Environmental problems and energy are closely related topics in that consuming energy without a significant impact on the surroundings is impossible. Humans primarily consume energy for various purposes, such as heating, lighting, air conditioning, and cooling. The natural flow of energy is determined by the equilibrium set on incoming and outgoing energy from the sun. The global environment has been stable until the introduction of activities which utilize fossil fuels affecting the equilibrium.
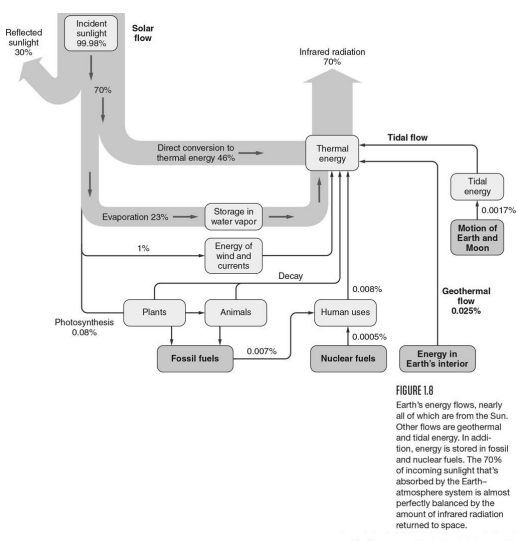
Figure 1.8 shows that energy used by humans is significantly low compared to the natural energy flow, as it is 0.007% from fossil fuels and 0.0005% from nuclear fuels. However, critical issue supporting human life on the planet has not been considered. Such factors include photosynthesis which is the base for human life. It consumes 0.08% of the overall energy as it crucial in supporting life (Wolfson 9). However, humans have introduced several activities which consume significant levels of energy compared to the natural flows. For instance, industrialization has led to the creation of large manufacturing companies which consume huge volumes of non-renewable energy sources such as fossil fuels.
Other developments, such as automotive and agricultural machinery, are also among the leading consumers of fossil fuels. Burning fossil fuels produces a high volume of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide. This affects the earth’s energy flow leading to global warming impacting the earth’s environment. Despite human energy uses being little, human activities have significantly promoted changes to the global environment because of the increased use of fossil fuels leading to massive carbon dioxide levels.
Water power is not fundamental in energy flow because it is a way of producing power and is an essential renewable energy source. Its development is affected by the degradation of the environment. Hydroelectric power fits in the energy flow because it is a form of energy that harnesses the strength of water in motion. Additionally, it fits in the system because it uses flowing water to produce kinetic energy, which is used to generate electricity (Breeze 9). The gravitational effect of the moon and the sun on the earth causes tides. This causes cyclical movement of the sea, which can be used to generate electricity when the tidal generators draw energy from the water currents. This tidal energy contributes to thermal power in the energy flow.
It works by creating a water reservoir to control how much water flows out of it and an outlet where the water flows out. Before the water in the pool spills over, it gains potential energy converted to kinetic energy as the water flows down the hill. The water can turn the turbine blades to generate electricity (Breeze 14). However, hydropower relies on the water cycle, which has three steps. Firstly, solar energy heats water on the surface of water bodies which causes the water to evaporate. Secondly, the water vapor condenses into clouds and falls as snow and rain. Lastly, Precipitation collects in streams and rivers, which empty into lakes and oceans. From there, the water evaporates again, and the cycle continues.
In conclusion, human energy use is significantly low compared to natural energy flow. However, industrialization significantly affects the global environment by producing greenhouse gases which affect the earth’s energy flow. This promotes global warming, which promotes global environmental changes. Waterpower is not significant in energy flow because it is renewable energy. However, it fits in the energy flow due to tidal energy, which is used to produce electricity.
Works Cited
Breeze, Paul. The Cost of Electricity. Elsevier, 2021.
Wolfson, Richard. “Energy, Environment and Climate.” 2017.