will be discussed in relation to the marketing component is hybrid technology. Since the company started manufacturing hybrid vehicles, it has managed to gain markets in different parts of the world.
Volkswagen’s marketing team captures its target markets by the use of selective distribution channels. The group relies on a few intermediaries situated in different countries to carry their products. The company delivers its hybrid cars to markets in North and South America, Western, Central, and Eastern Europe (Plunkett 2013). In addition, its hybrid brands are distributed in Asia, with China being the major market. The diverse distribution channels have a long term positive impact on Volkswagen’s hybrid models. Due to this, their value has increased. The hybrid cars are manufactured in different locations worldwide. However, the major factory and distribution centre is based in Wolfsburg (Long 2014). The base was the first one and has been in operation since the company was founded.
To ensure increased and timely deliveries to its clients, Volkswagen Cars Company uses a mix of different distribution channels. The group uses a direct sales- force team to deal with large customer bases (Schrott 2014). To deal with smaller consumers and prospects, Volkswagen distribution channels utilise agents. In India, for example, the major distributors are India-Pune.
Assessing Volkswagen’s 4Ps Marketing Mix for an Engineering Product
Volkswagen Cars Company focuses on exceptional technological products for different markets around the world. Over the years, the group has invested billions of dollars in producing highly advanced car brands operating on unique features. One of Volkswagen’s technological products is Neat Ethanol Vehicles. The initial Volkswagen do Brasil neat ethanol cars were manufactured and sold in the Brazilian market (Long 2014). However, the production was stopped after the invention of a more complex technology named Flex Fuel. The new vehicle brand was well received in the local market. The success was influenced by various factors. At the time, Brazil was facing an oil crisis. After the car’s launch in the market, the government started promoting the use of bio-ethanol fuel.
To continue with its technological advancements, Volkswagen modified gasoline-powered engines to support and facilitate the use of hydrous ethanol. Within a period of six years, 75% of all passenger vehicles in Brazil were equipped with ethanol driven engines (Maurer 2013).
The manufacture of neat ethanol vehicles for the Brazilian market was one way of the company’s utilisation of the component of place in the marketing mix. Under place, car manufacturers produce automobiles that are distributed in key locations where consumers need it the most. In addition, targeting a specific area ensures proper channels are put in place to promote easy access and delivery of the products (Kotler & Armstrong 2012). In the case of the neat ethanol vehicles, the cars were manufactured in Brazil and sold in the same country. Through the initiative, Volkswagen Cars Company was able to penetrate the Brazilian automobile market and maintain its dominance.
Professional Market Analysis of Volkswagen’s Consumer Products
Consumer Analysis in Relation to the Company’s Consumer Product
When customers acquire a new car, the last thing they expect is an unscheduled trip back to the manufacturer to fix a problem that was undetected before the machine was sold to them. Each year, consumer reports and auto-reliability surveys reveal that some vehicle owners return to the dealers a number of times (Maurer 2013). As such, it is important for a company to conduct consumer analysis to identify some of these problems.
Consumer analysis is also referred to as a client profile or target market evaluation. It is noted that the component is the most important aspect of a business plan. The reason behind this is because for a company to be successful, the managers should be able to demonstrate to the customer base the reliability of their goods and services. To this end, the customer segments should be clearly identified (Leverenz 2014). In addition, strategies on how the business will meet its customers’ needs should be formulated and put in place.
Since 1937, the Volkswagen Company has produced a wide range of customer products. One of the inventions is the XL1 passenger car brand. The model is the most economical vehicle in the world. The car was unveiled in 2011 at the Qatar Motor Show. The two-seater brand is fitted with a plug-in hybrid system. In addition, the car consumes 0.91 litres of diesel per 100km (Maurer 2013). The plug-in hybrid system allows the automobile to cover a distance of up to 50km in electric mode. To achieve the status of the lowest fuel consumption vehicle in the world, XL1 is manufactured with lightweight materials. It also has a streamlined body and an engine and transmission system that is configured for the economy.
