Introduction
A range of factors can influence businesses at the macro- and micro-environmental levels. To discuss any company’s performance, one should conduct an industry analysis to determine this firm’s place in the market and internal analysis to identify competencies that make organizations become market leaders (Worthington & Britton 2015). Nike is a multinational company founded in the United States in 1964. For about ten years, the company was known as Blue Ribbon Sports. What does Nike need to improve? A thorough analysis of Nike’s resources and capabilities is necessary to determine it.
Today, Nike specializes in manufacturing athletic footwear, apparel, and accessories (Nike, Inc: home page 2016). In the United Kingdom, Nike became one of the leaders in the athletic footwear market, whose sales in 2015 were more than £11 million compared to about £4.5 million in 2014 (Gibson 2016). The company’s revenues continue to rise. The purpose of this report is to analyze sources of Nike’s competitiveness in the UK market, conduct the Nike Five Forces Analysis, and discuss Nike’s internal analysis. It will also provide a SWOT analysis of Nike, outlining its strengths, threats, opportunities, and weaknesses and proposing the strategy for the company’s future development.
Porter’s Five Forces: Nike
Michael Porter developed the Five Forces Analysis in the 1980s. The objective of this analysis is to determine which aspects influence the completion within this or that market with the focus on its structure and profitability (Worthington & Britton 2015). Five main factors affect the development of industries. These factors are the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of consumers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among competitors (Figure 1). This section provides the Five Forces Analysis of the UK athletic footwear market.
Nike—Bargaining Power of Suppliers
In the United Kingdom, a variety of factors can influence the development of the athletic footwear industry. The bargaining power of suppliers is a weak force in this market. The reason is that companies operating in the market have access to many suppliers which compete to sell their raw materials to companies. The availability of high-quality resources and different types of suppliers is high, and it cannot influence the market negatively (The latest trends in the running sector 2016). As a result, the availability of resources is a key factor to determine the impact of this force on the industry.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of consumers is another important factor to discuss. This force is moderate because customers influence the development and profitability of the market directly (Worthington & Britton 2015). According to national reports, in 2015, the British buyers spent about “£600 million on running footwear and apparel” (The latest trends in the running sector 2016, para. 1).
Furthermore, in comparison to the results for 2010, “consumer spending increased by 50 percent” (The latest trends in the running sector 2016, para. 1). Prices and brand names remain to be key factors that influence buyers’ decisions. While discussing the tendency regarding the example of Nike (UK), it is possible to state that this brand name attracts more consumers each year, but a high price can be a risk factor because buyers can select inexpensive products. The consumers’ buying capacity in the United Kingdom is influenced by economic factors.
Nike: Threats of New Entrants
The threat of new entrants in the UK market of sports footwear is a weak force because of such barriers as high costs of establishing and promoting a new brand and high economies of scale (Worthington & Britton 2015). As a result, new entrants can experience significant difficulties while competing in the market.
Referring to the case of Nike, it is possible to state that the company takes a leading position in the athletic footwear industry of the United Kingdom, and new entrants cannot compete effectively against this firm (Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016). The reason is also in the fact that market leaders have developed supply and distribution networks that allow them to remain competitive in the industry.
Nike: Threat of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes in the market is moderate. It depends on such key factors as the price of sports footwear, the price of substitutes, and the consumers’ buying capacity. The problem is in the fact that, although the athletic shoe market develops actively, there are many substitutes in this industry that have attractive prices (Davis 2016). Buyers use athletic footwear not only for running, sports activities, or cycling but also for walking and leisure activities (The latest trends in the running sector 2016). As a result, consumers are often not interested in specific qualities of these shoes, and such companies as Nike can face challenges associated with the fact that buyers choose different substitutes instead of the promoted athletic shoes.
