Introduction
The world has evolved dramatically with automobiles, steel, tire and various other industries had erupted during the industrial revolution. A number of countries came into the limelight like Japan, Germany, and Taiwan against the European Union. Organizations make up a nation because they provide jobs, earnings, standard of living; they influence lifestyles and at times culture. Without organizations a country can never grow. Some developing nations are dependant on imported stuff and that has adversely affected their domestic market which is the main reason why these countries never develop and are either taken over by an influential culture or vanish from the face of the earth. On the other hand who makes the organizations? It’s the people who make an organization and without people the organization is just a still building with equipment which is useless because it’s the human mind that commands control over these still things and turns them into gold for nations.
Human resources refer to the people of an organization. Human resource managers seek to facilitate the contribution people make to achieve an organizations goals and strategies. As a slogan at a Union Carbide Plant puts it, “Assets make things possible, people make things happen.” It is important that human resource strategies support organizations objectives because they play a significant role in helping companies to achieve their objectives and goals.
The central challenge facing organizations is the continued improvement of our organizations, both private and public. The people make an organization so they are responsible.
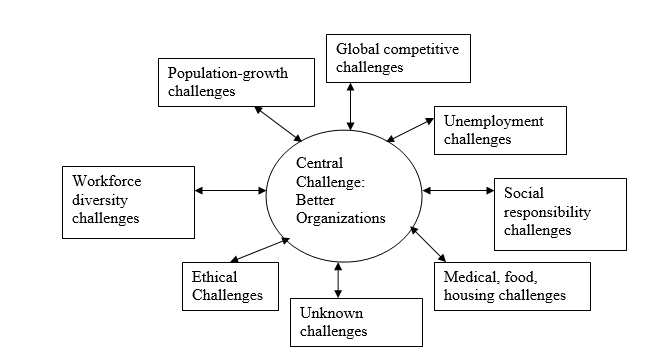
The purpose of human resource management is to improve the productive contributions of people to the organization in ways that are strategically, ethically and socially responsible. Human resources determine every organizations success! HR simply manages the people of an organization and not the factors that shape the employee’s contribution in an organization like capital, materials and procedures. Thus, HR can be termed as ambitious in this sense of the word.
Very few large organizations existed during the thousands of years between Moses and the Industrial revolution. But with the revolution numerous organizations erupted like lava out of the volcano. The industries for automobile, steel, locomotives, press etc spread like ants on the earth. From then emerged the problems of handling the people and satisfying because initially the people needed employment and a source of living so originations were taking advantage of it by using cheap labor for more work.
Gradually, things evolved and there were more employment opportunities then people needed them so that is when human resources kicked in because companies had to take strategic steps to reduce turnover and retain the useful employees. This marked the beginning of importance of human resources and in order to be more precise strategies were developed to offer a strategic fit. This gave birth to strategic human resources management.
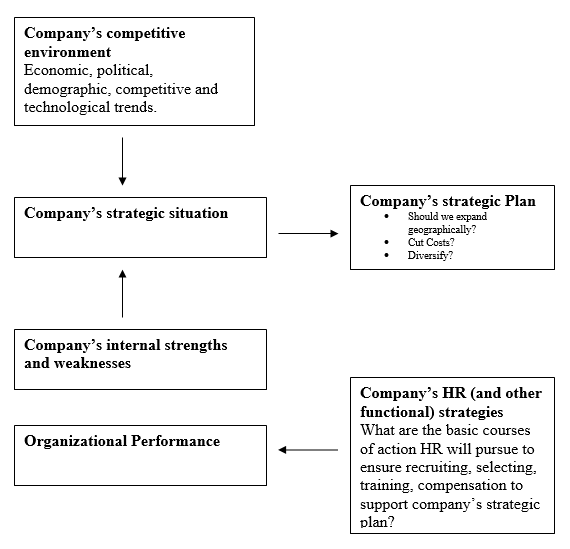
A strategic plan is the company’s plan for how it will match its internal strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats in order to maintain a competitive edge. The essence of strategic planning is to ask that where does the company stand currently and where does it see the company in the future but a strategic plan helps devise the plan of how to get there accordingly. It is the responsibility of the manager to formulate specific human resources and other resources plus strategies to take the company from where it is now to where the company aspires to be. A strategy is a course of action like Ford’s strategies regarding closing plants or terminating employees are an apt example.
