Introduction
Today’s emphasis on genetic technology and its application has major implications for healthcare now and in the future. Nurses need to understand the importance of integrating new knowledge of genetics into their practices and be able to help patients cope with the genetic basis of disease. Nurses also need to examine their own attitudes, values, and beliefs concerning genetically acquired diseases in order to provide adequate and ethical nursing care to the people (Behrman and Stanton, 2007). Tay-Sachs is a genetic disease that in most cases is inherited from parents. It is a fatal genetic disease that leads to disorders in the storage of lipids. In this case quantities of harmful fatty substance known as ganglioside starts developing in the nerves and tissue cells inside the brain. The condition is generally as a result of the ineffective action of an enzyme known as beta-hexosaminidase. This enzyme assists in speeding up the biodegradation of fatty acid materials commonly known as gangliosides which are accumulated and biodegraded rapidly during initial brain development of the fetus. Infants with this condition appear to grow just normally for the initial stages of life. As time goes by nerve cells tend to be distended with those fatty acid materials, followed by deterioration of physical and mental abilities. The condition can make the child deaf and blind. Also the child may develop a problem during swallowing. At this stage the child may have paralysis (Behrman and Stanton, 2007).
Diagnosis of a genetic disorder
Chorionic villus is a test of sampling done especially at the early stages of pregnancy and is used to identify some problems which might occur to the fetus. It is basically done when the mother or the father of the child has a similar disease revolving in the family trees of both parents. It may be also done when the mother is over 35 years. This is because at this age there is a likelihood of having a child having a chromosome defect. Villi are small and tiny finger-like structures usually located at the placenta. Genetic component in chorionic villus is just like the one in the cells of the child. A sample is taken from the villus cells for testing. Chorionic villus cells are tested for such problems. The protocol or procedure is done late in the first three months; it is usually conducted at 10 to12 weeks of pregnancy. The sample may be taken by inserting a thin tube through the vagina into the placenta. Sample may also be taken through a thin needle usually put in the belly and into the placenta. The Ultrasound assists in guiding the needle into the right point so as to collect the sample. If there is a family history of tay-sachs diseases then, CVS may be used to assist in determining the genetic disorders. It may be also used to locate chromosomal birth related defects. This may include Down syndrome among others. CVS is not in a position to locate neural tube related defects and therefore it is not advisable if the child’s lungs are a bit developed. The sampling is usually done early in pregnancy (10-12 weeks) than that of amniocentesis (15-20 weeks). The report enables you to be aware of the health status of your child and decide if you will terminate or continue with the pregnancy (Johnston, 2007).
Symptoms of Tay-sachs
The symptoms for tay-sachs include seizures, dementia and a higher reflex startle to noise. In addition another type of the condition happens in victims in their late twenties and thirties and is usually characteristics by a gait which is unsteady and continuing neurological deterioration. Persons suffering from Tay-Sachs have also spots which are “cherry-red” in their eyes. Occurrence of Tay-Sachs is mostly high among individuals from Eastern European countries and people belonging Jewish descent. Victims and or Tay-Sachs disease carriers may be identified using a simple test of the blood that determines the activity of beta-hexosaminidase. For the offspring to born with this condition then both the father and mother must be carriers of such a mutated gene. Analysis of genetic inheritance shows that almost 1/4 of the offspring may end up inheriting the condition of tay-sachs with every successful pregnancy (Simpson and Otano, 2007).