Nike Competitors Analysis
It is also important to focus on the degree of rivalry among competitors in the sports shoe market of the United Kingdom. This competition is strong, and its main drivers are the increased growth of the market, the focus on competitive strategic plans, and the comparably low number of leaders in the industry. The British people’s interest in a healthy lifestyle has resulted in increasing the popularity of athletic footwear (Davis 2016). In 2015, the UK market was led by such companies as Nike, Asics, and Puma (Davis 2016).
Such type of competition is known as the oligopoly that is characterised by an appropriate differentiation of products and high entry barriers (Worthington & Britton 2015). Nike’s competitive advantage in this context can be viewed as high, but the constant development of rivals makes the company focus more on innovation and new marketing strategies (Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016). Thus, the competition within the market can be discussed as constantly growing and affecting companies’ strategies.
Reflective Account
To conduct the Five Forces Analysis for the athletic footwear market in the United Kingdom, it was necessary to find information about the industry’s development in the country. The analysis of the collected data was the next step to understand what factors could affect each force. It was rather difficult to evaluate the bargaining power of suppliers in the context of the UK market. Still, there was a lot of information about the power of consumers and threats of new entrants and substitutes. To provide examples, it was appropriate to refer to the case of Nike. The conclusion about the competition in the market was made regarding the conducted analysis, and the strong rivalry was determined as a key feature of the oligopoly typical of the industry.
Nike: Internal Analysis
Nike’s internal environment can be analysed with the help of two auditing tools. The resource audit model demonstrates assets that form the strategic capability of the firm. It is based on resources and core competencies. In their turn, resources can be divided into tangible, intangible, financial, physical, technological, and human ones (Worthington & Britton 2015). One more model to use is the value chain analysis which helps to determine which primary and support activities are important to create value for Nike. Figure 2 demonstrates the principles of the resource audit model as a scheme.
Nike—Resources and Capabilities
For Nike, tangible resources include such physical assets as stores, facilities, and distribution centres. Manufacturing activities are outsourced. Much attention is paid to controlling the quality and performance of facilities located in developing countries. Financial resources can be discussed as contributing to the company’s development because Nike’s financial ratios are high (Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016).
While speaking about technological resources, it is important to note that Nike invests in research and development, and the value is created regarding developing such innovations as NIKE Air, Dri-Fit, Zoom, Flywire, and Flyweave among others. Human resources include more than 70,000 qualified specialists who work in the United Kingdom and abroad (Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016). Intangible resources also include knowledge, laboratory test results, design, brand recognition, and customers’ loyalty.
These resources are associated with such Nike’s capabilities as effective management, successful marketing and advertising, teamwork, product design, brand reputation, and customer services. These capabilities are the basis for Nike’s core competencies that contribute to forming the strategic capability of the firm. Thus, core competencies are the combination of specific resources and capabilities that add to the company’s advantage (Worthington & Britton 2015). These core competencies include marketing and advertising, brand awareness, innovativeness, outsourcing, and performance.
Thus, Nike has developed successful marketing and advertising strategy based on attracting celebrities and promoting a unique experience. Potential consumers recognise the benefits of purchasing Nike’s shoes. They associate these products with a healthy lifestyle, action, and success. The company’s logo (the Swoosh) and slogan are easily recognised (Gregory 2016). Innovativeness as a part of Nike’s strategy is another core competency. The Research and Development Department of the company works to explore new qualities of materials and new designs to address customers’ needs and propose unique products that are difficult to imitate. The focus is on presenting new models and features of products annually. Outsourcing also remains to be one of Nike’s core competencies because of the high-quality management of processes at different levels is the company’s advantage (Nike, Inc: home page 2016). The control and supervision are characteristic features of the company’s work that contribute to its perfect performance and reputation within the market.
Value Chain Analysis of Nike
The value chain analysis is used to explain what value-adding approaches can be applied to improve the company’s competitive advantage (Worthington & Britton 2015). It is important to note that Nike proposes a unique product which value can be discussed as rather high. To understand how resources and capabilities add to Nike’s value and image, it is necessary to analyse primary and support activities according to Figure 3.
