Description
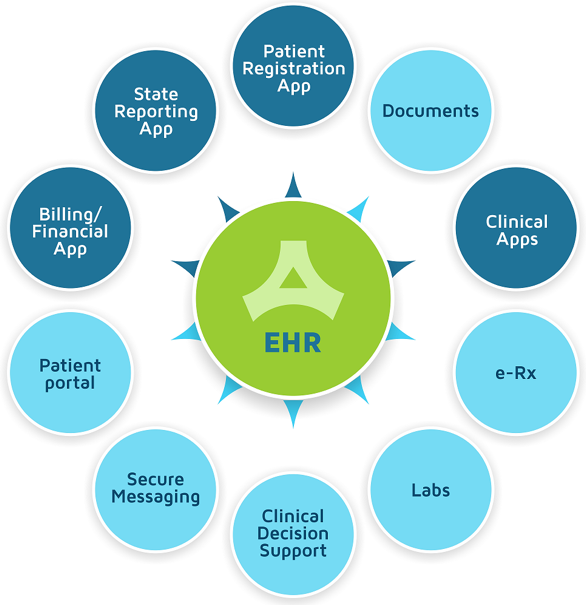
Meditech is an electronic health record system with a wide range of options that facilitate the provision of high-quality healthcare services, ensure patient safety and confidentiality (McMurtrey, 2013). This is an efficient platform for storing and sharing data concerning lab test results, patient vital signs, images, and graphs, medication and treatment plans, as well as important commentaries and notes.
Meditech can be used through various devices including tablets and smartphones, as well as computers and laptops. Different healthcare professionals can access the necessary data and makes decisions based on the detailed information available at any part of a day and in any part of the facility.
Patient Confidentiality
Meditech ensures patient confidentiality in several ways.
- It has the option of providing different access levels and details. Thus, healthcare professionals will access data of patients who are currently in their department.
- Access can be granted to particular practitioners who are engaged in cross-functional projects.
The system is a convenient platform for sharing information as it enables practitioners to make some notes. This form of communication makes it easy to share information as well as ideas without any discussions that are often associated with confidentiality breach as may involve third parties (Mosa, Yoo & Sheets, 2012).
Meditech security
The system is characterized by a high level of security. It is also constantly updated, which contributes to data safety (McMurtrey, 2013). The IT department is trained and able to maintain the system.
However, it is still important to make sure that nursing professionals have the necessary skills to use the system properly, especially when it comes to data security. Nurses should be able to access information, make certain changes within the scope of their responsibilities, and save the changes. They should also be aware of basic strategies to ensure data safety.
Making Decisions
Nurse administrators can use the system to make effective decisions on its implementation and constant improvement. It will also be beneficial for the development of nursing staff as nurses will be able to provide high-quality services. To use the system efficiently a nurse administrator should undertake the following steps:
- Hold regular meetings where the implementation of the system is discussed. These meetings will help improve the system, adjust it to the peculiarities of the facility and motivate employees to implement the change (Payne, 2016).
- Collaborate with the IT department that will adjust the system to the needs of the healthcare facility (Amadi, 2015). Collaborate with other healthcare professionals. Consider adding such options as alerts occurring if some data are missing.
- Monitor records, alerts, and nurses’ reports on the system’s malfunction. All these data will help improve the EHR and make it more efficient.
Meditech and Standards
When using any EHR, it is essential to make sure that it aligns with major healthcare information standards (Huang, Behara & Goo, 2014).
- Meditech is one such system. The EHR should ensure a high level of data security, and Meditech has the necessary tools to avoid the system breach.
- Meditech also aligns with the standard of interoperability that involves the use of the system by practitioners (Memon, Wagner, Pedersen, Beevi & Hansen, 2014).
It is necessary to add that Meditech can improve the health care services provided as well as nursing professionals’ performance. The nurse administrator can help nursing practitioners use the EHR system effectively. This will result in a decrease in workload, an increase in motivation and job satisfaction.
References
Amadi, E. (2015). Electronic health record implementation success: Lessons learned and best practice. Journal of Technology Research, 6(1), 1-12.
Huang, C., Behara, R., & Goo, J. (2014). Optimal information security investment in a healthcare information exchange: An economic analysis. Decision Support Systems, 61, 1-11.
McMurtrey, M. (2013). A case study of the application of the systems development life cycle (SDLC) in 21st century health care: Something old, something new? Journal of the Southern Association for Information Systems, 1(1), 14-25.
Memon, M., Wagner, S., Pedersen, C., Beevi, F., & Hansen, F. (2014). Ambient assisted living healthcare frameworks, platforms, standards, and quality attributes. Sensors, 14(3), 4312-4341.
Mosa, A., Yoo, I., & Sheets, L. (2012). A systematic review of healthcare applications for smartphones. BMC Medical Informatics Decision Making, 12(1).
Payne, S. (2014). The implementation of electronic clinical documentation using Lewin’s change management theory. Canadian Journal of Nursing Informatics, 8(1&2).