Quality Policy for the company in accordance with the ISO 9001:2008 requirements
Oberoi Hotels & Resorts is a five-star company that is governed by the ISO 9001:2008 quality policy (Oberoi Hotel, 2010). The reputation of the hotel both locally and internationally called for the need to formulate documentation that helps check and evaluate the quality management system to enhance the effectiveness of the hotel. The amazing services have enhanced recognition from all over the world, bringing forth a number of awards.
We are looking to position ourselves well globally and to ensure our presence is largely felt.
We attest to the fact that people are a great company asset and the company aims to demonstrate leadership to ensure these peoples’ needs are satisfied.
We strive to be an organization that is environmental friendly. The company is aiming to recycle products after use and encourage the usage of natural resources.
To realize this, the following measures will be undertaken:
- We are looking to undertake intensive research to ascertain the tastes of our guests and subsequently develop a product that meets their expectations.
- The company opts to employ from the wider world market. The individuals selected will be from different parts and have an exposure to different cultures. This will ensure the employees have a wide exposure.
- We bank our trust in the competent staff employed to provide state of the art services to the guests as the firm is committed to thriving economically. In addition, the company has an organizational culture that ensures mutual understanding and trust upon her employees. This is a positive move towards a cordial working relationship among the company workers.
Stakeholders
Chairperson
He/she is the nerve of the hotel. He is at the top of management organ responsible for decision-making and his/her decisions and actions have a direct impact on the organization performance. The major role of the chairperson is to monitor the welfare of the hotel and its organs. Company profitability, friendly environment to both the guests and employees are major needs of the Chairperson.
Bank
The bank’s service of advancing loans to the hotel makes it a major investor. The need for the bank is accountability in handling the accounting books. In addition, the bank is relying on the hotel revenue base and reputation.
Shareholders
Given the status of the hotel as a public limited company, shareholders are a vital component in the company. These individuals inject their fortune into the business and are responsible in the election of the members who make up the executive board.
Employees
They are responsible for the day-to-day operations of the hotel. The success of the company in terms of performance lies on them. The important need of the employee is an excellent working environment that ensures his health and welfare is taken care of.
Suppliers
These compose of individuals who provide external support to the company. Their services are unique as they cut across the entire operations of the hotel. They range from consultancy to provision of high-quality products used in the daily running of the hotel. Suppliers’ need is constant flow of services and goods to the company.
Five processes required to fulfill stakeholder needs
- Ensuring provision of state of the art services and luxury to the hotel guests
- Enhancing efficient management of interest and dividends; this incentive will protect the shareholders.
- Efficient maintenance of accounting books to keep the bank trust.
- Nurturing a comfortable environment and adopting an employee sensitive working culture.
- Monitoring of suppliers contract and making renewals after appraising its services.