Screening
Suspected carriers
- Rita’s paternal grandmother
- Rita’s paternal grandfather
- Rita’s father
- Peter’s paternal grandfather
- Peter’s paternal grandmother
- Peter’s mother
Afflicted suspects
- Rita father’s brother
- Peter father’s brother
- Peter father’s sister
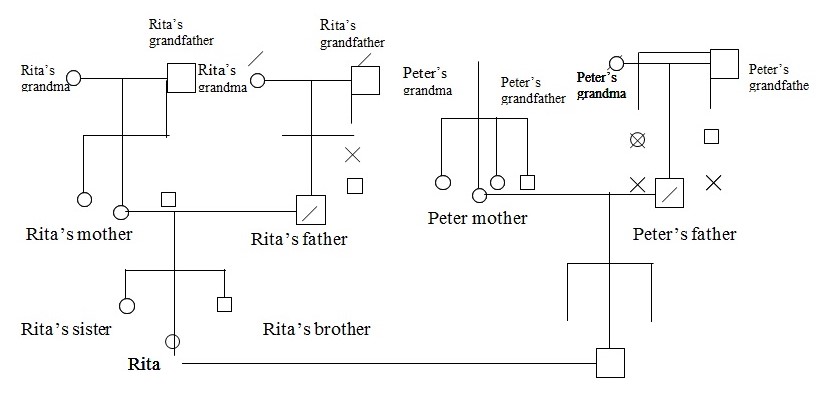
Analysis of the Genogram
Inheritance of lethal genes
The information from the genogram demonstrates that the family lineage of the two couples have been having genotypes that contain lethal genes. According to the information disclosed, brother to Rita’s father lost his live through unknown disease. The most probable reason is that, the father’s brother had a pair of defect genes which he received from each of his parents. Rita’s father did not get the disease in the early and even in his adult stage. He had received one normal gene from one of his parents while the other gene was abnormal from either one of the parents. This made him to be heterogeneous with the normal dominant gene expressing itself and suppressing the recessive defect gene. He thus lives to his adult stage to marry Rita’s mother who is having both normal genes. When Rita’s father and her mother try to bear offspring, the mother will produce normal gene while his father will produce to his child either a normal gene or the defect gene. This implies that if the normal gene is “H” and the defect is “h”, then some of the offspring will be HH- free from defect genetic disease and others will Hh- free from defective genetic disease whom will be carriers. This means that Rita was to having a defect gene and thus a carrier.
In addition, Peter’s paternal grandparents are both carriers of the defective gene. This implies they can have their child having HH, Hh or hh. Those having a pair of the defective recessive genotype hh will suffer from the genetic disease, but those with a pair or single normal gene H will live without the genetic disease. The Hh genotype will be normal however they are gene carriers. This mean the early death of the sister and brother of Peter’s father was because of the disease the resulted from the hh genotype. Peter’s father did not suffer from the unknown disease because his genotype was either HH or Hh. The later confirmation on July CVS test of the genetic disease on their baby showed that both Rita and peter were having the Hh genotype (Bowden, 2009).
Genomic influences
The disorder being expressed in the Rita’s case may be explained in much different way. The genomic influences may have been playing a role in emergency of the problem in the family. When brothers to Rita’s father and Peter’s father receive gene from either mother of father, they are likely to suffer from genetic diseases. When the genetic disease problem is exclusively relate to particular source of the couple, that the male of female partner, we expect the son of the offspring to be affected if the disorder is caused by genomic influence from father. Otherwise, in case this was caused by the maternal gene, the genetic disease will be expressed in both son and daughters. In the Rita’s case, the brother to Rita’s father died while the Rita’s father lived. This shows that the Tay – Sachs disease at this was not caused by father gene. Furthermore, brother to Peter’s father and his sister lost their lives. The death of both portrays neither mother’s gene was either responsible of the disorder. However, the above statement is challenged under the consideration that Peter’s father is alive. Due to the fact that Peter’s father had received the one gene from the father and one from the mother and he still living, we may therefore say that the disease is not influenced through genomic ways. Hence, the problem should be induced through other genetic means.
Genetic factor
Genetic studies have revealed that the Tay – Sachs disease is an inherited disease. According to information analysis of couple genotypes, the result apparently indicates that their cells have heterogeneous genes composed of dominant H and defective recessive h (Niebyl and Simpson, 2007). The genotypes of the couple are thus Hh. The offspring of such couple will be having genotypes as follows:
- HH- a quarter of the offspring, these individual will be normal and live without suffering from the disease.
- Hh- those offspring will form a quarter of the total offspring. They will be normal and are not likely to die at their early childhood. This is because they will be able to produce the enzyme hexosaminidase A in the body cells like “HH” individuals.
- hh- the probability that they will have offspring whose genotype is hh is fifty half of the total. These are individuals who are at high risk of suffering from Tay – Sachs disease. The genotype hh prevents the production of hexosaminidase A, which places the child at high risk of Tay-sachs Infection. This implies that the couple may have half of their children die aged between four and eight months.
Environmental factor
It has been revealed that the mother and the father of the baby were cigarette monger sometime back. Since they only used to smoke many years back, there might be no impact of cigarette product on their baby. However, there is discloser that the Rita has been drinking alcohol. This may induce fetal alcohol syndrome problem on the child. This combines with other genetic related factors causing high risk of genetic infection. Apart from this, it is revealed that the couple lacks the knowledge of the nature of the occurrence or inherited genetic diseases. Their ignorance and lack of enough advice on this genetic disease nature is likely for the couple to ignore the counseling concerning corrective measure towards their child protection (Bowden, 2009).