Upon its release into the market in mid-2013, Volkswagen produced a limited 250 units. Each car was priced at €111,000 (Plunkett 2013). The product had a positive market reception. By mid November 2014, all the units produced for the UK market had been sold. The model also appeared in the top five list of World Green Car of the Year. The vehicle’s positive reception was influenced by a wide range of factors. They include the body and frame designed with crush zones and keel-over protection. According to Volkswagen Group, XL1’s safety is similar to that of GT racing cars. In addition, the vehicle is fitted with anti-lock brakes and pressure sensors. It also has high stability level (Schrott 2014). The consumers were also pleased with the capability of driving through a six-speed transmission. The process integrates stick-shift, weight, mechanics, and drive efficiency with automatic ease and efficiency controls. Appendix 1 shows a picture of Volkswagen XL1.
Marketing Analysis of Volkswagen’s Consumer Products
To keep up with changing market trends and remain relevant, companies focus on developing unique consumer products (Kotabe 2009). Volkswagen, being a leading automobile manufacturer, has produced a wide variety of brands. One of the group’s consumer products is Golf GTI. The brand has been in production since 1974 and is marketed globally. Currently, the product is in its seventh generation. The vehicle has undergone different body modifications and changes in names. According to market reports, Golf is Volkswagen’s best-selling brand. Globally, the model is the second highest seller. By 2012, the company had produced more than 29 million units (Plunkett 2013). The initial Golf brands had 3 doors. However, the group advanced and started developing 5-door models.
Due to the mark set in different markets, Golf has won numerous awards since its inception. The grants include World Car of the Year in 2009 and 2013. The two brands that topped the list were Golf Mk6 and Mk7. All through the Volkswagen’s model history, each generation has been a runner up in the European Car of the Year prize (Long 2014). The other brand to claim the annual award is Renault Clio. In addition, the model has appeared in the yearly car and driver ranking severally. The honours reveal Volkswagen’s dominance in the automobile market. According to Test Track Consumer reports, most people are anticipating the launch of the seventh-generation redesigned model of 2015 Golf GTI. The reason behind this is because Golf has for a number of years been one of the most remarkable small private cars in the market. Appendix 2 is a picture of Volkswagen Golf.
Competitive Analysis of Volkswagen’s Consumer Products
The competitive nature of the automobile industry requires companies to manufacture unique consumer products that meet market needs and demands. One competitive consumer product associated with Volkswagen Cars Company is the Jetta brand. The vehicle is a small family car. It has been in production since 1979 (Mullineux et al. 2000). The brand’s idea was based on Golf. The manufacturer produced the model by modifying the existing Golf hatchback. The modifications involved the addition of a trunk. In addition, the car was fitted with more stylish designs on the interior and front areas. The model has been marketed under various names throughout its six generations. They include Atlantic, Vento, Jetta City, GLI, Sagitar, Bora, and Clasico.
It is noted that in the competitive global market, a few small sized vehicles match Volkswagen Jetta’s capabilities and success. The car is one of the group’s bestselling brands in the United States (Plunkett 2013). It is favoured by buyers due to its unique specifications that are not offered by most competitors. They include the upscale design, strong and powerful engine, and a refined cabin. With the automobile, Volkswagen closed the gap that existed in the market.