A strategy is the present and future direction of the organization and it covers certain aspects such as assessing the organization’s internal competencies and capabilities, assessing environmental threats and opportunities, deciding the scope of the organization’s activities, creating and communicating a strategic vision, managing the process of change in an organization. A strategy forms the basis for the analysis of a firm’s relationship with its environment specifically in achieving competitive advantage through distinctive competencies and also unique relationships (Kay, 1993). A strategy is implemented in the form a process which has layers and it cascades downwards in three ways and these are as follows:
- First-order (Corporate level): which sets the long term direction of firm; it incorporates the scope of its activities and its market positioning.
- Second-order (Business Level): which includes the internal operating procedure and relationships between different parts of the organisation
- Third-order (Functional Level): It involves different functions devising broad strategies to support business strategy.
Strategic Human Resource Management attempts to integrate the use of human resources with the wider business strategy of the organisation, i.e. “strategic integration based on external fit.” It is formulating and executing HR systems that include HR policies and activities which produce the employee competencies and behaviours the company needs to achieve its strategic aims; for e.g. FedEx has a strategic aim that is to achieve superior levels of customer service and high profitability via a highly committed workforce and most preferably a non-union workforce. SHRM is as discussed is to match strategy with human resources and this can be done along certain lines such as conscious matching only strongly relevant for those taking classical approach, most matching models are normative, focusing on HRM fit with development stage and/or management style, development stage focuses on either organisational life-cycle or degree of diversity and Schuler/Jackson developed a strategic orientation typology using Porterian model – Its essence is that it specifies the need for different HRM policies of different parts of overall strategy like Innovation, Quality Enhancement and Cost Reduction.
Section A
The talent management at Standard Chartered is unique and it accordingly adapts to the environment in the organization but it does purport to the features of SHRM as well.
Banks are based on numbers and they count their success and achievements in numbers as well. Standard Chartered implemented a talent management program to analyse its workforce and also its contribution to the success of the organization. SHRM has three main features organizational level, focus and framework. Organizational level illustrates the major policies, key goals and allocation of resources of an organization since they support the implementation of the strategy so this feature of SHRM has to be considered on top of all during strategy implementation. Talent management in Standard Chartered was much needed regarding their current position in the market especially with the financial downturn.
The talent programme at Standard chartered is well tuned with the organizational policies, aims and allocation of resources since they provide a service and for a service organization the most important factor of the marketing mix is “people.” Since talent is limited in the market so the bank aims to build its own people via training. The bank wants to increase its leadership capacity by 2011 which is an aim and the talent management programme is assisting in achieving this strategic aim.
The bank is spread across 50 countries around the world with 60,000 employees with 100 different nationalities. The bank is fighting for a limited pool of talent which has led it to implement the talent management programme which will help achieve the organizational aim strategically and this is a good example of strategic human resource management. The talent management programme at Standard Chartered does abide by this feature of SHRM since their programme aims to achieve the organizational aims and policies effectively. This limited pool of talent aims to achieve a leadership capacity in order to have a significant workforce.
The programme will help appraise the performance of all managers since the bank needs good managers who can motivate the staff and kinder excellent performance in all. This will help to identify talent and retain the best or even train and improve the rest. Leadership is essential for any organization and this being the aim of the bank it shows their talent management programme fits with the first feature of SHRM.
It has been twenty years since Meindl, Ehrlich and Dukerich observed in their provocative article ‘The Romance of Leadership’: ‘it has become apparent that, after years of trying, we have been unable to generate an understanding of leadership that is both intellectually compelling and intellectually satisfying (1985.p. 78). Two decades on it would seem an opportune time to take stock of this diffuse and ubiquitous field by examining the diverse arguments and analyses of leadership processes that have emerged during the intervening period.
