Introduction
Working capital is really important for any kind of business organization. It is known as life blood of any firm. Khan and Jain (2007) purports that an industry needs working capital to operate its organizational activities Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis is necessary to make industry stable for the future. It is assisted to take the future decisions of any manager. If any manager would not properly analyze how much sales will be made in the next fiscal year he will not be known the profit relating to cost and the industry will be in danger. However this study will discuss about the term working capital and cost-volume-profit.
Managing Working Capital
As it is discussed in earlier that working capital is the lifeblood for a business firm so this study can say that without working capital a business can’t properly run. There are several items which makes working capital healthy and when we pay some debts then our working capital decreases. So be careful in the balance of working capital. Maximum firms are destroyed for the lack of working capital rather than the lack of profit. So, first we should know from which sources we can collect our working capital and the sources are:
- Capital of the business
- Accounts Receivables
- Profits (when you secure it as cash !)
- Payables (credit from suppliers)
- New equity or loans from shareholders
- Bank overdrafts or lines of credit
- Long-term loans
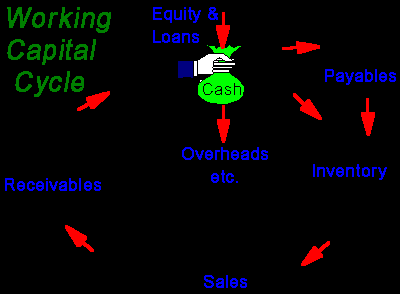
The manner of administration of working capital determines to a large extent the success or failure of overall operations of an enterprise. In the following graph we can see that working capital is coming from several directions such as receivables, equity and loans, inventory, payables, sales and overheads and they all are generating in the name of cash.
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
It is a management accounting tools to show the relationship among sale price, variable cost, sales volume, sales mix and fixed costs (Hilton, 1991, p.203) To analyze CVP we need to use Break-even analysis, that is “break-even point is the sales volume at which revenue equal to cost” (Thompson, 1993). So in CVP when break-even point can be seen then we can say that there is a situation of no profit and no loss and if any firm are in this situation then we can say the condition of the firm is improving. After break-even point if firm can sale more goods then fixed cost is stable and profit will be seen.
For giving decisions of this requirement this study need to use the application of break-even analysis, here an example is cited:
Particulars Amount percent
Break-even sales $ 65000 100
Variable costs 39000 60
Contribution 26000 40
Fixed costs 26000 40
Net income nil nil
Here we can see that net income is nil in break-even point, if this company wants to earn a profit of 14000 then required sales volume =( fixed expenses + desired operating profit) + P/V ratio =(26000+14000)/0.40=100000
If this company wants to see net profit $ 13500 after tax and if tax rate is 45% then
Required sales volume is = fixed costs + (desired income after taxes/ 1-tax rate)
P/v ratio
= $ 26000 + ($ 13500/1-0.45) / 0.40 = $ 126364
This study can say in here if a firm needs more profit after break-even point then they should increase their net volume of sales.
According to the requirement of this study the Accountant wants more payments for preparing Management Accounts, if he makes a proper CVP analysis of your firm then your net profit will increase. If your products line is in Break-even points then you can pay him higher for CVP analysis. Once your can make higher profit then your working capital will increase automatically for the following reasons:
- Your debtor turnover ratio will increase
- Creditor turnover ratio will increase
- Availability of cash will be seen
- Receivables will be higher
- Sales ratio will increase
So my advice is to my friend to pay account higher fees for proper CVP analysis and increasing of working capital.
References
Arsham, Hossein (2004-2008). Time-Critical Decision Making for Business Administration, 9th Ed., Web.
Hilton, Ronald W (1991) Managerial Accounting, New York: McGraw-Hill, 1991.
Khan, M Y and JAIN, P K (2007) Financial Management- Text and Problems, Fourth ed., Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi. 2007.
Thompson, Kevin D (1993) Business Management: Planning for Profit, Black Enterprise, 1993.