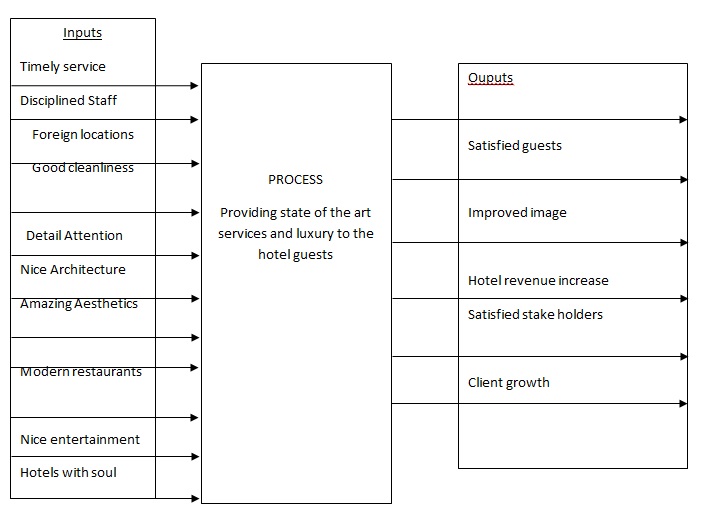
Task Inputs and Outputs
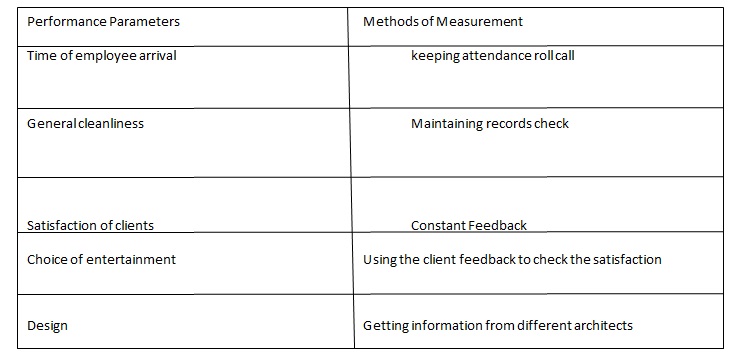
Parameters of performance
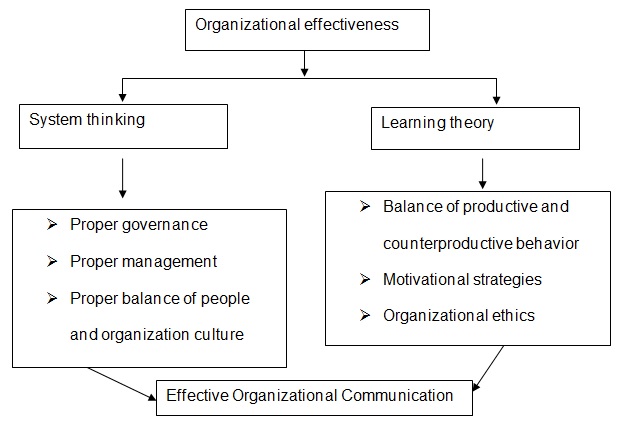
Key elements
- Top-level management is vital for the motivation of employees. Their commitment towards formulation of sound motivational policies is paramount to the development of the company. Reward and benefit schemes are some of the ways to demonstrate commitment by the top management. The process of continual development calls for the allocation of enough resources by the management; this will keep many people in the course of development.
- The company needs to be well versed with the feelings of the guests. Daily feedback from these guests ensures that their comfort is taken care of, and keeps in course the development of the hotel. The feedbacks from the guests help during decision making by management to ascertain whether the firm is on the right path.
- Continuous feedbacks from employees helps keep the firm in its continuous development course. Employees are responsible for the growth of the firm because of their day-to-day operations. Maintaining equality among employees is paramount in enhancing motivation and building of confidence. The feedback information is important in evaluating feelings of employees towards the working environment.
- Evaluating the information from the aforementioned procedures keeps the firm continuous development on track. Implementation of the above procedure is important if the company is to realize ultimate development.
- The information in the above procedure is important for the company’s decision-making organ. The company management needs to set goals and lay out plans on how to achieve the set goals. The employees’ and stakeholders’ views are necessary to contain conflicts if need be. In addition, the shareholders fortunes are invested in the company and therefore have a say in relation to the set goals. The goals are important in enhancing the company’s continuous development.
Legislation requirement
Australian government is keen in the conservation of environment. Mining sector has been identified as the greatest contributor of environmental pollution. BHP Billiton is an example of companies in the mining sector. The company deals with an array of products ranging from uranium to petroleum mining. Considering the sensitivity of mining uranium and to help prevent environmental risks, strict legislative statutes have been formulated. BHP Billiton was undergoing expansion and therefore the need to abide with some federal and state legislation related to environmental control. Some of these are explained below.
Federal legislation
- Environmental Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (BHP Billiton, 2009):
- The legislation postulates that the state is mandated to look into the projects that impact on the natural ecosystem or any nuclear project before tendering an approval.
- Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Act 1998 (BHP Billiton, 2009):
- The act is responsible for protecting the welfare of the public. Moreover, it helps protect the environment from the negative effects of radiation.
- Environmental protection Act 1981 (BHP Billiton, 2009):
- The act addresses matters of the sea especially the disposal of materials into the sea. The aforementioned project needed shipment vessels to transport the raw materials, therefore the act is applicable to check the dumping of materials.
- National Greenhouse and energy reporting Act 2007 (BHP Billiton, 2009):
- The undertaking of the project could lead to gas emissions above the required levels. The National Green House and Energy Reporting Act postulate the levels of regulated gases.
State Legislations
- Northern Territory Environmental Assessment Act.
- The act is responsible for the assessment of the project environmental impact on the entire state (BHP Billiton, 2007).
- Adelaide Dolphin Sanctuary Act 2005:
- The act is responsible for the protection of the dolphin family of Adelaide estuary. The company is in a bid to construct an additional port and there is need to comply with the act.
- Environmental Protection Policy 2007 (BHP Billiton, 2007):
- This is a policy responsible for the regulation of noise pollution. The policy therefore helps foster a favorable working environment.
- Environment Protection policy 1994 (South Australia):
- The aim of the legislation is to help in the reduction of emissions into the air by a project. Its main intention is to maintain good quality of the air. The initiation of the project will lead to emissions that might reduce the quality of the air. The project entails fuel burning.
Stakeholders of the organization and their needs
Investors
The investors of the company are those who have injected their savings in the company to facilitate its projects. These individuals include the shareholders and other business partners with the BHP Billiton. Their primary need is good financial returns on investment. This is achievable through the employment of sound business practices. Another need is the mitigation of risks. Effective mitigation of risks ensures the firm is kept on a strong financial footing (BHP Billiton, 2007).
Customers
The customers of this company are always corporate. The customer base is made of large organizations that have an interest in the mined raw materials. Their primary need is the quality of the output. Customers need value for their money and therefore a high quality product is of the essence. Getting after-sale services from the company is another customer need. The services are in the form of technical and commercial support.
Employees
They are an important component in the organization. They have several needs that include a favorable working environment. Another need is a good working culture that enhances career growth and development while creating opportunities.
Government
The term government encompasses both central and local government. The main objective is to ensure that the firm operates within the established legislation. In addition, they follow the company performance to ensure issues related to environment and other parameters are addressed.
Suppliers
These include both the local and international companies that help in the project. They are interested in timely payment for their services. In addition, they are keen on the quality requirement of the company in relation to its suppliers.
Processes that describe the organization’s operations
Mining
Mining is a below the surface process that involves drilling into the earth surface before using a hoist to remove the mineral.
- Boring: This is the use of a machine designed well to cut into the mine. Boring machine services comes after the cutting into the mine. This enlarges the surface area for human access. The process enhances the safety of the workers.
- Hoisting: This is the use of a hoist shaft to remove the minerals that have been extracted from the mine. A stopping mechanism is important in the process to help prevent hazards as the process involves a pull against gravity laws, which is dangerous (BHP Billiton, 2007).
Processing
The harvested treasure needs to undergo filtration processes to remove the unwanted material and remain with the required mineral. The sub processes include:
- Comminution – This is the process of breaking down the minerals and channeling them for filtration.
- Floatation – This is the stage where filtration is done. The lighter materials are easily filtered at this stage.
Order processing
This entails the reviewing of available orders to ascertain their completion time. Mini processes of this are:
- Contract review: At this state, the review is done to already established contracts to ascertain any differences in agreement. Given any difference, the customer is updated accordingly.
- Order confirmation letter. This is done after successful review on the contract has been done. The letter is official and sending it to the client is paramount as it acts as order reference point.
Supply
This implies the transfer of the minerals to the end user. The sub processes include:
- Pre-loading inspection – This ensures the checking of quality of the product as well as the space available for product placement.