The concept of leadership has been an enigma of social democracy since the classical philosopher-kings of Plato. It also remains an elusive and enigmatic issue in management studies, with significant debate about how to understand, interpret, and otherwise give meaning to the nature and role of leadership. Most leadership research of the last 50 years has been conducted in the U.S., Canada and Western Europe. This places stress on the individual and managers rather than workers.
The result is that our perception of leadership might well be affected by a series of learnt assumptions (for example, ‘leaders make a difference’) that depends on fundamentally assumed theories that stress causal laws and relationship between variables’ (for example,leadership styles and behavior are influential and important for organizational activities and outcomes).
Focus is another feature of SHRM which purports the importance of strategies that bring organizational effectiveness and this means employees are human resources that have to be managed in order to meet the strategic business goals. The talent management program at Standard Chartered aims to manage its human resources in order to meet the strategic business goal that is to develop a limited pool of talent and leadership capacity within the Bank since the availability of talent is limited and existing employees if are talented shall be retained or the rest can be trained. But the underperformers have to be removed and planted in some other profession or what may suit. Simply placing employees in jobs does not ensure their success.
They need guidance to understand their roles and responsibilities. Training helps a person do his/her current job but training has benefits a person throughout the career path and helps to develop a person overall for future responsibilities. The bank has also had an effective recruiting program implemented which is called “Right Start” and this further helps find new talent and achieve the strategic business goals of the Bank. Talent management has helped Standard Chartered create a focus that will assist in achieving their strategic business aims and goals. The Program fits the second feature of SHRM as well and quite appropriately.
The third feature of SHRM is Framework which includes strategies that provide a broad, contingency-based and integrative framework. HR goals and activities need to be different according to different environments in order for them to be mutually reinforcing. The talent management program at Standard Chartered has different appraisal systems and these include either 180 degrees appraisals or 360 degrees appraisals but different types are implemented in different environments; for e.g. Standard Chartered in Africa uses 360 degrees appraisal but in China they more reticent so they use 180 degree appraisals and it’s a fact that it entirely depends on the local manager and what he/she thinks fits best with the environment.
A service centre in India produces regular human capital score cards so that the bank can show to the local managers with these numbers that how have they been performing in comparison with other branches. The employees according to the program are classified according to their performance appraisals but these classifications are not announced openly to prevent resentment so according these appraisals the talent is retained, some are trained and others might be removed.
The concept of talent management strengthens SHRM and does not replace it due to which the program fits all features of SHRM. The program strengthens SHRM in various ways such as follows:
- It facilitates management through measurement.
- It provides guidance on what to measure, how to measure and provide the concluding results for it.
- It provides a direction to HR strategies and that superior people management provides superior results.
- Creating value through people using HR strategies.
- Connecting HR and business strategies.
- HR specialists are business partners.
- Human resources are the most important asset for an organization.
The talent management program fits all three features of SHRM that include organizational level, focus and framework. Thus, the talent management program that also helps managers find their strengths via strengths finder test and capitalize on their strengths particularly; fits with the third feature of SHRM as well and it provides a framework that supports all organizational policies and aims thus it enables the achievement of all strategic business goals with a focus (Vere, 2007).
The talent management program shall help Standard Chartered to maintain a limited pool of talent and also develop a leadership capacity. This program is strategic to the success of banks in this financial turmoil since all banks of a credible decree have implemented an innovative approach to strategic talent management and also recruiting in order to strengthen their workforce. This program shall help the bank maintain its dignity in the market and also survive in the long run. Being employer of choice has always proved to be profitable for an organization in terms of credibility and productivity in the market.
This program shall help the bank understand the importance of a successful recruiting program like “Right Start” in the case of Standard Chartered. A successful recruiting program can help adopt certain approaches such as data mining, customer relationship management, competitive intelligence, assessment metrics from other functions of the business and niche marketing. For e.g. First Merit Bank has a strategic and innovative approach that has been extremely successful and it has been called the benchmark firm that other organizations must follow. The talent management program can enable the bank to become the employer-of-choice brand and a leader since this program shall help to prioritize jobs, cut costs and focus more on “game-changers” or a person who shift rapidly which is an issue with bank during this financial meltdown.
