Introduction
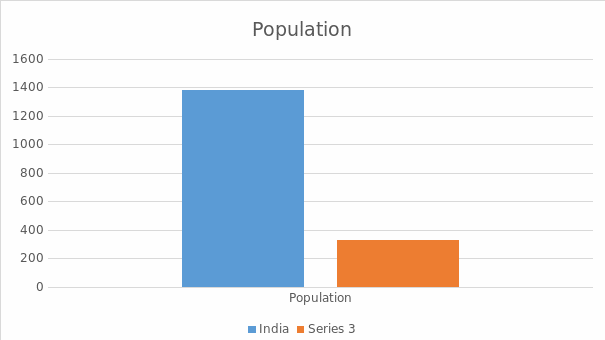
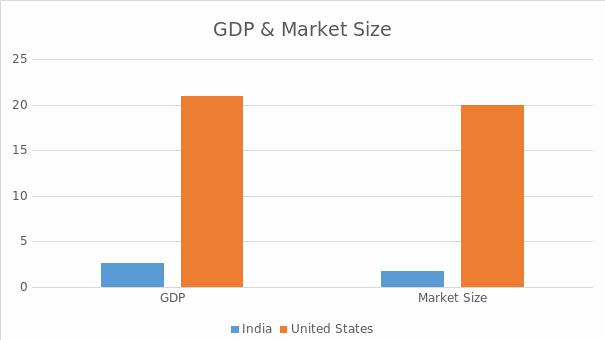
The study’s purpose is to evaluate the cultural and economic issues that will impact Winmark Corp, an organization seeking to expand its operations from the United States to India. The company operates by buying and selling already used goods such as clothing, sportswear and video games. Winmark Corp was influenced by India’s monetary policy to expand its operations to the country. The policy does not have many regulations since it seeks to enhance the country’s economic growth rate. There is a difference in culture between the two countries, affecting how the organization operates in India. The two countries also have significant differences that will affect expansion to the Indian market. India has about 1378.6 million people, while the U.S has 329.5 million people. This shows that India has a high number of consumers than the U.S hence increased chances of profitability. India’s GDP was estimated to be at 2.623 trillion dollars, while for the U.S, it was at 20.94 trillion dollars, indicating a great difference between the two countries.
Another difference between the two countries is seen in their economic growth, with that for the U.S is at 6.9%, whereas that for India was at 8.3%. This shows that India’s economy will grow significantly in the coming years compared to that of the United States. India proves to be more religious and ethnically diverse when compared to the U.S. The U.S has a twenty trillion dollars’ market size, with that for India being at 1.7 trillion dollars. The bigger market size for the U.S makes it have a better market potential than that of India. India has a parliamentary government form that follows a federal structure headed by the president. The prime minister of India governs the council of ministers and offers advice to the president. The U.S is headed by a federal government that is made up of the legislative, executive, and judicial systems.
Culture
Globalisation and Culture
When an organization seeks to expand its operations from a developed country to a developing country’s market, it must consider the culture it will encounter. Each nation has a unique culture that defines the ideas, traditions, and behavior that make it differ from others (Twose, 2019, para. 2). For an organization seeking to expand its services from the United States to India, it must understand that acceptable business practices in the two countries are different because of varying cultures (Relocate, 2018, para. 7). Such an organization has to consider how culture is likely to affect the implementation of international business (TMF Group, 2018, para. 5). A proper understanding of culture will help to ensure that an organization expanding its services from the United States to India presents itself to the market in the most appropriate manner.
Culture is a significant factor that has to be considered in the globalisation process since it greatly influences consumer patterns and behavior. Consumer patterns and behavior are necessary to understand what potential clients are likely to purchase and the chances of market success (The European Business Review, 2020, para. 2). Consumers from the United States and India have different behavior patterns that rely greatly on their culture. Culture will also have a great influence on organizational interaction with Indian local people. Different cultures have varying patterns of communication and negotiating styles which can limit business processes (Kumar, 2021, para. 10). An organization expanding its operations to India has to learn and understand how the local people negotiate and communicate for business operations to be successful. Without an understanding of the Indian people’s culture, a U.S.-based organization cannot successfully expand its services to the nation.