- Railway- This mode of transport enables the transportation of bulk and therefore necessitating the transportation of minerals through trains.
After- sale services
This is meant to enhance customer satisfaction and enhance the bond with the company. The sub processes include:
- Follow-up – This is meant to acquire feedback information from the customer.
- Technical assistance – The Company taking responsibility of providing expertise to help the customer helps nurture healthy relationships.
Main processes and environmental aspects
Mining
Processing
Environmental impacts
Mining
Processing
Objectives
Mining
Processing
Actions for targets
Mining
Processing
Methods that can be used to measure or monitor the progress.
Mining
Processing
Occupational Health and Safety Management System
Legislative requirements for a commercial construction company.
Construction is a necessary element in the day-to-day developments of an economy. The legislative organ is mandated to devise statutes that guide this industry. The various requirements covering the construction industry are discussed here.
Prevention of fall
This legislation ensures the safety of the public. It provides stiff penalties to issues of negligence in the side of the constructor.
Boom-lift safe work procedure
The workers on the side of welfare need guarantee from the constructor and therefore the machines used need to be safe to prevent hazards.
Noise
The law is instituted to regulate the nuisance caused by the construction machinery. Construction sites are not conducive for habitation because of the noise pollution.
First-Aid
This is the medical attention given to an individual at the first instance of an injury. The legislation requires all firms to comply with this provision to ensure safety of workers is maintained.
Health and safety induction for employees
The safety of citizens is paramount and this legislation covers the regulations of inducting workers. Ways of protecting oneself together with the description of how to operate machines are envisaged in this legislation.
Prepare a health and safety co-ordination plan
The legislation is looking to ensure the coordination plan is in line with the safety requirements.
Safe brick laying procedure
The foundation of a building is important in supporting the entire structure. The legislation seeks to ensure safety in accordance to the materials used.
Risks for company’s operations
- Faulty Scaffolding – This is an essential procedure in accordance to height requirements. It is a hazard that causes injury if it fails to be controlled by the company worker. Rechecking the scaffold before using it is a control measure.
- Boom Lift Movement- This lift is important in reaching peaks of tall buildings. The load being carried may injure the worker below it. Constant communication between the lift operator and the workers is paramount to prevent this.
- Noise – Workers may develop health implications when exposed to a lot of construction noise. Machine maintenance is important to control the noise. In addition, workers need provision of mufflers to control sound effects
- Amputation – Heavy machines can cause serious damage to individuals if not properly operated. Workers need to be well versed with the operations of machines and the danger zones.
- Lesions – Working with some machinery causes wounds to the workers of the company. Training and availing gloves to the workers is a sure way to prevent them.
- Collision – This occurs when several lifts are operating at the same time. Collision causes injuries to both the worker and operators.
- Explosion – Construction sites contain tanks i.e. the gas tanks that are of high pressure. Improper handling of these items is dangerous to the workers. The explosions can cause death in most cases. Storing these pressurized containers in a secure location helps curb the accidents
- Excavation – This entails the use of material when establishing a building foundation. This can cause injuries to the workers as it entails the use of heavy machinery.
- Manual material handling – This involves the use of manpower to extradite some tasks. Man is prone to error and mishandling of these equipments causes injuries to the worker responsible and other colleagues. These errors are controllable with the use of equipment handlers.
- Fatigue – This is tiredness of the workers. It is caused by many working hours, which makes workers lose concentration and subsequently causing injuries. Workers need to be given enough resting time and work for small durations.
Risk assessment chart
Actions for the risks
List of References
BHP Billiton. 2007, BHP Billiton’s stakeholder’s relationship. Web.
BHP Billiton. 2009, Olympic dam expansion draft environmental impact statement. Web.
Oberoi Hotel. 2010, Group – Dharma. Web.
Oberoi Hotel. 2010, Mission and Vision Statement. Web.