This program will assist in planning, redeployment, utilizing analytics and also leveraging internet so it shall help make effective use of contingent workers usually the ones about to retire. The program shall also strengthen brand equity in the market and develop the employer brand of the company. Helping employees capitalize on their strengths will help develop a competitive workforce that will be the major strength of the bank in the longer run.
The program will assist in workforce planning and will also help all employees grow personally which will benefit the organization in the long run since a motivated workforce guarantees increased productivity. Being proactive in every way especially in retaining talent and strengthening internal plus external equity shall be beneficial in the longer run. Through this program effective compensation programs can be devised in order to motivate employees further. Thus the talent management program shall prove to be a driver in the longer run for Standard Chartered.
The measurement of the impact of SHRM is essential since that will tell the effectiveness of the implemented policies and strategy. The impact measurement of SHRM will show the HR strategies fit with organizational goals, integration of SHRM in the organizational policies, the involvement of HR in the senior management, development of HR practices in the line managers and value addition of SHRM in the organizational success.
The resource based view (RBV) of firms has been explained with certain positioning dimensions (Millimore, 2007)).These theories represented by innumerable theorists in this field have helped to identify various firms in different positions in the market. All firms have capabilities that are unique in some way and they help achieve sustained competitive advantages. But there has been no research as such that dips into ways and means for the firms to leverage their capabilities with their resources. Also that these capabilities are complex and have to be realized and understood effectively has not been addressed in any such research up till now.
The question to be addressed is “What resources are necessary to achieve and sustain specific competitive positions in today’s market place?” Thus it is important to measure SHRM and its impact (Anderson, 2005).
The impact of SHRM can be measured with 10 items in relation with business objectives strategies being met. The items are as follows:
- HR practices helping to achieve business objectives or not.
- HR practices are useful in implementing business strategies or not.
- HRM strategy is based on Business strategy.
- Involvement of HRM in business decision making.
- HRM and Business strategies are in synch with each other.
- HRM’s role in coordinating business and also easy access to HR information.
- Alignment of HR and business strategies.
- HRM’s role in development of employee programs.
- HRM’s role in development of work procedures.
- HR is an important part of the mission statement.
Other measurement criteria are as follows:
- Line management involvement: It studies the involvement of line managers in implementing HR practices and values in the organization.
- Line management training in HR: How well have the line managers been trained in the execution of effective HR in the organization.
- Financial performance of the firm: With the implementation of SHRM and talent management in the case of Standard Chartered the financial performance of the bank should improve in the long run.
- Control variables: These help to ensure the positive impact of SHRM.
Section B
HRD has gained credibility in leading SHRM activity and this can be proved with case studies. HRD helps SHRM to reduce the challenges that it usually faces because it provides a framework to develop new strategies that reduce the challenges and help the organization come up with innovative ideas. SHRM faces three challenges one as at Dell is the need to support corporate productivity and performance improvement efforts since globalization has led to competition.
Dell runs its HR via its web where its employees handle applications. The company has been involved in cost cutting but via the web all tasks can be performed via applications on the web which is easier plus they can even administer their own 401(k) plans via the web and even check for job postings etc. This is an effective and low cost strategy employed by Dell. Second is employees play an expanded role in employer’s performance improvement efforts like all the high elements associated with Toyota and third is that employers see that their human resource units must be more involved in designing and not just executing the company’s strategic plan.
HRD helps SHRM activities to be implemented effectively. An important issue in organizations is employee turnover similarly there are other HR issues that HRD identifies and SHRM then devises a strategy on that basis in order for activities to be implemented in a flow. Similarly, training is essential for employees to work efficiently and this comes under HRD which then signal SHRM to devise a strategy to solve the issue.
Employee development related actions emphasize the importance to help the employees grow personally by helping them to fulfill their self actualization needs (Richard, 2007). It is also important to check for employee obsolescence that is when the employees do not posses the knowledge or abilities to perform competitively and that is where they require training and development programs to boost their careers. In this case the management style of the manager is highly incompetent and obsolete (Reilly, 2004).