Culture and Communication
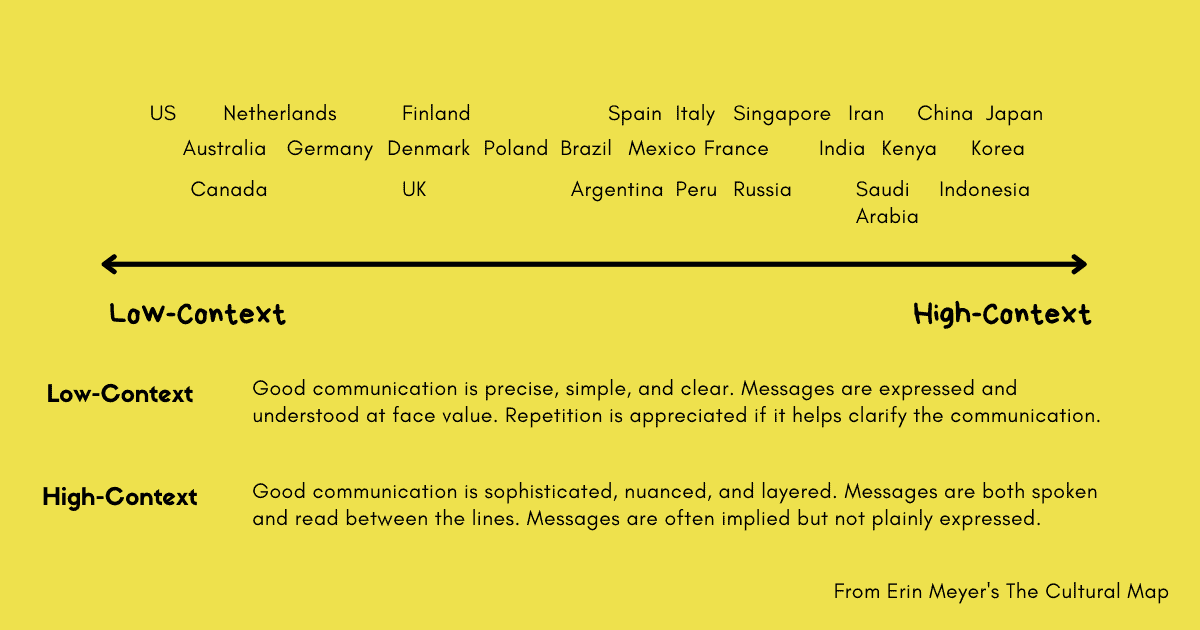
Culture has a significant influence on how people from a particular region communicate. This indicates a great need for an organization choosing to expand its operations from the United States to India to understand how culture in the country is likely to affect how people communicate (Reynolds, 2018, para. 4). The United States and India have a difference in their cultures, which means that the mode of communication differs. India is a high-context culture, whereas the United States is a low-context culture; hence there are significant differences in how people in the two nations communicate (Hough, 2021, para. 11). Individuals from a low context culture focus on the message being spelled out explicitly, while those from high context cultures rely mostly on background information (Khan & Law, 2018, para. 10). A business expanding to India has to consider how the high-context culture in the country will affect operations. Understanding India’s culture will help eliminate any communication challenges that are likely to arise when interacting with the local people.
Culture also significantly influences the language people choose to use during communication with others. Differences in culture can easily lead to misinterpretation since words can have varying means when used in various cultures (Hendrith, 2018, p.15). Language can act as a significant barrier to conducting business operations, especially when expanding service offerings to international levels. Understanding how India’s culture influences people’s communication will inform the effective strategies to use in marketing. Views and ideologies vary from one culture to the other hence utilizing a marketing campaign that does not align with the local people is a great barrier to success (Brown, 2019, para. 4). An organization expanding its operations to India from the United States has to consider how differences in culture are likely to affect the success of business communications.
Cultural Differences
An organization seeking to expand its operations from the United States to India has to consider the cultural differences that are likely to influence the process greatly. Such an organization should avoid interpreting the behavior of the Indian people from the perspective of the American culture (Association of MBAs, 2020, para. 4). The cultural differences can only be overcome by learning the other people’s cultures to ensure that business operations act as a reflection of values and beliefs. Cultural differences between the U.S. and India will also influence how employees respond to issues in the workplace (Asialink Business, 2021, para. 4). If the organization expanding to India will rely on services from Indian employees, it has to consider how culture will influence working behavior. Failure to address culture’s influence on employees will contribute to significant challenges in the workplace. Indian culture is characterized by collectivism, while Americans are more focused on individualism (Commisceo Global, 2018, para. 6). In this case, the organization expanding its operations to India has to lay out strategies that promote collectivism.
