Introduction
Organizational Theory and studies focus on the systematic explorations of and analysis of how people as individual and as groups function within organizational operational frameworks. Robbins, Stephen P. adds that, “In this view Human resource management is thus viewed as a strategic and coherent approach to the management of an organization’s dynamic, versatile yet precious assets, the personnel who function within organizations both as groups and as individuals towards the accomplishments of organizational objectives.”
From another perspective organizational culture is defined as the aspect that entails the attitudes, values, beliefs as well as experiences of an organization. Organizational culture is largely viewed as the particulate assortment of the values and customs commonly shared by the people within an organization, from personnel up to the top structures of management. Handy, C.B. notes, “These are perceived to the very influential in determining manners in which the people within the organization will interact with one another as well as with external stakeholders of the organization”.
Main body
This line of thinking has continued to present an outline of organizational values ads the beliefs and thoughts on the type of goals individuals an groups that form an organization should pursue as Well as ideas about the fitly forms of conduct and behavior that organization members must adhere to both as individuals and groups for the effective functioning of the entirety of the organization towards the accomplishment of shared goals and vision.
It this outlined theoretical and conceptual framework That in this paper I endeavor to present an application of relevant human resources management (HRM) and organizational culture theoretical tenets and concepts onto I explore and analyse the dynamics of the field trip I was involved in recently. I was involved recently in Camp Karingal field trip in which a lecturer we had the team leader elected a captain to guide and assist the members of the team various activities.
Organizational culture and HRM theoretical concepts and tenets can not be explored in isolation of other organizational aspect. In the trip I was involved in, one of the first things the Lectures had to do was to ensure that our team had a leader. The move can be well explored in the conceptual frameworks of Organizational leadership models and theoretical tenets. Our group was assigned a team leader.
The team leader was among other core dues tasked with guiding us the entirety of the stages of various team activities. The assignment and tasking of a team leader was evidently done in taking a cue from the tenets of the transformational models of leadership which holds in its core the importance of providing the needed support for organization or in this case team members as a way of helping individuals realise and fully tap their potential.
Our expedition demanded that we have a motivational kind of leader who would edge us on in face of stern challenges and hurdles. We needed someone who would inspire our energies and make us realise that impediments ahead of us can be overcome. The Lecturer selected the kind of a person who had similar leadership traits as our team captain. The idea around the selection of the kind of person with needed leadership traits was in tandem with some tenets and perspectives embraced by the transformational leadership model. Bass, B. M. (1985) posits that in transformational leadership thrusts individuals will follow someone who inspirational to them. He notes that, “A team leader with vision and passion has a lot to achieve since the feasible way of getting things efficiently done is to infuse enthusiasm and energty to team members and the team will function effectively ad a unit.”
In an overview of the way in which out team leader masterminded the activities and assisted us across the challenges we faced in various team-building activities, we can we had a great experience as we manage to do everything out of passion and shred understanding as well as the desire to surmount the hurdles. Legge, Karen (2004) presents that transformation which is largely inclined to the process and demands of organizational change makes the team work experience a great and uplifting experience. He notes, “Transformational leaders will ensure that team members function with their full support and that everyone operates with passion and energy in all tasks. Transformational leaders want their followers to succeed in what they are undertaking”. This was true of the experience we had in undertaking various tasks under the leadership of our team captain.
Our team endeavors were carried out in the understanding that team work ha tremendous effectiveness in getting things done in organizations. This view especially held by the captain, team members and the lecturer is commensurate with McGregor’s X-Y Theory which is useful in illustrating the reasons why empowered teams achieved great results in their undertakings.
In our team members were glued together by the towering challenges of tackling novel challenges as a team. In one task we were assigned to make use of the leverage principle to set up the other side of the wooden bridge to get items. W had to set up a limited tool and communicating with team members as well as coordinating the whole process with the use of the limited tools of this project was the biggest problem.