HRD helps to identify performance deficiencies like in the case of South West Airlines since they used HRD to implement SHRM and then their policies help produce the employee competencies and behaviors the company needed to achieve its strategic aims. Thus, with their highly motivated staff they developed a low cost strategy and convenient service. HRD also helps to identify reasons for that cause deficiencies so SHRM can develop particular strategies that might benefit.
Being unprofessional and self-centered by being concerned with only personal growth and development, lacking leadership characteristics, lack of empathy to understand employees, to be able to motivate and provide direction and to be able to communication effectively. It is important for a good manager to know the four factors of leadership namely- understanding the follower, being an effective leader, good communication and understanding/ responding to situations as proposed by HRD that a good manager yields good staff management and that is what Standard Chartered is looking for as well.
These actions will help to incur employee development, satisfaction and retention. HRD proposes ways and means by which management shall recruit and then place the right people for the right jobs. These actions will help to overcome the performance deficiencies and also go beyond them to improve the overall conditions in the working environment in order to benefit the manager, top management and the employees (Reilly, 2008).
HRD identifies issues for organization on the basis of which SHRM devises a strategy and HRD initiates the flow in order to generate a smooth flow of activities and in the light of cases mentioned in the answer it does prove that HRD does lead to SHRM activities in an organization.
This answer is a discussion of the importance of the role of HRD in achieving SHRM in the organization. Human resources Management is a system that consists of many interdependent activities. A system consists of two or more parts or subsystems that work together as an organized whole with identifiable boundaries. The HRM Model and subsystems are illustrated below:
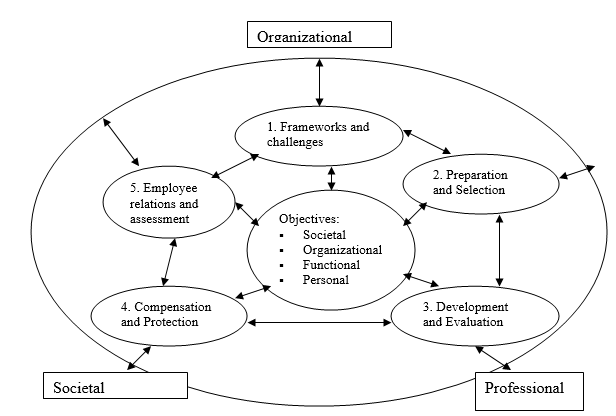
HR is done on a proactive basis which is to anticipate the HR problems and take corrective actions beforehand and also reactive basis which is to take corrective actions after the problem has occurred (Drucker, 2004).
HR perspectives or viewpoints include the following:
- Strategic approach: HR should be managed in a way that it contributes to the success of the organization.
- Human resource approach: HRM is the management of people and each human being is important and has a certain sense of dignity and self respect that must not be ignored at any cost.
- Management approach: HR management is the responsibility of every manager in an organization. It’s a two way operation with the manager guiding and monitoring and the subordinate to interact, obey and work with utmost devotion.
- Systems approach: HR management takes place within the larger organization and the HR efforts need to be analyzed with respect to the contribution they make in an organization.
- Proactive approach: This is to manage HR effectively by anticipating HR challenges and taking the corrective actions before the thunder strikes.
Very few large organizations existed during the thousands of years between Moses and the Industrial revolution. But with the revolution numerous organizations erupted like lava out of the volcano. The industries for automobile, steel, locomotives, press etc spread like ants on the earth. From then emerged the problems of handling the people and satisfying because initially the people needed employment and a source of living so originations were taking advantage of it by using cheap labor for more work.
Gradually, things evolved and there were more employment opportunities then people needed them so that is when human resources kicked in because companies had to take strategic steps to reduce turnover and retain the useful employees (Baron, 2007). The scientific management by Frederick W. Taylor emerged with its Fordist and Post-Fordist view. Henry Ford’s automobile giant was the beginning of HRM in organizations. Then from the World War I and until the Great Depression in 1930’s the Hawthorne experiments revealed certain facts.