Interdisciplinary team
The following disciplines were identified: two from biomedical discipline, three from clinical sciences associated with genetics and one genetic counselor.
- Biochemistry is one of the disciplines, used for identification of cellular components functioning and allowing disease development observation;
- Life saving blood transfusion process contributes to organization of the care team;
- Medical genetics;
- Pathology (this branch contributes to formation of care team to investigate pathological impact on disease development)
The rationale for the above disciplines is that they have a foundational knowledge concerning genetic principles and also have the ability to apply these principles to patient care and various interactions with health care professionals who form part of the Rita’s health care team.
The information required from biomedical discipline is the application of the genetic disorder to victim care team on the other hand professionals from clinical science has knowledge about the structure and significance of the genome in the cell.
Rationale for Interdisciplinary Team
The disciplines required for care team creation are considered to be the following: biochemistry, blood transfusion, medical genetics and pathology.
Biochemistry is selected as the science for care team formation through the necessity to concentrate on chemical processes analysis. This science is concentrated on such areas as genetic code and protein synthesis, which are centralized ijn a particular case analysis.
Medical genetics stresses the analysis of hereditary disorders. It helps to conduct scientific researches investigating the application of medical care to genetics.
Blood transfusion as a science performs a life saving role in diseases analysis. Its role in care team formation will contribute to investigation of disease development in accordance with person’s blood type.
And, finally, pathology as the discipline is related to genetics, analyzing tissues, organs and diseases processes.
Teaching Plan
The teaching plan is made to assist the couple to know more about the disease and also how to deal with the child if at all they decline to have an abortion. The teaching plan for the initial visit may include:
- Compilation of a medical history of family pedigree: Family pedigree history is presented to the couple for realization of possible inherited diseases.
- Analysis of the tests: Tests analysis discloses genetic data and perspectives of pregnancy continuation development.
- Counseling session for the couple: Counseling session for the couple is directed at investigation of their feelings and thoughts as to decision to be made. It is the process of assessment the situation and its perception and vision by the couple.
- Repercussion of alternatives involved: This stage gives an opportunity to the couple to develop some plans for the future and analyze alternatives.
Advocacy
Most countries have no legal restrictions against abortion and making a decision they apply predominantly to ethical norms and values. Nevertheless, there are some points to be considered:
- If the pregnancy is continued then the couple should be prepared to give the baby the support it needs for the few years the child will survive
- If the couple considers abortion, then they should be aware of the emotional and legal implications of the same.
- Then they should also consider counseling as a way of dealing with abortion from the view of the society. Most communities and religions do not advocate abortion. Rita’s faith does not allow abortion and therefore need to form a care team that will act professionally.
Ethical Implications
It is necessary to underline the fact that ethical norms impact decision making process as to pregnancy. There are some ethical implications to be taken into account:
- Clinical Issues: This implication unites models of care providers’ integration characterizing illnesses and health within family history. It represents genetic service models dedicated to genetic services changes.
- Care Philosophy: Specific diseases treatments can be based on genetic testing, covering the analysis of interventions contributing to lifestyle changes. It impacts decision making process as to the difficulties connected with prenatal genetic screening.
- Family Impact: Psychological limitations and benefits are resulted from genetic screening and testing. It is necessary to underline the fact that there is a number of personal information responses impacting family interference. Genetic information contributes to future family relationships to be considered by the couple.
Personal View
Genetics role in pregnancy decision making plays an important role. Considering all legal and ethical implications, abortion should not be perceived as the method of birth control. Couple should be aware of responsibility to be taken for their decision before giving a life to a child.
Making a decision, the couple should consult specialists in genetic diseases development; one should analyze family genetic history and its impact on child’s health. The disciplines mentioned above contribute to problem investigation through care team creation and careful assessment of genetic issues.
References
Behrman, J. & Stanton, B. (2007). Textbook of Pediatric: Saunders Elsevier.
Bowden, V. (2009). Children and Their Families: The Continuum of Care: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Johnston, M. (2007). Neurodegenerative Problems of Childhood: Klieg man RM.
Niebyl, J. & Simpson, L. (2007) Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies, New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone.
Simpson, J. & Otano, L. (2007). Prenatal diagnosis.