In outlining nuances from McGregor’s theory Burns, J. M. (1978) states that empowering team members is about attitude and behavior towards the personnel that the essence of the manipulating of tools and processes. He adds that, “Ways of enhancing the merits of teamwork border on the fostering the aspects such as respect, enthusiasm and courage for personnel opposed to exploiting and riving people”. The diagram below illustrates tenets of McGregor’s X-Y theory in way of demonstrating its applicability to the dynamics and merits of team work.
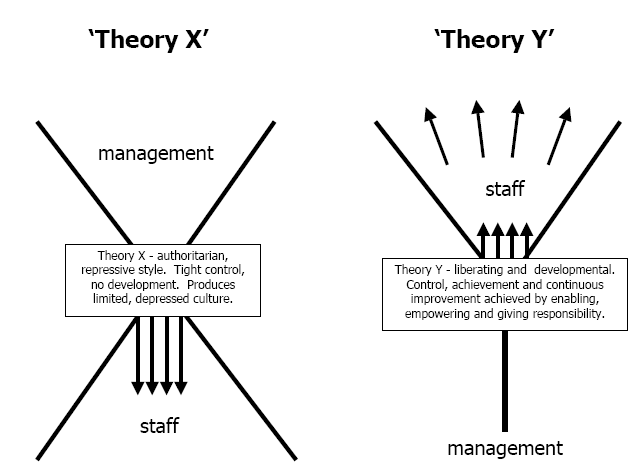
McGregor’s model suggests that Theory X which represents that authoritarian and repressive personnel management models results in crippling control of an organization’s personnel which results in a lack of development and thus produces a limited and depressed culture. On the contrary the model’s “Y” theory hold that liberating and pro-developmental personnel management models are the feasible paradigms for employees’ management. The theory suggests in its core that much accomplishment is obtained through enabling, empowering and sharing of responsibilities across an organization’s personnel.
The other task we were involved with as team was the mind project which demanded team players to think. The task was based on coming up with feasible ways of nailing sticking up to nine (9) nail on a vertical plane. The task was beneficial to me as it exposed my lack of patience for unexpected ideas form fellow members. The task a came as test of character t o us as team member but more importantly the task managed to rally us despite of our communication variances. The task demanded an integration of feasible ideas and the underlying motivation as championed by the team captain as the trip mastermind, out lecturer, was to facilitate cultural exchange and advancement on the part of the team members.
The mind project task objectives were in tandem with the theoretical tenets of Frederick Hertzberg motivational theory. Hertzberg’s theory holds that key motivational channels in team work an individual performance in organization is tied to the inclination of personal development or advancement that exists in individuals. Hertzberg’s work has largely been related to other insight coming from the psychology research work around domains of motivation. The motivational theory hinges on the proved inclination of personnel to various forms and degrees of desired Psychological development.
Conclusion
The tasks we were involved in collectively helped to grow as individuals as I personally learn to be tolerant and accommodative to members with divergent opinions. The underlying objective of the trip and team work activities was to facilitate individual advancement and growth towards the merits of functioning effectively as individuals and a team.
References
Bass, B. M. (1985). Leadership and performance beyond expectation. New York: Free Press.
Bass, B. M. (1990). From transactional to transformational leadership: Learning to share the vision. Organizational Dynamics, (Winter): 19-31.
Burns, J. M. (1978). Leadership. New York: Harper & Row.
Robbins, Stephen P. (2004) Organizational Behavior – Concepts, Controversies, Applications. 4th Ed. Prentice Hall.
Simon, Herbert A. (1997) Administrative Behavior: A Study of Decision-Making Processes in Administrative Organizations, 4th ed.The Free Press.
Legge, Karen (2004). Human Resource Management: Rhetorics and Realities, Anniversary Edition, Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Handy, C.B. (1985) Understanding Organizations, 3rd Edn, Harmondsworth, Penguin Books.
Schein, E.H. (1985-2005) Organizational Culture and Leadership, 3rd Ed., Jossey-Bass.
Johnson, G. (1988) “Rethinking Incrementalism”, Strategic Management Journal, NYK Press.