Cultural differences also influence how people act and respond to various issues in the workplace. Cultural differences between India and the United States are reflected in the goals they set and their respect for hierarchies (Bryant, 2021, para. 5). In the American culture, each person is empowered to have decision-making authority, while in India, those having higher ranks in a hierarchy have more power to make decisions. Cultural differences are also likely to greatly influence business management styles applied in India (Bajorek, 2017, para. 5). This might require the business to expand its operations to India to learn about the people’s culture and adapt to business management styles that align with the nation. Aligning management styles to the culture of the Indian people will enhance the chances of success for the U.S based organization.
Managing people in the International Business Environment
A U.S.-based organization expanding its operations to India must acknowledge that the strategies applied in managing people in the U.S. have to be different in India due to cultural differences. In this case, those given the role to manage people in the international business environment need to have cultural awareness and be able to respond to changes in the new environment (Chron, 2020, para. 1). Cultural differences require people to be managed differently to ensure that individuals do not respond negatively to business management practices (Singa, 2018, p.71). Business management practices in an international environment have to acknowledge varying cultural practices and ideologies.
Failure to acknowledge cultural differences when establishing business management practices in an international environment limits the success of a business. Ignoring cultural differences can lead employees to understand that they are not valued and feel disrespected (Gavin, 2019, para. 20). When managing people in an international business environment, it is necessary to enhance cross-cultural collaboration (Northwest Executive Education, 2021, para. 11). This can be achieved by ensuring that each person plays a significant role in meeting organizational goals, making them develop a perspective that they are empowered. A factor to consider when managing people in the international business environment is ensuring that an organization complies with all labor laws (Seah, 2021, para. 14). Regulations that govern employment vary from one nation to the other hence it is necessary to address them to avoid legal procedures.
Managing Cross-Cultural Negotiation and Conflict
When negotiating and managing conflicts in an international business environment, an organization must consider the cultural differences that are likely to establish limits. This might be the case for the organization seeking to expand its operations to India since the two nations have different negotiation styles. Failure to consider cultural differences when making negotiations contributes to misunderstandings which act as a barrier to reaching effective solutions (Shonk, 2021, para. 2). This indicates that successfully engaging in negotiations that involve different cultures requires one to understand the other party’s culture. Understanding other people’s cultures enable individuals to engage in interactions regardless of differences in culture (PSU, 2019, para. 3). Cultural awareness is the first step in promoting cross-cultural negotiation and conflict management effectiveness.
When managing cross-cultural conflict, it is necessary to identify some of the biases that might be having an influence. This helps ensure that one of the parties in a conflict does not need to feel disadvantaged in the conflict resolution process (Rose, 2021, para. 4). Cultural conflict is effectively managed by addressing cultural discrimination in the workplace and establishing strategies to minimize it. In cases where conflict arises from cultural issues, it is necessary to have a mediator to help in conflict management to enhance the balance between conflicting parties (Mahan & Mahuna, 2017, p.17). Conflict can also be eliminated by ensuring that people from various cultures have equal opportunities for participation when airing out their concerns (Richard & Hibbert, 2017, para. 8). This helps ensure that all the issues that might contribute to conflict in the workplace are adequately addressed.
Global Economics
Globalisation and the World Economy
Globalisation has significant effects on the world economy, benefiting developed and developing nations. Globalisation enables organizations to access larger markets and a bigger customer audience (Management Study, 2018, para. 6). This enables organizations that choose to expand their operations to international markets to record increased sales and profits, thus an economic boost. Globalisation also has an effect on world economies since it enhances the likelihood of consumers accessing products at lower prices than what it would have been when dealing with local businesses (Ivory Research, 2019, para. 10). Globalisation seeks to ensure that consumers receive high-quality products at low prices. Globalisation allows international organizations to identify low-cost alternatives for goods production, thus reducing prices (Velocity Global, 2020, para. 8). The availability of products at lower prices enables people to live better on the minimal financial resources available to them.
Globalisation also affects global economies since individuals in developed nations are likely to lose their jobs if an organization chooses to outsource labor from a developing nation. Employees who lose their positions are forced to compete for jobs in the lower cost sectors, thus negatively impacting their standards of living (National Geographic Society, 2019, para. 8). However, globalisation has a negative impact on small local businesses since they cannot maintain the competition they face from international organizations (Kuepper, 2021, para. 6). Expansion to the international market enables organizations to realize economies of scale, facilitating increased growth. This makes it hard for local companies in the market to keep up with the pace and might cause them to close down.