The study says that the organizations improved the lighting and hygiene (motivational or satisfaction factors) so the employee performance improved but later it was found out that it was the concern and that care shown by the organization that actually motivated the employees to work better. The theory also talks about dissatisfiers and that the absence of these factors is not enough because there have to be effective motivational factors. But although the presence of dissatisfiers can cause dissatisfaction among employees and that will result in poor performance and eventually increasing turnover. The external challenges faced by an organization are as follows:
- Workforce Diversity: This occurs from differences in demographics like age, race, origin, religion, race, culture, creed etc. The differences in generations have also contributed to this factor. From the baby boom late 1950’s and to the bust into 1970’s. The trends changed by 1990’s and then the Generation “X” (20-24yrsold) turned out be independent, rebellious and different. Cultural differences are based on differences in attitudes, beliefs and lifestyles. Immigrants have also caused diversity because they migrate from different places with different cultures and lifestyles.
- Technological challenges: Technology has come a long way and has contributed a lot to HRM on the whole. Artificial intelligence, robots and other technologies have all contributed to a better and well managed organizations. But it has caused worker alienation because technology is replacing humans and this will adversely effect the world’s population.
- Organizational Challenges: There have been unions and information systems to complement the organization and its problems. Each organization has its own culture and philosophy and there are bound to be conflicts.
- Professional Challenges: Each organization now requires a formal degree or certificate in order to be applicable to work in the company. The education requires brains and money and not everyone has both. This is a challenge people have to face inevitably.
HRD is essential and programs like talent management or recruitment of talent help implement SHRM effectively since it is important to have a strategy. HRD provides the basis for SHRM to develop strategies that attract new and effective talent and also retain talent within the organization. It is important to find out what is important to the staff and interaction is a better way to know the employee personally. But the company can follow certain strategies to retain staff and these strategies will also help to attract new talent and they are as follows:
- Ask: It is important to ask and inquire in order to know what the employee is going through and what they need. But there is a simple warning that asking increases expectations among the employees.
- Exit interviews: It is important to do exit interviews with the employees who are leaving the organization because they can tell the truth about what is going on within the organization. The data collected can be used to overcome the problems and that which is lacking within the firm. This will help to provide to the employees the best in order to retain them.
- Post-employment checkups: This is a proactive strategy since it suggests to interview employees when after a certain time period to which they have been hired. It is favorable to do check up interviews within 60-90 days.
- What works for you? The managers should themselves analyze their position to what they want from the organization and things they like or dislike about the company. This will help provide an insight of what employees would like or dislike. Since one should like for another for what one likes for oneself.
- MBWA: Management by walking around. This might lead to suspicion but employees will get used to it eventually. Walking around and carrying out significant conversations with employees will help to know what they are going through at work. Observing while talking rounds can be helpful in collecting a lot of employee related data.
HRD also helps to train managers to take the right decisions like in the case of Standard Chartered they have a regular appraisal and it depends on the local manager to take an effective decision that is good for the company. Managers can take certain steps to retain employees and attract new ones and the strategies are as follows (Kaye, 2004):
- Don’t be a Jerk: As the saying goes that “People join a company but leave a manager.” This means that the manager was the reason to why the employee left. If all sorts of motivational techniques are used and provided to the employee but if the employee has a bad relationship with the immediate manager then the employee would prefer to leave the organization. The manager is to whom the employee is answerable to and if the relationship with the manager is bad then the employee will be adversely affected and will eventually leave the organization. The manager should be a proper guide and a leader who can inspire in his employees to work efficiently and not instigate negative feelings in them. So managers need to be understanding and empathetic with their employees (Munzell,2004).
- Avoid the Peter Principle: Often managers start their venture from the bottom of the hierarchy and they get promoted due to commendable performance and technical skills. But it is important to provide opportunities to these skilled and talented people in the organization. They need to be provided with good training and development and also that providing dual career tracks can help employees.
- Set Clear Expectations: It is important to be clear about what is expected of employees at work because when people understand what is expected of them they can put in their best efforts.