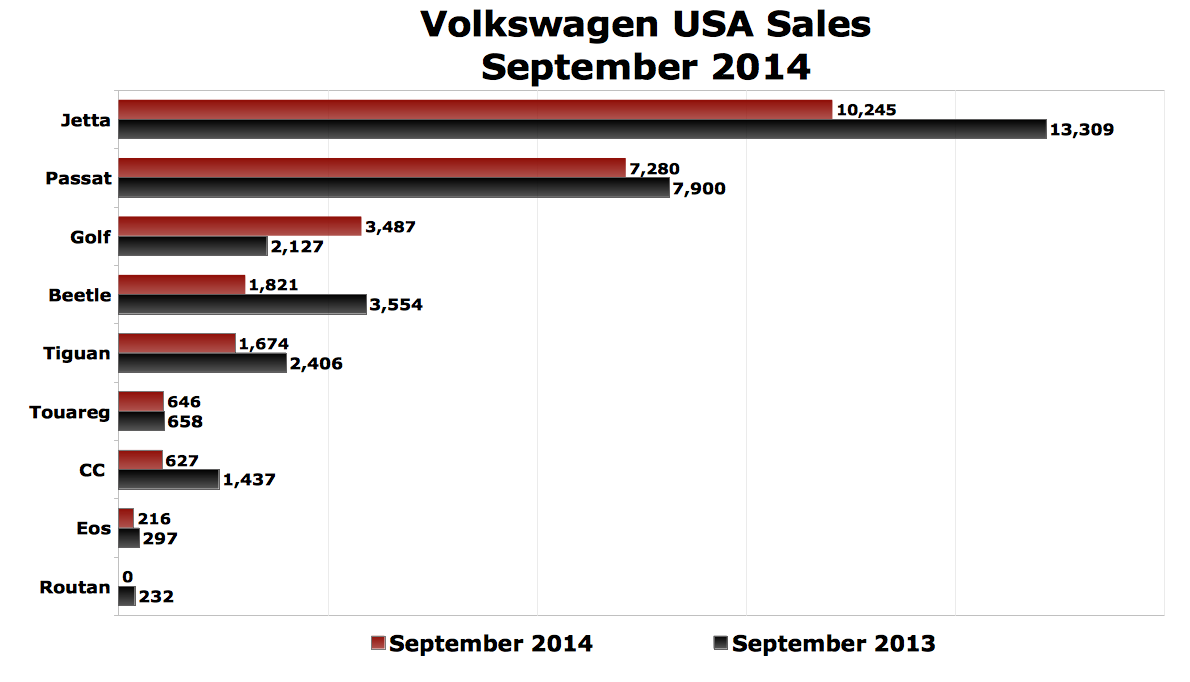
By 2005, the Volkswagen Group had sold over 6.6 million Jetta’s across the globe. More than a third of the sales were in the United States. By mid 2011, the number of units sold had risen to over 10 million. By April 2014, the figure had risen further. The company had processed more than 14 million orders for the design (Long 2014). Due to this, the brand has become one of the company’s bestselling brands. The 2015 Jetta is ranked at position 19 out of 41 in the list of Affordable Small Cars. Appendix 3 is an illustration of Volkswagen Jetta deliveries in the US.
Distribution Channels for Volkswagen’s Consumer Products
Distribution channels in marketing are key components of a business strategy. Their primary goal is to help organisations expand their reach and increase their revenue. Depending on their size, companies can sell their products through a single or multiple distribution channels (Kotler & Armstrong 2012). In addition, the process of making the products and services available to different consumers can be direct or indirect. Indirect means entail the use of intermediaries to reach a wide range of clients. The channel designs range from intensive to selective and exclusive distribution. To enhance performance, businesses are required to monitor their interdependent organisations from time to time (Stone & Desmond 2007). In various firms, the distribution channels are designed by the marketing department. In this section, the author will analyse Volkswagen’s distribution channels.
Volkswagen Cars Company produces a wide range of consumer products, which are distributed in different markets around the globe. Its manufacturing plants are based in various countries, such as Germany, Mexico, the US, Russia, and Argentina. According to the company’s reports, the group has more than 70 dealerships in 56 cities across 18 states. The diverse assembly bases work with marketing teams to ensure the products manufactured are distributed to the target markets. To remain competitive and enhance consumer satisfaction, companies recognise the need for an extensive dealer network (Brassington & Pettitt 2003).
One consumer product whose distribution channels will be analysed in this report is Volkswagen Jetta. The vehicle has recorded significant success since its launch. Due to this, it has been in high demand in different markets across the world. To meet the rise in consumer orders, the company invested millions of dollars in setting up effective distribution channels. As a result of effective reach to customers, the sale of Volkswagen Jetta helped the group achieve the position of number one brand in different nations, such as China. In 2010, Volkswagen was named the number 1 automobile company (Schrott 2014).
Through effective distribution, Jetta brand reported an above-average increase in deliveries to customers in the United States market. The cars are distributed by use of a strong dealer network base. Lack of strong distribution channels leads to poor delivery of consumer products (Jeannet & Hennessey 2004). When entering Jetta into new markets, Volkswagen Cars Company ensures it has identified natural partners. The group looks for distributing agencies with stable relationships with the end-users. With the help of effective distribution channels, the sale of Jetta model in India recorded a growth of 100% (Dent 2011). To support the distribution channels, Volkswagen Company’s marketing team keeps track of its clients. The members ensure customers in different countries get the Jetta product. The selective distribution channels are made to work for both the rural and urban client population.