International Trade
Openness in international trade positively impacts economic growth since there is increased access to resources and products at lower prices. International trade affects long-run economic growth positively, and the relationship is influenced greatly by imports (Esaku, 2021, para. 26). International trade is an effective strategy to eliminate poverty in developing nations since it increases available opportunities. Countries that promote international trade have an increased ability to foster growth and innovation (World Bank, 2018, para. 1). Innovation helps ensure that high-income employment opportunities are available for local people. Despite the opportunities available for developing countries, they face a challenge in competing globally.
International trading activities positively influence the level of productivity since producers have access to advanced operations and knowledge. Many producers shift to technological input, which is necessary to enhance production (Rijesh, 2019, p.2). International trade relates positively with technology since there is an increased probability of technology diffusion. Increased market opportunities also act as a driving factor to the increasing production rates. Competition in the international market can force producers to upgrade their technologies to enhance their capabilities (United Nations, 2018, p.5). Local companies that participate in the global value chains receive technologies as a strategy to boost their operations. The quality of institutions in a nation greatly influences the level of international trade that the country engages in (Abreo et al., 2021, para. 6). Institutional quality promotes bilateral trade, and the effect increases with time as operations continue. Weak institutions have the power to regulate international trade with a similar effect as that of tariffs.
The Macroeconomic Environment and Policy
A U.S.-based organization seeking to expand its operations to India has to consider the macroeconomic environment and policy in the nation to enhance its chances of success. India has continued to rely on its fiscal policy to achieve swift economic growth (Financial Express, 2019, para. 2). India’s government relies on fiscal policy to control the flow of tax revenues and residents’ expenditures. India’s current fiscal strategy is focused on enhancing protectionism by promoting tariffs and providing incentives that stimulate production (Rai, 2022, para. 6). Incentives for production have been provided to increase the employment opportunities available for Indian people.
India’s monetary policy is focused on retaining price stability while also enhancing the chances of growth. Price stability is considered an important factor that fosters sustainable growth (Clear Tax, 2022, para. 2). On the other hand, monetary policy in the United States is based on interest rates and citizens’ credit access (Investopedia, 2021, para. 9). An organization expanding its operations to India must maintain prices for various products at current levels to stay in line with the monetary policy. India’s government maintains price stability through inflation, with a target being set for every five years (George, 2021, para. 11). Inflation is a key economic factor and can influence the purchasing power of the U.S. dollar.
Exchange Rate and Competitiveness
An organization seeking to expand its operations from the United States to India has to consider the exchange rate and competitiveness in the international market. India has managed to increase external competitiveness by maintaining the real effective exchange rate at a benchmark level for fifteen years (ENS Economic Bureau, 2021, para. 1). In the future, a large capital inflow is likely to lead to an appreciation of the exchange rate for the Indian rupee. India follows a floating exchange rate which implies that the currency’s price is influenced by the forex market (Jyoti, 2021, para. 3). Currency price depends on the demand and supply relationship with currencies from other nations.
Current exchange rates in India indicate an overvalued rupee due to increased foreign investment. Many foreign investors have increased the demand for the Indian rupee, thus increasing its value (Mohan, 2018, para. 3). This has caused the price of Indian products in the international market to increase greatly. In this case, an international organization can consider producing its products in India and selling them to other international markets.
A depreciation in exchange rates causes an increase in the number of exports. In this case, an international organization operating in India has to look out for depreciation in exchange rates and consider framing its operations to handle exports (Gopinath, 2020, para. 19). An appreciation in exchange rates causes a shift in demand from local to international products, thus increasing profits. Exchange rate volatility is influenced by macroeconomic factors and the nature of the business environment in which an organization operates (Morina et al., 2020, para. 7). An organization seeking to expand its operations to the international market must consider the volatility of exchange rates when making investment decisions.
The New Economy: Knowledge, Technology and Network Effects
The new economy is characterized by increased reliance on technology to facilitate various organization operations. New technologies have allowed the efficient production of improved goods and services for consumers (Hausmann & Dominguez, 2019, para. 2). The new economy will see organizations continue to rely on emerging technology to carry out various operations more efficiently than when relying on human labor. The new economy has also seen organizations automating traditional manufacturing operations using new technologies (Kenton, 2022, para. 4). Reliance on technology in various operations has enabled organizations to maintain competitiveness and efficiency in the international market.