- Establish High Standards and Accountability: It is important to set high standards and when people achieve them there should be a system of accountability so that people are responsible of their actions. High standards without accountability will discourage employees.
- Feedback: Managers need to set standards and, goals and milestones that need to be achieved by employees and then feedback of the quality of work should be given to employees. Negative feedback must always be given in private and positive feedback must be given publicly and this will motivate employees to work harder.
- Spend Time and Make Time: It is important for managers to take out time for their employees in order to get close to them and also to get to know them. Often managers consider this useless. Although its very important and this helps to understand the employees better and provide them with what they want and expect. This will satisfy workers and the honest concern from the manager will help to retain employees.
- Be Enthusiastic: Enthusiasm is contagious and it spreads plus managers must know the importance of it and that it should transfer to employees.
- Provide resources and support: It is important to provide all resources to employees since the absence of resources that are necessary to carry out the job cause dissatisfaction. Managers need to help and support employees so that they can overcome challenges and meet objectives.
- Job Enrichment: This is to provide ample opportunities to move upwards in an organization. Although this is not feasible in certain organizations. This will help improve the morale of employees and help them develop their career and fulfill their need of self actualization. If this need is fulfilled then employees are most likely to stick to the organization.
- Recruit well: Managers need to be careful while they recruit. They must observe and recruit the right person at the right time and for the right job. Personality job fit is essential to make the duo work. But its important to keep in mind the qualifications required for workers to be able to fit a job. This will reduce turnover. Since recruitment and turnover are both costs for a firm.
- Communicate: Effective communication is essential since then only the employees will be able to understand the organization’s culture and philosophy. This will help them adapt to the corporate environment and put in their best efforts.
Thus HRD plays a vital role in SHRM since it provides the framework to SHRM to formulate the effective strategy that proves to be good for the company (Brown, 2004).
Conclusion
This case study was a detailed analysis of SHRM in the light of HR specifically in Standard Chartered. Thus, HRM is essential for every organization in today’s world and the role of HR has become very significant lately. HRM is all about people and they make an organization. The employees have needs and if their needs are not satisfied then they tend to switch to other organizations and that increases turnover for the employees. The companies can adopt strategies that help to improve attraction of new employees and help retain employees. There are policies that a company can adopt in order to become the employer of choice in the market. An organization can adopt strategies and become the best in the market and be able to retain the best employees and attract the best ones in the market.
Bibliography
Anderson, K & Cooper, Brian, 2005. The Impact of Strategic Integration and Development of HR Practices on Firm Performance: Some Evidence from Australia. Web.
Baron, A. and Armstrong, M. (2007) Human capital management. London: Kogan Page.
Brown, D., Caldwell, R. and White, K, 2004. Business partnering: a new direction for HR. A guide. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development. Web.
Kaye, Beverly and Sharon Jordan-Evans, Love’Em or Lose’Em, Getting Good People to Stay (San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler publishers, Inc., 2004).
Munzell and Moore, 2009. To Retain Key Employees- Develop the Boss. SHRM whitepaper. Web.
William B Werther, JR and Keith Davis (2004) Human Resources and Personnel Management. Arizona: Arizona State University Press.
Marcus Buckingham and Curt Coffman (2004), First, Break All the Rules New York, NY, Simon & Schuster.
Millmore, M., Lewis, P. and Saunders, M. (2007) Strategic human resource management: contemporary issues. Harlow: Financial Times/Prentice Hall.
Peter F. Drucker (2004) Management and the World’s work Harvard Business Review. pp. 65-76.
Reilly, O Brian (2004) The New Deal: What companies and Employees owe one another. Fortune. P.52.
Reilly, P. (2008) Strategic HR? Ask yourself the questions. HR Director. No 44. pp. 12-14, 16-17.
Richards, J. (2007) Aligning HR with the business: two steps forward, one step back. IRS Employment Review. No 866. pp. 6-12.
Boxall, P. and Purcell, J. (2008) Strategy and human resource management (2nd edition). Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Vere, D. and Butler, L. (2007) Fit for business: transforming HR. Research into practice. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development.