Assessing Volkswagen’s Consumer Products using the 4Ps Marketing Mix Framework
The company is a large entity in the global market. The attribute has supported its growth and survival in the competitive automobile industry. To keep the consumers satisfied, the group produces a wide variety of brands. Each is meant to meet the needs of specific clients based on their preferences. The consumer products in Volkswagen’s marketing mix include Up, Jetta, Passat CC, Polo, and Golf (Schrott 2014). Other models are Sirocco, Tiguan, and Beetle. The products of the automobile company are made with salient features. They include high quality vehicles with a brand name to support it in the market. Other features include excellent distribution channels and presence of few escalated consumer complaints.
A consumer product to be discussed under marketing mix is Volkswagen Polo. The car was made by a team of engineers from Wolfsburg. The vehicle has five different versions (Plunkett 2013). They include Comfortline, Cross Polo, Trendline, and GTI. Each brand is meant to meet the needs of different consumer bases. The clients chose between the models by comparing their different aspects. One feature is the range of engines. A consumer can go for a petrol, diesel, or diesel Blue Technology. GTI is one of Polo’s brands in the sports sector. In addition, it is considered to be a small SUV. Due to the car’s quality features, affordability, and safety, Polo won the World Car of the Year Awards in 2010 (Long 2014). The major competitors in the field are Audi A1, Ford Figo, SEAT Ibiza, and Nissan Micra.
Price of consumer products in Volkswagen’s marketing mix vary depending on the size, level of exclusivity, and engine power. Similar to other car makers, the prices of Volkswagen brands range from affordable to expensive (Maurer 2013). However, the group stands out compared to its competitors. The reason is because it focuses on manufacturing vehicles that are affordable to the average person.
There is also the element of promotion of consumer products by the company. To this end, the firm utilises the services of ATL media. A case in point is the use of TVC. Together with print media, the channel was used by the firm in its first 12 months of operations in the Indian market. After experiencing stiff competition from other automobile manufacturers, Volkswagen adopted different promotion strategies (Long 2014). They included use of BTL, Digital platforms, and out-of-home media.
Professional Market Analysis of Volkswagen’s Services
Consumer Analysis of Volkswagen’s Maintenance Plan Service
Volkswagen Group provides a broad range of services to its new and existing customers. One of the services is the maintenance plan. Through the initiative, the company takes good care of the customers’ vehicles at affordable prices. Clients choose their preferred level of cover by considering the age and mileage of their automobile (Long 2014). According to a consumer analysis report, the plan is favoured by a large number of clients. The reason behind this is because of the wide range of its benefits.
The gains include flexible pay plans, which range from simple fixed monthly payments to a one-off fee up-front arrangement. The service also helps spread the outlay of Volkswagen car maintenance and avoid inflation. In addition, both new and existing customers are free to visit over 200 retailers when their cars need fixing. The biggest benefit cited by consumers is the guarantee that the vehicles will be fitted with genuine Volkswagen parts by the corporation’s trained technicians (Plunkett 2013). All the new parts and labour have a two year warranty. The benefits ensure the clients can maintain the highest probable resale value of their cars.
A Market Analysis of Volkswagen’s Financial Services
To remain relevant in the market and attract more customers, Volkswagen Cars Company provides a number of services to its global consumers. One of them includes the financial services plan developed in 1994 (Mullineux et al. 2000). When purchasing and insuring a vehicle, it is important to seek the help of a trusted partner. Volkswagen Financial Services (VWFS) offers finance and insurance overhauls to all consumers across the whole group in various parts of the world. The company believes that choosing a new car is a personal matter. Due to this, car finance is also considered to be a private thing. The primary purpose of the service is to help clients develop an individual and personalised finance solution, which matches their current budget and lifestyle (Schrott 2014).
