Introduction
Company Background
Emirates Telecommunications Corporation (Etisalat) is one of the largest companies in UAE which started offering its services in 1976. The UAE federal government controls a 60% share in the company that is now offering its services in the UAE market and beyond, through its subsidiaries and partners in 18 nations (Etisalat 1). The main purpose of Etisalat was to own, operate and manage GSM and 3G mobile telephone networks together with the provision of mobile internet services. The company capitalized on the low broadband and data infiltration rates which were quite low at inception but have now been expanded greatly. The services have covered both rural and urban centers a fact that has tremendously increased the customer base with both 3G and 3.5G technologies of mobile telephony. To match with emerging technologies, the company agreed with and integrated other telecommunication companies towards building, deploying and operating the region’s largest fiber-optic network (Maha 3).
Research Methodology
The initial stage in this research paper mainly involved a thorough comparative study of the Etisalat Company and other telecommunication companies in the region. Topical relevant issues in an attempt to fully comprehend and identify the required scope and goals of the proposal were reviewed leading to the choice of having Etisalat as the company of choice in the study. Various quantitative and mixed research methods were examined for use but the qualitative survey method was adopted in this particular in which interviews were preferred for use among the staff of Etisalat and explore the organization’s business environment.
The research design consisted of different frameworks that were used for the collection of the data. According to Salgae (11), qualitative research is ‘subjective’, and Goh, (22) argues that a study is qualitative if the purpose of the study is primarily to describe a situation, phenomenon, problem, or event. He believes that it is unstructured, flexible, and has an open methodology. Goh, (19) also stresses the fact that qualitative research, even when theoretically informed (Haugun 21), is the most open-ended and hence least biased type of study. Kaufman, (15), likened qualitative research to a movie where things evolve by starting with one image and then moving on to others. Exploratory research is an important aspect of qualitative research; In this case, the interview technique was selected as a method of data collection. This is what the study intends to employ in collecting data to get raw and current information.
Organization environment
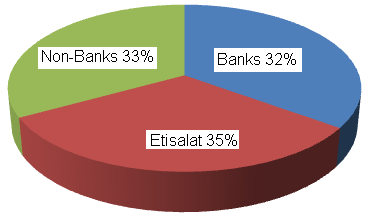
This study has identified Etisalat as one of the biggest firms based on its share equity as compared to other enlisted companies in the UAE market as it commands more than AED 35.46 billion. The company is also leading in the Abu Dhabi listed companies in terms of capital investment as it has a capital base of AED 7.2 billion that has further been increased by the recent allotment of bonus shares to stand at its current AED 7.9 billion. The company shared dividends to its shareholders in 2009 with a total value of AED 4.3 billion which was about 35% of the total dividends that had been distributed in all the firms in UAE during the same financial year. The dividends by Etisalat were more than that issued by all banks by 11% and all non-banking companies who only distributed dividends worth AED 4.09 billion. The chart below summarizes this distribution (Maha 6).
The organization of Etisalat strongly believes in the value of every customer and has therefore divided the market into small segments to be able to address the needs of each group of people in a more customized way. The segmentation of the population is based on age, level of income culture, and ethnicity norms. The organization’s strategy is also geared towards addressing the immediate need of the end-users through well-defined distribution channels, customized sales, strategic stores, and commercial support as shown in the flow chart below (Maha 7).
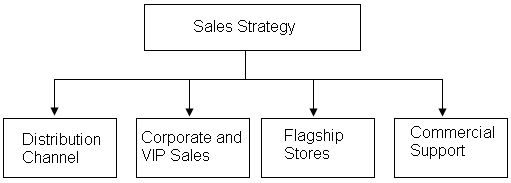
The company’s distribution strategies are guided by direct sales, indirect sales, and co-branding. The direct sales channel is fed through some flagship stores distributed out through the region and are well-staffed by Etisalat personnel. The company also depends on its distribution partners to increase its pace in distribution and make indirect sales. The company is widening its co-branded outlets to ensure that its dependence on resellers is minimized.
Mechanistic and Organic structures
Organization Structure
The firm’s top management is headed by a chief executive officer (CEO) who leads the company in ensuring that accurate strategic plans in mobile technology are emphasized and that the market growth is utilized to its full potential. The company has expanded significantly to raise its market share from 16% to 31% through its ambitious launches of innovative services and products that have always been received positively in the market as they brought a revolution in communication that seemed popular with the end-users. The firm has been offering quality services at very affordable prices to its customers and the management has recently decided to focus on differentiation strategies that would raise the customer base and improve the revenue margin.