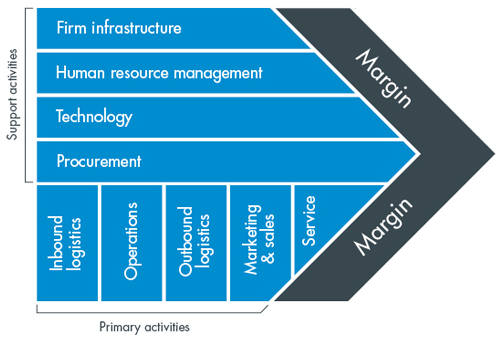
Primary activities that add to manufacturing athletic shoes directly are inbound and outbound logistics and developed operations. These activities are based on the active use of raw materials from countries where manufacturing facilities are located, as well as on low production costs. Furthermore, much attention is paid to controlling technologies, inventories, and processes.
The supply chain management is organised effectively to guarantee the work of the manufacturing facilities, the development of designs, the work of the Research and Development Department, the quality and performance control, and the on-time distribution of products in the United Kingdom and other countries (Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016). More primary activities include marketing and services. Nike focuses on supporting the brand recognition, keeping the price leadership, and advertising its innovative products. The marketing and service strategies are based on influencing the target audience and addressing specific needs.
Support activities include procurement, infrastructure, human resource management, and technology. Nike’s procurement strategies are based on strong relationships with suppliers and distributors. Therefore, innovative products are provided for sales in the most efficient manner. Nike’s infrastructure is also developed, and it consists of the work of IT and e-commerce departments (Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016). Human resource management in the company is based on strong leadership and effective teamwork. Furthermore, the development of the successful design is a result of using technologies and results of research. Thus, all these strategies lead Nike to high sales and profits.
Reflective Account
The analysis of Nike’s resources and core competencies was an easy task because a lot of information is available online and in the company’s reports. The application of the resource audit model was important to demonstrate how core competencies could add to the development of the specific strategic capability. Moreover, the value chain analysis was also selected for this task to provide more details and differentiate activities in terms of their priority to influence Nike’s competitiveness in the UK footwear market.
Nike: SWOT Analysis
To discuss what internal and external factors can influence the development of Nike with the focus on its strengths and weaknesses, it is necessary to refer to the SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis. This analysis is effective to identify advantages and disadvantages in companies’ strategies (Worthington & Britton 2015). Figure 4 represents the scheme according to which this analysis is applied.
Nike’s Strengths
While focusing on internal factors, it is important to discuss Nike’s strengths which are the main forces that contribute to the company’s growth and development in the UK market of athletic footwear. The first strength is the popularity of the brand name. The company’s image and recognition play key roles in attracting customers (Worthington & Britton 2015). The second strength is the company’s focus on promoting innovation in its products. Athletic footwear is manufactured with the help of the latest technologies and according to findings of the recent studies in the field.
Furthermore, athletic footwear is promoted in the context of apps presented to support a healthy lifestyle (Gregory 2016). This approach contributes to increasing the product’s popularity. The third strength is the effective marketing strategy that allows Nike to accentuate the quality and uniqueness of its products. In the United Kingdom, Nike is a partner of many sports competitions and charity events (Nike, Inc: home page 2016). The fourth strength is the developed network of distributors that allows for taking the leading position in the UK market.
What Are Some of Nike’s Weaknesses?
Weaknesses are also discussed as effective to demonstrate whether Nike’s business strategy is appropriate for the environment of the United Kingdom. The company’s image in the country was affected by the discussion of Nike’s outsourcing activities. Another weakness is the company’s approach to differentiating products for the market of the United Kingdom.
The problem is in the fact that the company cannot take the leading niche in the market of athletic shoes in this country because of providing limited opportunities for adopting innovation in the UK market (Gregory 2016). It is necessary to pay more attention to diversifying the product mix presented in the United Kingdom.
