Introduction
Information Technology Infrastructure Library is the collection of practices that should be adopted for better and improved information technology services, information technology operations, and concepts. In literal terms, it is a collection of books that was developed by the British Government. The figure that is shown is a collection of books that make up ITIL. The main motive for the development of this framework was due to the fact that organizations were increasingly becoming dependent on IT for their objectives to be attained. It was believed that the growing dependency needed a framework for the IT services so that quality standards could be maintained. With these standards, the expectations of the corporate world would be in line with those of the customer (Boer, Andharia, & Harteveld, 2007). The main function of ITIL is that it provides the practices that would make IT operations to be efficient and effective so that the support for the business would be assured. ITIL is a technology that will stay long.
Strengths of ITIL
One of the biggest strengths of ITIL is the fact that it provides an internal structure where organizations can build their service management operations. With ITIL, organizations find it easy to manage their IT services (Meyler et al, 2007).
ITIL also has strength on the way it focuses on the customer service and process and continuous improvement. Other frameworks focus on the general applications of IT service management. What is more, the added focus of ITIL on resource management makes it the preferred option of improving efficiencies in the company. The McDonald Company has many outlets that are spread across Australia. All these outlets need to be integrated well so that the IT services in this vast growing company are well aligned and structured. The implementation of ITIL in each of the outlets will make the operations of the IT departments in an effective way (Blokdijk, 2008).
Weaknesses
One concern for any information system today is that of security of data or information. Information is protected from loss or unauthorized access. Threats to Business Continuity which have not been considered as part of Business Impact Analysis (BIA) include things like fire, flood, and terrorism. These were the days when business continuity did not go beyond disaster planning.
With the advent of information systems within organizations, there is a need for the organization to consider business continuity when information systems fail. This is where ITIL is lacking. There are no considerations that have been put in place to salvage the company when information systems (Desai et al, 2006). The case of McDonald Company, there are no strategies that have been put in place when there is failure in the information systems. When there were no telecoms in that company in 2005, the whole processes were shifted to manual means (Boer et al, 2007).
Another aspect is that it will be extremely difficult to operate a full system, when there are loopholes in the IT systems in place. ITIL has no framework that defines what assets to be accessed by which people in the organization. It is due to this that observers argue that there should be services in the ITIL framework that define the security in the context of information technology (Case, 2007).
Implementation of ITIL
For full implementation, one is required to have a dedicated pool of people ready for the system. What makes implementation also expensive is the fact that customization might be required for the vendor tools that could be used (Meyler et al, 2007).
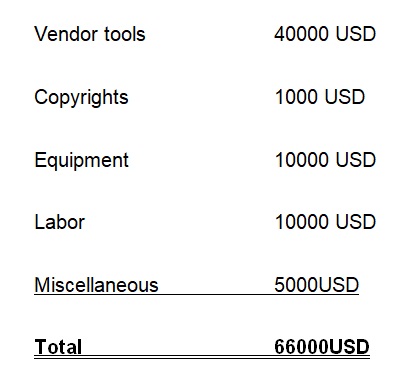
Impact of implementing ITIL in McDonald Company
For the two years that ITIL has been implemented in McDonald Company, there have been more positives than negatives in the company. One of the strengths of ITIL is that it gives a common language so that everyone speaks the same language (Blokdijk, 2008). This is so because ITIL provides the procedures, and processes that should be followed in managing IT services.
Another positive impact that this framework has brought is that it has made great deal of effort to cover many areas in the production environment. The production environment has for a long time been left behind in the management of services (Engle, Brewster, & Blokdijk, 2008).
Conclusion
In conclusion, ITIL is there to stay. There are developments which are being made so that the inclusion in this framework covers all aspects of IT management. The incidents that are hereby defined in ITIL are being worked on to provide a good network. All organizations are adopting this framework because of its comprehensive coverage of the issues that are being experienced in the IT world (Case, 2007). With security being a major factor in today’s world, there is need for the ITIL framework to be improved to cater well for the all the vulnerabilities that are in information technology. It is due to this that ITIL framework should be expanded and made to be standards just like the other standards that are defined in the request for comments (RFCs). I strongly support the adoption of this framework in any organization, big or small.
References
Blokdijk, G. (2008). Service management using ITIL.
Case, G. (2007). Continual service improvement. Cengage Learning.
Boer, S., Andharia, R., & Harteveld, M. (2007). Six sigma for IT management: A pocket guide. Van Haren Publishing.
Engle, C., Brewster, J., & Blokdijk, G. (2008). How to develop, implement and enforce ITIL V3’s best practices. Lulu.com
Desai, Jones, Anil, & Don (2006). The reference guide to data center automation.
Meyler, K., Fuller, C., Joyner, J., Dominey, A. (2007). System center operations manager 2007 unleashed. Sams Publishing.