This strategy by the management has helped to attract a big clientele as new services that employ the use of modern technologies are introduced in the market with a need of the corporate customers being met by the introduction of blackberry services whose use has recently become controversial in the region. The management has also put more focus on embracing the 3G and broadband technologies that have a greater liking among the young clientele in the region. The young customers’ population for those aged between 10 and 24 years constitutes 32% of the total customer base hence making it an important market segment whose special market requirements cannot be ignored (Maha 10).
Organizational Life Cycle
Historically the company has always financed its operations through equity generated from its growth in assets that is complimented marginally through borrowing. Etisalat has equity represented by 81% of the total capital with a market worth of AED 36.39 billion. By the beginning of 2010, the Loans from financial institutions were only AED 2.89 billion that attracted an average interest rate payable at 8.9% with loans from other sources totaling AED 1.59 and attracting an interest rate of 4.1%. At the same period, the company made a profit before tax amounting to 18.9 billion which was more than 14 times the total expenses from loan repayments (Maha 11).
With the recent global financial crisis, Etisalat was able to survive owing to its wide customer base that exceeds 10 million and its penetration rate that stands at more than 215%. To avoid such threats in the future the company has engaged in an ambitious international expansion that is also aimed at increasing its revenue base. The company has therefore secured mobile operation services in Pakistan, India, Nigeria, and Egypt that have emerged as the main drivers of the company’s growth. The international revenues for the company have grown by 65% which registered an increase of 2% from the year 2008 to 2009 despite the effect of the global economic crisis. The profits in 2008 were however boosted by the sale of equity in Mobily that was worth AED 1.78 billion (Maha 9).
The table below shows the Income account for Etisalat in the last 5 years.
Organization Culture
Etisalat management has used the strategy of concentrating more on the mobile market growth perspective. Initially, the company grabbed 16% of the market share in the first year of operation and 31% in the second year (Etisalat 2). This was achieved through the launching of innovative and new services in the market. The company offers services at lower costs than the incumbent operator focusing on a different strategy of building its customer base. Offering new services has been the capturing tool by attracting more customers into the system. To enlarge its customer base, the company also caters to the needs of corporate customers for example the introduction of the blackberry services in the region. The company also made acquisitions of other smaller companies that were dealing with data services to ensure that it remained solid and competitive. Etisalat organized a special arrangement with the giant Samsung Company to start the Largest WiMAX network that linked the Major UAE cities via wireless connection internet.
At Etisalat, buyer power is a major force that affects the value creation in the workplace which is determined by the distribution of the service users and the ability to access the services. The population of the customer base is currently large with the majority of them concentrated in the urban centers. The company has maintained a positive supply capacity which is on par with the customers’ rising demand. It has been able to retain the competitive advantage in most important variables including pricing, quality, and value addition. With the advantage, a big customer base the threat of substitutes from rival companies has not been significant because the revenue margin is high and therefore the company can comfortably dictate the pricing carry out research and development, and introduce innovative products to the market. The high capital required to start a telecommunication company keeps off many new firms that would want to gain entry into the sector keeping the competition within manageable levels. The UAE market has however been very attractive for mobile services as it has been witnessed by the high number of applications from both local and international firms to get a license of operation in the region. This force may be expected to be stiffer with the possibility of increasing threats of substitute products and the rising bargaining power of the customers and therefore the company is intensifying its advertisement strategies to woo customers (Maha 10).
The study conducted on the company reveals that the company has a professional management team that has put in place a strong brand in the market that is cannot easily be shaken by competitors. The company also has an advantage for having been able to maintain high-profit margins which have been able to effectively fund research for innovative technologies that have made customers stay satisfied with the quality of the services and customized services offered by the company. The company has also been able to maintain high network coverage through its 3G technology operated and monitored by well-motivated employees most of whom have been retained in the company for a long time. The company however has a big base of pre-paid customers that reduces the potential of investments for short terms. This can however be overcome given the fact that the company has a big opportunity to increase its market share in mobile broadband and change the market trends from voice to data. The company’s big capital base also gives it an enormous potential to buy other firms and roll out value-added programs and services. This advantage also makes it the best option for new entrants to seek partnership from a chance that can lower its cost on some of the overheads that can be shared with the partner.