Volkswagen team of dedicated experts assists customers in every step of the automobile purchase and insuring procedure. The aid ensures the buying process is quick and unproblematic. Volkswagen’s main focus in the market is steering success. The group provides benefits not enjoyed by clients of other companies in the market. In the United Kingdom, for example, its financial service products are offered by over 700 retailers across the nation. The services are provided to private individuals, as well as small and large organisations (Plunkett 2013). The initiative has had a positive impact on both national and global markets.
Volkswagen holds the top spot as the largest provider of car financial services in Europe. The group operates on a total sum of 115.1 billion Euros. The current contracts add up to 107 million Euros (Maurer 2013). To keep up with the market demands, the company has over 10,945 workers across the globe.
Competitive Analysis of Volkswagen’s Product Cycle Services
Competitive analysis is an important component of an organisation’s marketing plan. The evaluation enables the businesses to determine the aspects that make its products unique compared to those of the competitors. The initial step in competitive analysis entails determining existing and probable competition (Blythe 2009). To study the rivals, managers place them in different strategic groups. They are divided in accordance to the manner in which they directly offer competition in the market. For each rival, various aspects are analysed. They include a list of their products, their growth pattern, current and past strategies, as well as strengths and weaknesses. Other factors to consider are marketing objectives and assumptions. The best and easy way to compare rivalry in the market is by developing a competition grid (Choudhry 2010).
Volkswagen Cars Company has strived to develop various consumer services to keep up with the stiff competition in the industry. One of its services is the product cycle. In the Los Angeles Auto Show, the group announced the plan to shorten its product cycle to increase market share and boost profitability. The arrangement entails replacing vehicles after a span of five years. The mid-cycle refreshments will be conducted every three years after a brand’s launch. The initial replacement time was seven years, while refreshment was four (Maurer 2013). The new initiative helps Volkswagen to keep up with the pace of its European competitors. In addition, the move helps the Company to be in sync with the competitive U.S market.
Analysing Distribution Channel’s of Volkswagen’s Hire Purchase Services
The company’s services play a key role in strengthening a consumer market base (Fleisher & Bensoussan 2008). Consequently, different companies come up with new offers to compete with their rivals in the industry. However, for the services to be known by the customers, proper distribution channels need to be put in place to market them. In addition, a team of experts is needed to ensure the services are accessible to different clients as required.
One dealer service offered by Volkswagen Cars Company is hire purchase. Majority of people who wish to purchase a new car are weighed down by the total cost of the vehicle. Volkswagen Group has worked hard to offer help to such individuals. The company has a policy that enables customers to buy their preferred brands on a hire purchase basis (Hill 2013). The marketers guarantee customers on the manageable aspect of using the monthly payments. The service works on affordable fixed interest rates. To enjoy the service, clients are required to pay a fixed deposit determined on the basis of the total price of the vehicle. The rest of the payment is made in monthly instalments. The period set to clear the debt is one to five years. After the end of the contract, the vehicle becomes the owner’s property. The service is offered to both new and second hand automobiles (Schrott 2014).
For customers to get the required information on the service, Volkswagen ensures the marketing team has proper data distribution channels. The channels include social media and different advertisement platforms. In addition, the company has teams of dedicated agents whose primary goal is to enlighten the public on the services (Long 2014). Without proper channels to relay information, the service will only be enjoyed by a small group of people. The aspect results in loss of clients. The reason is because customers migrate to seek services offered by other companies.
Analysing Volkswagen’s Rent-to-Own and Rent-to-Buy Services using the 4Ps Marketing Mix Framework
Marketing mix is an important component when determining a brand’s offer. The component is linked to the concept of four Ps (Fleisher & Bensoussan 2003). They include product, price, promotion, and place. All products have a life-cycle. The cycle entails growth, maturity, and decline. The fall results in decrease in prices. Due to this aspect, marketers are tasked with the duty of conducting research on their product’s lifecycle. In addition, they focus on the probable challenges that may face the brand at different phases. In marketing mix, the price plays a key part. The amount paid by consumers determines the company’s profit margins and endurance in the market (Hill 2013). Volkswagen, with is sheer size, implements the four Ps marketing mix.
Volkswagen, as one of the leading car manufacturers in the world, offers a wide range of services to its customers. Each market has its own unique set of services meant to benefit both the clients and the company (Dent 2011). When consumers are satisfied with what an organisation is offering, they make the brand their favourite. In the end, it gains a broad customer base and keeps up with competitors.