The new economy has also caused organizations to move towards open innovation, causing an increase in knowledge flow. Businesses have partnered with learning institutions and research facilities to develop new products and technologies. Businesses in the emerging economy are looking for educated and skilled individuals to handle various operations (Kuriakose, 2020, para. 7). Such a workforce is considered to have the ability to create and utilize knowledge in the most appropriate manner. Organizations also use global knowledge to adapt to local needs and develop new technologies. Knowledge is also necessary for the new economy since it helps to ensure that an individual is aware of routines, processes, and routines that are likely to affect an organization (Choong & Leung, 2021, para. 16). An organization must rely on existing knowledge to inform business management practices that are likely to promote success.
The growth of businesses in the new economy will significantly impact network effects. Network effects cause an increase in the value of a product or service if it has a high number of users (Stobierski, 2020para. 8). In this case, an organization is likely to experience an increased network effect for its products after expanding operations to an international market. Such an organization is likely to be successful in the long run due to a growth in its market share.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, an organization seeking to expand its operations from the United States to India must consider the cultural and economic issues likely to influence the process. The two nations have varying cultures; therefore, an organization cannot apply similar business practices. It has to come up with business operations that reflect the culture of the people it seeks to expand its operations to enhance the chances of success. Culture influences how people communicate since it has unique values and ideologies. An organization also must consider managing negotiations and conflicts in a cross-cultural environment. This is achieved by having strategies that acknowledge cultural differences and seek to identify fair solutions.
Globalisation enables organizations to access larger markets and customer audiences hence an increased likelihood of a rise in sales and profits. Globalization has a significant positive impact on economic growth in the long run since it provides more opportunities and enhances living standards. An organization expanding its operations to the international market also has to consider the macroeconomic environment and policy of the target nations to inform on strategies to apply. It is also necessary to address exchange rates since they have an influence on the demand for various products based on fluctuations.
One of the recommendations for the organization’s proposed strategy is that the business should enhance the cultural awareness of the members who will move to facilitate operations in the new market. This will help ensure that they are culturally competent to facilitate diversity in the workplace. Cultural competence will also enhance the ability to manage negotiations and conflicts in the workplace. This is also an effective strategy to eliminate any communication barriers affecting business operations. The organization should also focus on identifying the quality of Indian institutions that influence international trade in the country. If the quality of the institutions is high, they promote bilateral trade; hence the country is a good one to expand operations.
References
Abiera, C. (2021) Navigating Low and High Context Culture Communication. Medium. Web.
Abreo, C., Bustillo, R. and Rodriguez, C., (2021) The Role of Institutional Quality in The International Trade of a Latin American Country: Evidence from Colombian Export Performance. Journal of Economic Structures, 10(1), pp.1-21. Web.
Association of MBAs. (2021) Doing Business in India: Why Culture Matters. Association of MBAs. [online] Web.
Asialink Business (2021) Indian Business Culture and Business Etiquette. [online] Asialink Business. Web.
Bajorek, M. (2017) The Differences Between Indian & American Businesses. [online] Web.
Brown, M. (2019) How Can Cultural Differences Affect Business Communication? [online] Web.
Bryant, S. (2021) 8 Cultural Differences Between USA and India. [online] Country Navigator. Web.
Choong, K.K. and Leung, P.W., (2021) A Critical Review of the Precursors of the Knowledge Economy and Their Contemporary Research: Implications for The Computerized New Economy. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, pp.1-38. Web.
Chron. (2020) Role of Human Resource Managers in Internationalization of Business. [online] Web.
Clear Tax (2022) RBI Monetary Policy of India 2019 – Objective, Monetary Framework & Monetary Policy. [online] Cleartax.in. Web.
Commisceo Global. (2018) Three Key Cultural Differences for Indians Working in The USA. [online] Commisceo Global Consulting Ltd. Web.
ENS Economic Bureau (2021) ‘Rupee’s Real Value Stable, Showing Better External Competitiveness.’[online] The Indian Express. Web.
Esaku, S., (2021) The Short-And Long-Run Relationship Between Trade Openness and Economic Growth in Uganda. Cogent Economics & Finance, 9(1), p.1999060. Web.
Financial Express. (2019) What is Fiscal Policy in India? [online] Financialexpress.com. Web.
Gavin, M. (2019) How to Manage Global & International Teams: 6 Tips. [online] Web.