Appropriateness and Efficiency of Technology
There is a general paradigm shift in the mobile phone industry from voice to data services which has increased the need to expand broadband services. For this reason, Etisalat has is focusing on increasing its revenue on data revenues which should contribute about 15% of its total revenue by the year 2012 (Maha 9). The current company’s drive is to focus on advancing technology aiming at specific population segments like the youth and females in providing specialized quality services. The company is also aiming at increasing network coverage so that there could be increased usage by indoor customers. In 2007 the firm started special services commonly known as “push-to talk” which was made available to both the post and pre-paid customers. This is a modern technology where the communication is carried in the form of GPRS or the 3G configuration ensuring that there is no tapping of communication by busybodies. The company was also the first to start blackberry services in UAE in conjunction with RIM and EMS. To further embrace technology the company also became the first in introducing value-added services (MMS) and the famous location-based servicing call me as well as roaming services.
The 3.5 G services represented a market share of about 58% and the structures of operation were set by Erikson and Huawei. The firm also introduced an ambitious plan to expand its 3G infrastructure to more areas within the UAE major cities and by June 2007, the speed of the broadband had increased by 100% through the use of HSDPA technology to attain a speed of 3.6 Mbps. Later in the year, the firm started the use of 7.2 Mbps modems that revolutionized information servicing in the UAE and was also based on the new HSDPA technologies (Maha 12). Today the company has continued to embrace technological innovations and cooperation with international data service providers to ensure that the region is not left behind in communication and data transfer technologies. The company has also been in the front line in ensuring that the fiber optic cabling is done to enhance more fast data transfer in both mobile and fixed services.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In the light of the market development witnessed at different levels in the study of Etisalat Company the following recommendations can be made:
- With the observation of the fact that the customer base that is not covered by mobile services is still high, it can be recommended that the company increases its 3G mobile services. This particular service has been seen to be preferred by many customers as the services move from voice to data and therefore it can be an appropriate avenue to capture new customers.
- It has also been found that the company’s customer base is largely prepaid. This can be a challenge to the company’s short-term investment plans and therefore it is recommended that the company launch campaigns increase the base of the post-paid customers. This can be done by ensuring that the speed e.g. HSPA and mobile broadband for such consumers is widened.
- The company should also research on best strategic companies that can be acquired to firmly consolidate its position in the telecommunication sector. This would reduce the threat of new entrants in the market and the threat of substitute products and services for the company shall have the financial muscle to carry out wide research and development on innovative technologies at a level that will be difficult for the rivals to reach.
- The position of Etisalat as a market leader in the region is not disputable. Going forward, the firm should aim at encouraging fixed-mobile convergence and to develop wholesale sales strategies from a single handset and deliver superior, efficient, and convenient services.
With penetration rates in UAE going beyond the 100% mark, there is still good potential for investment and expansion. The expansion strategies for Etisalat in both domestic and international markets are a welcome move but the ground is still full with new opportunities. The economic growth in UAE can be seen as a stimulant to the need for mobile services, especially among the young generation. The competition and innovative services may also increase the need for mobile services for those who are not using the service. Etisalat is in a position that can be able to take advantage of the market scenario and its presence in the market will set a pace for other competitors towards offering more innovative services.
The future for Etisalat lies mainly on broadband and the 3.5G services and with the company’s advantage of a large capital base, it is expected to take a competitive edge in commanding this business niche.
Works Cited
Etisalat, Website (2010). Corporate Information. Web.
Goh, Kim et al (2000). Internal Quality Audit as a Measure of Effective Implementation of ISO 9000 Quality Management System, BAS Thesis, RMIT University/Singapore Institute of Management, Singapore.
Kaufman, James (2001). ‘Value Management – Creating Competitive Advantage’. Kent: Financial World Publishing.
Haugun, Kerzner (2001). Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling and Controlling, 7th Edition, John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Maha, Kanz (2010). Emirates Telecommunications Corporation. Web.
Salgae, Dassonville (2000). Handbook for Implementing a Quality Management System in a National Mapping Agency, Journal of project management Vol. 5(3) 2000.