Variable Q1 has a mean of 37.28, as shown in Table 1.0 below:
Table 1.0: Q1 descriptive.
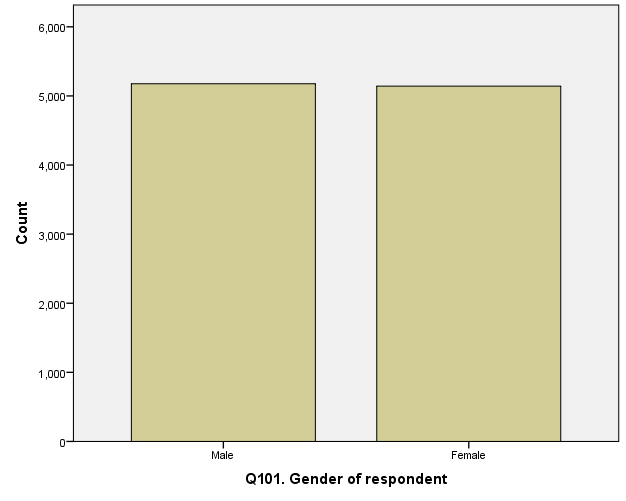
Variable gender respondent, labeled Q101 in the data set, is a nominal variable that measures the type of response that the researcher is recording. When collecting data for a particular research study, it is essential to avoid biassness. In this case, the researcher implements collecting data from both genders, i.e., male and female. This groups are crucial because when analyzing the data, a researcher may want to identify the differences in response and other vital activities between the two groups, which is the core of various tests such as t-test and ANOVA.
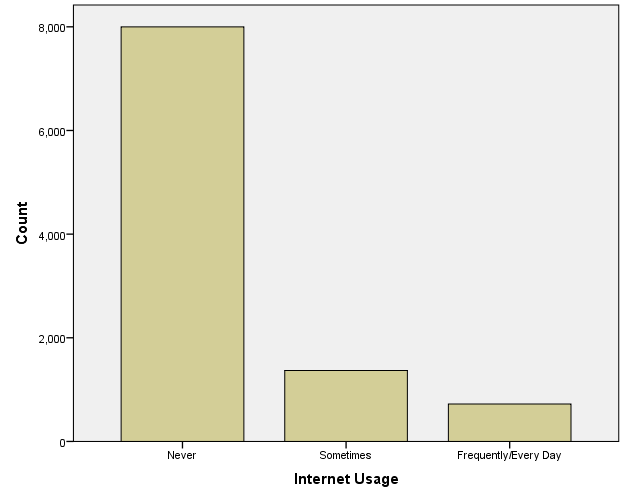
Variable internet usage is an ordinal variable that measures the internet usage by different individuals. This variable categorizes the internet users into three groups; the first group is individuals who do not use the internet. The second group is of individuals who use the internet at certain times, and the third group is of individuals who use the internet most of the time, i.e., frequently. This variable shows the researcher how different groups prefer using the internet. In the analysis of the data, these groups can be compared to the type of gender, and the researcher can use the data to compare and make conclusions on how different groups make use of the internet.
Social change is the significant change in behavior patterns, cultural values, and norms by a given group of people or community over time (Wilson, 2020). With these variables, i.e., gender respondent, age, and internet usage, a researcher can investigate an upcoming social change over some time. Currently, the internet has dramatically expanded worldwide, and almost everybody has access to a smartphone with an internet connection.
People’s behavior is changing in that nowadays, most people prefer online greetings, groups, and even conversations (Zhong, 2020). These variables help identify various age groups that use the internet frequently, sometimes and those that do not use it at all. Furthermore, the internet is composed of various variables such as online games, movies, dirty sites, etc., which can be studied with these variables.
From the current state of online activities, millions of people, both male, and female use the internet to complete their daily activity tasks, which is a social change (Lopez-Sintas et al., 2020). For example, the purchase of goods and services is currently made online with the development of companies such as Alibaba and Amazon (Mack et al., 2017). Independent of age, everyone one to complete their tasks online. Furthermore, the current global state since the onset of the COVID 19 pandemic has pushed most of the purchases and sales online.
The change might not be fast but gradual, which implies that after some time, global activities that are independent of the physical presence of parties may tend to move to online events such as trade, education, banking, etc. The variables age, internet, and gender respondent imply that social change within internet usage is inevitable. This is because technology is expanding globally, and the use of the internet is also expanding; hence it is forecasted to increase.
References
Karaca, A., Demirci, N., Caglar, E., & Konsuk Unlu, H. (2021). Correlates of Internet addiction in Turkish adolescents. Children And Youth Services Review, 126, 106050. Web.
Lopez-Sintas, J., Lamberti, G., & Sukphan, J. (2020). The social structuring of the digital gap in a developing country. The impact of computer and internet access opportunities on internet use in Thailand. Technology In Society, 63, 101433. Web.
Mack, E., Marie-Pierre, L., & Redican, K. (2017). Entrepreneurs’ use of the internet and social media applications. Telecommunications Policy, 41(2), 120-139. Web.
Poy, S., & Schüller, S. (2020). Internet and voting in the social media era: Evidence from a local broadband policy. Research Policy, 49(1), 103861. Web.
Wilson, H. (2020). Discomfort: Transformative encounters and social change. Emotion, Space And Society, 37, 100681. Web.
Zhong, B. (2020). Social consequences of internet civilization. Computers In Human Behavior, 107, 106308. Web.