Nike’s Threats and Opportunities
External factors include opportunities and threats. For Nike, opportunities are associated with the focus on differentiation strategies and diversification to attract more consumers. According to the market reports, today, women and non-athletes buy more footwear in comparison to the data for 2014. Thus, “the female market grew by 10 per cent, a much more dynamic rate compared to the male market” (Female sports apparel and footwear sales are on the rise 2016, para. 3).
From this point, it is important to develop strategies to address the needs of these buyers and focus on Nike’s product mix in the United Kingdom. The purpose is to increase sales by 20% (Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016). More attention can be paid to developing innovative consumer-oriented products that can be used for different types of activities and be attractive to both women and men.
Despite a range of opportunities for the growth within the market, Nike can also face some threats associated with the current company’s strategy adopted for the UK market. Nike’s main competitors, including Puma, Asics, and Adidas, remain to be leaders in the industry, and their marketing strategies can be discussed as rather proactive in comparison to Nike’s approaches (Davis 2016). Thus, the company’s competitive strategy should be revised. One more threat is the consumers’ interest in inexpensive substitutes or alternatives for Nike’s brand shoes. Although Nike has many opportunities to expand within the market, it is important to address the identified threats to achieve high results.
What Does Nike Need to Improve?
A competitive advantage can be discussed as an area in which a certain company performs better than its competitors (Worthington & Britton 2015). In the context of the oligopoly typical of the athletic footwear market in the United Kingdom, Nike should pay more attention to overcoming weaknesses and addressing potential threats to create a sustainable competitive advantage. Currently, Nike in the United Kingdom is focused on the differentiation strategy with the element of the cost leadership strategy (Gregory 2016). The purpose is to reduce production costs, refer to innovation and changes in technology, and offer customers to buy unique products that can address their needs despite their activities and interests.
However, even though Nike proposes differentiated products that are promoted with the help of effective marketing campaigns, the competition within the industry increases annually (Davis 2016). Nike requires focusing on another unique strategy to attract more buyers. Diversification can be viewed as an appropriate strategy to improve the company’s competitive advantage (Gregory 2016). The reason is that today, Nike can produce a range of supportive goods as part of athletic footwear collections. Currently, consumers are interested in purchasing products that are associated with the sphere of sports and their lifestyle (Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016). Therefore, a diversification strategy applied in the context of the UK market can have potential benefits for Nike to increase its competitive advantage.
Reflective Account
The SWOT analysis is one of the most effective techniques to describe and evaluate internal forces and potential external factors that can influence the company’s development significantly. The task to conduct the SWOT analysis for Nike was rather easy to complete. Furthermore, it allowed for concentrating on specific aspects of Nike’s strategy that could be regarded as weaknesses and threats. As a result, it became possible to determine areas for revision and improvement. Moreover, the SWOT analysis provided the background for the development of the future strategy that would be used to improve Nike’s competitive advantage in the UK market.
Conclusion
The UK athletic footwear market is highly competitive. However, Nike takes the leading position in this industry. The Five Forces Analysis demonstrates that there are many opportunities for the market’s growth in the future. Consequently, Nike requires an effective strategy to create a sustainable competitive advantage. The analysis of available resources, competencies, strengths, and weaknesses indicates that Nike can succeed while developing its differentiation strategy and paying more attention to diversification with the focus on proposing innovative products to increase the customer base.
Reference List
Davis, J 2016, Athletic footwear market size, price trend, competitive market share and forecast by 2023: Global Market Insights, Inc, Web.
Female sports apparel and footwear sales are on the rise 2016.
Gibson, R 2016, Nike (UK) profits soar as products continue to ‘resonate well’ with retailers and consumers.
Gregory, L 2016, Nike, Inc: generic strategy and intensive growth strategies.
Nike, Inc: 2016 Form 10-K 2016.
Nike, Inc: home page 2016, Web.
The latest trends in the running sector 2016.
Worthington, I & Britton, C 2015, The business environment, Pearson Education, Harlow.