George, A. A. (2017) Monetary Policy of India – Everything You Should Know About. [online] ClearIAS. Web.
Gopinath, G. (2020) Dollar Dominance in Trade: Facts and Implications. India Exim Bank. [online] Web.
Hausmann, R. & Dominguez, J. (2019) Knowledge, Technology and Complexity in Economic Growth. [online] Web.
Hough, M. (2021) Know About Business Culture in India – Global Business Culture. [online] Global Business Culture. Web.
Hendrith, M., (2018) The Effects Culture and Communication Have On Businesses. Integrated Studies. Web.
Investopedia. (2022) What Is a Macro-Environment? [online] Web.
Ivoryresearch.com. (2019) The Positive and Negative Impact of Economic Globalisation. Ivory Research. [online] Web.
Jyoti, (2021). Impact of Exchange Rate Fluctuations On India’s Manufacturing Exports: An Empirical Investigation On Long-Run Relation. Journal of Asian Economic Integration, 3(1), pp.61-73. Web.
Khan, M.A. and Law, L.S., 2018. The Role of National Cultures in Shaping the Corporate Management Cultures: A Three-Country Theoretical Analysis. IntechOpen.
Kenton, W. (2022) New Economy. [online] Web.
Kuepper, J. (2021) How Globalization Impacts International Investors and Economic Growth. [online] The Balance. Web.
Kumar, R. (2021) As Managers Initiate Business Dealings Overseas, They Are Tasked with The Necessity of Understanding the Culture. [online] Linkedin.com. Web.
Kuriakose, S. (2020) In The New Economy, Knowledge Is King. [online] Tralac.org. Web.
Mahan, L.N. and Mahuna, J.M., (2017) Bridging The Divide: Cross-Cultural Mediation. International Research and Review, 7(1), pp.11-22. Web.
Management Study. (2018) What Is Globalization? Positive & Negative Impacts of Globalization. Management Study HQ. [online] Web.
Mohan, D. (2018) Why India Needs a More Competitive Rupee. South Asian Voices. [online] Web.
Morina, F., Hysa, E., Ergün, U., Panait, M. and Voica, M.C., (2020) The Effect of Exchange Rate Volatility On Economic Growth: A Case of The CEE Countries. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 13(8), p.177.
National Geographic Society (2019) Effects of Economic Globalization. [online] National Geographic Society. Web.
Northwest Executive Education. (2021) 10 Ways to Manage a Global Team Successfully. [online] Northwest Executive Education. Web.
PSU. (2019) The Best Way to Resolve or Handle Cultural Conflicts Is by Learning About Other Cultures. [online] Psu.edu. Web.
Rai, S. (2022) India’s New Budget Reveals a Shift in Fiscal Strategy. [online] Carnegie India. Web.
Relocate. (2021) Understanding Business Culture in India. [online] Relocatemagazine.com. Web.
Reynolds, K. (2017) How cultural differences impact international business in 2017. HULT International Business School. Web.
Richard, & Hibbert, E. (2017) Managing conflict in a multicultural team. [online] Missionexus.org. Web.
Rijesh, R., (2019) International trade and productivity growth in Indian industry: Evidence from the organized manufacturing sector. Journal of South Asian Development, 14(1), pp.1-39. Web.
Rose, V. (2021) Preventing and Addressing Cross-Cultural Conflict in The Workplace – Pollack Peacebuilding Systems. [online] Pollack Peacebuilding Systems. Web.
Seah, L. (2021) How to Successfully Manage Global Teams. [online] Airswift.com. Web.
Singha, S. (2018) International Business Environment. Research Gate. Web.
Shonk, K. (2021) How to Resolve Cultural Conflict: Overcoming Cultural Barriers at The Negotiation Table. [online] PON – Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School. Web.
Stobierski, T. (2020) What are Network Effects? HBS Online. [online] Web.
The European Business Review. (2020). Impact of Culture On Consumer Buying Behavior. [online] The European Business Review. Web.
TMF Group (2018) Cultural Considerations When Doing Business in India. [online] Tmf-group.com. Web.
Twose, R. (2019) How Does Culture Affect International Business? [online] Web.
United Nations. (2018) Leveraging Technology and Trade for Economic Development. [online] ESCAP. Web.
Velocity Global (2020) Globalization Benefits and Challenges. [online] Velocity Global. Web.
World Bank. (2018) Stronger Open Trade Policies Enable Economic Growth for All. [online] World Bank. Web.