One of Volkswagen’s services offered to the consumers is the rent-to-own and rent-to-buy plan. Most clients find the process of applying for vehicle finance through the bank a challenging task (Choudhry 2010). Due to this, Volkswagen adopted the rent-to-own initiative as an alternative to help such people. Clients can get a wide variety of cars, such as Polo Hatch and Sedan, using this system. To apply for the service, no credit checks are required. However, to qualify, it is mandatory for the client to be a resident of the area where the service providers are situated. The rent-to-own deal has various regulations. They include a pre-checked, accident free, low mileage car, and annual licensing. In addition, there is an option to return the vehicle after five days in instances where the client is not pleased with its capabilities and features (Schrott 2014).
All rent-to-own Volkswagen vehicles are of high quality. In addition, they are chosen by a team of qualified mechanics. To apply, the major documents needed are national identity cards, driver’s license, and current payslip. In cases where the client is self employed, the company officials ask for bank statements. To ensure the company utilises the promotion aspect of marketing mix, Volkswagen uses different forms of media to advertise its services (Long 2014). The commonly used channel is social media. They include Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and LinkedIn. In addition, the group has dedicated sites where clients can visit to view the wide range of services.
Conclusion
Professional marketing strategies determine the success of an organisation. When the plans are diverse and well utilised, the company gains long term positive rewards. In instances where a firm operates on poor marketing plans, the chances of downfall and loses are high. The analysis of Volkswagen Cars Company reveals the importance of these tactics in the marketing of its services. Since the 1930s, Volkswagen Group has employed diverse marketing strategies to emerge as one of the leading car manufacturers in the world. The corporation’s services have gained significant success in all the markets the company has ventured into. The outcomes of its strategic plans are increased sales and a strong customer base. In addition, Volkswagen has managed to maintain a sustainable competitive advantage over its major rivals, such as Toyota.
Appendix
Appendix 1

Appendix 2

Appendix 3
References
Blythe, J 2009, Key concepts in marketing, SAGE, Los Angeles. Web.
Brassington, F & Pettitt, S 2003, Principles of marketing, 3rd edn, FT/Prentice Hall, Harlow, England. Web.
Choudhry, M 2010, Capital market instruments: analysis and valuation, 3rd edn, Palgrave MacMillan, Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire. Web.
Dent, J 2011, Distribution channels: understanding and managing channels to market, 2nd edn, Kogan Page, London. Web.
Fleisher, C & Bensoussan, B 2003, Strategic and competitive analysis: methods and techniques for analysing business competition, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, N.J. Web.
Fleisher, C & Bensoussan, B 2008, Business and competitive analysis: effective application of new and classic methods, 3rd edn, FT Prentice, Upper Saddle River, N.J. Web.
Hill, M 2013, Marketing strategy: the thinking involved, SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks. Web.
Jeannet, J & Hennessey, H 2004, Cases in global marketing strategies, 6th edn, Houghton Mifflin, Boston. Web.
Kotabe, M 2009, The SAGE handbook of international marketing, SAGE, Los Angeles. Web.
Kotler, P & Armstrong, G 2012, Principles of marketing, 14th edn, Pearson Prentice Hall, Boston. Web.
Leverenz, C 2014, Principles of marketing, Hunt, Kendall. Web.
Long, S 2014, International directory of company histories, St. James Press, Detroit, Michigan. Web.
Maurer, M 2013, Automotive systems engineering, Springer, Berlin. Web.
Mullineux, N, Southworth, A & World, I 2000, The Volkswagen Group, Informa Pub. Group, London. Web.
Plunkett, J 2013, Plunkett’s automobile industry almanac 2014: automobile industry market research, statistics, trends & leading companies, Plunkett Research, Houston. Web.
Reuvid, J & Sherlock, J 2011, International trade: an essential guide to the principles and practice of export, Kogan Page, London. Web.
Schrott, P 2014, Strategies of German car companies in China, Diplomica Verlag, Hamberg. Web.
Stone, M & Desmond, J 2007, Fundamentals of marketing, Routledge, London. Web.